
Gyroelongated triangular cupola
Encyclopedia
In geometry
, the gyroelongated triangular cupola is one of the Johnson solid
s (J22). As the name suggests, it can be constructed by gyroelongating a triangular cupola
(J3) by attaching a hexagonal antiprism
to its base. It can also be seen as a gyroelongated triangular bicupola
(J44) with one triangular cupola removed. Like all cupolae
, the base
polygon
has twice as many sides as the top (in this case, the bottom polygon is a hexagon because the top is a triangle
).
The 92 Johnson solids were named and described by Norman Johnson in 1966.
e for volume
and surface area
can be used if all faces
are regular
, with edge length a:
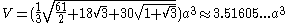
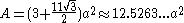
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, the gyroelongated triangular cupola is one of the Johnson solid
Johnson solid
In geometry, a Johnson solid is a strictly convex polyhedron, each face of which is a regular polygon, but which is not uniform, i.e., not a Platonic solid, Archimedean solid, prism or antiprism. There is no requirement that each face must be the same polygon, or that the same polygons join around...
s (J22). As the name suggests, it can be constructed by gyroelongating a triangular cupola
Triangular cupola
In geometry, the triangular cupola is one of the Johnson solids . It can be seen as half a cuboctahedron.The 92 Johnson solids were named and described by Norman Johnson in 1966.-Formulae:...
(J3) by attaching a hexagonal antiprism
Hexagonal antiprism
In geometry, the hexagonal antiprism is the 4th in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps.If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.- See also :* Set of antiprisms...
to its base. It can also be seen as a gyroelongated triangular bicupola
Gyroelongated triangular bicupola
In geometry, the gyroelongated triangular bicupola is one of the Johnson solids . As the name suggests, it can be constructed by gyroelongating a triangular bicupola by inserting a hexagonal antiprism between its congruent halves.The gyroelongated triangular bicupola is one of five Johnson solids...
(J44) with one triangular cupola removed. Like all cupolae
Cupola
In architecture, a cupola is a small, most-often dome-like, structure on top of a building. Often used to provide a lookout or to admit light and air, it usually crowns a larger roof or dome....
, the base
Base (geometry)
In geometry, a base is a side of a plane figure or face of solid, particularly one perpendicular to the direction height is measured or on what is considered to the bottom. This usage can be applied to a triangle, parallelogram, trapezoids, cylinder, pyramid, parallelopiped or frustum. By...
polygon
Polygon
In geometry a polygon is a flat shape consisting of straight lines that are joined to form a closed chain orcircuit.A polygon is traditionally a plane figure that is bounded by a closed path, composed of a finite sequence of straight line segments...
has twice as many sides as the top (in this case, the bottom polygon is a hexagon because the top is a triangle
Triangle
A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted ....
).
The 92 Johnson solids were named and described by Norman Johnson in 1966.
Formulae
The following formulaFormula
In mathematics, a formula is an entity constructed using the symbols and formation rules of a given logical language....
e for volume
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
and surface area
Surface area
Surface area is the measure of how much exposed area a solid object has, expressed in square units. Mathematical description of the surface area is considerably more involved than the definition of arc length of a curve. For polyhedra the surface area is the sum of the areas of its faces...
can be used if all faces
Face (geometry)
In geometry, a face of a polyhedron is any of the polygons that make up its boundaries. For example, any of the squares that bound a cube is a face of the cube...
are regular
Regular polygon
A regular polygon is a polygon that is equiangular and equilateral . Regular polygons may be convex or star.-General properties:...
, with edge length a:
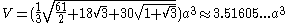
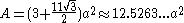
Dual polyhedron
The dual of the gyroelongated triangular cupola has 15 faces: 6 kites, 3 rhombi, and 6 quadrilaterals.| Dual gyroelongated triangular cupola | Net of dual |
|---|---|

