HD 2039
Encyclopedia
HD 2039 is a yellow dwarf
or yellow subgiant star
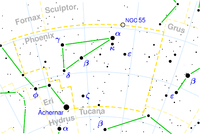
in the constellation
Phoenix
. The star is not visible to the naked eye, and lies approximately 330 light years away from the Sun
. HD 2039 is a relatively stable star, and an exoplanet at least three times the mass of the planet Jupiter
has been discovered in its orbit; this exoplanet, known as HD 2039 b
, was the 100th exoplanet to be discovered.
. The catalogue, which was published between 1918 and 1924, was based on the work of Annie Jump Cannon
and her team between 1911 and 1915. HD 2039 does not have a common, collaquial name that is characteristic of stars like Sirius
, Procyon
, and Aldebaran
.
. In terms of mass, the star exhibits almost identical properties. HD 2039 exhibits a radius approximately six-fifth times the size of the Sun's. The star is slightly hotter than the Sun; while HD 2039 has a temperature of 5984 K, the Sun's surface temperature lies nearly 200 kelvins lower at 5778 K. HD 2039 is unusually metal-rich, which has attracted the attention of astrophysicists.
as observed from Earth is 9; this signifies that the body is not visible with the naked eye
, but can be seen with a telescope. HD 2039 lies roughly 330 light years from the Sun, which is about as far from the Sun as the second brightest star in the night sky, Canopus
.
was found by the Anglo-Australian Planet Search
team to be orbiting the star in a very eccentric
orbit
. It has a minimum mass
more than three times that of Jupiter
and has a orbital period
of over three years. The planet orbits its star at a distance of approximately two AU
away; the planet Earth
, in comparison, orbits at a distance of one AU away from the Sun. HD 2039 b's discovery was reported quietly; no press release was provided by the observatory that discovered the star's planet, and no formal announcement of the planet's existence was made. The entity was the 100th exoplanet to have been verified by the scientific community.
Yellow dwarf
A G-type main-sequence star , often called a yellow dwarf, is a main-sequence star of spectral type G and luminosity class V. Such a star has about 0.8 to 1.2 solar masses and surface temperature of between 5,300 and 6,000 K., Tables VII, VIII...
or yellow subgiant star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
in the constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
Phoenix
Phoenix (constellation)
Phoenix is a minor constellation in the southern sky. It is named after the Phoenix, a mythical bird. It is faint: there are only two stars in the whole constellation which are brighter than magnitude 5.0...
. The star is not visible to the naked eye, and lies approximately 330 light years away from the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
. HD 2039 is a relatively stable star, and an exoplanet at least three times the mass of the planet Jupiter
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
has been discovered in its orbit; this exoplanet, known as HD 2039 b
HD 2039 b
HD 2039 b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star HD 2039. It is almost five times as massive as Jupiter and has a very eccentric orbit.-External links:* *...
, was the 100th exoplanet to be discovered.
Nomenclature
The designation HD 2039 from the Henry Draper CatalogueHenry Draper Catalogue
The Henry Draper Catalogue is an astronomical star catalogue published between 1918 and 1924, giving spectroscopic classifications for 225,300 stars; it was later expanded by the Henry Draper Extension , published between 1925 and 1936, which gave classifications for 46,850 more stars, and by the...
. The catalogue, which was published between 1918 and 1924, was based on the work of Annie Jump Cannon
Annie Jump Cannon
Annie Jump Cannon was an American astronomer whose cataloging work was instrumental in the development of contemporary stellar classification. With Edward C...
and her team between 1911 and 1915. HD 2039 does not have a common, collaquial name that is characteristic of stars like Sirius
Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. With a visual apparent magnitude of −1.46, it is almost twice as bright as Canopus, the next brightest star. The name "Sirius" is derived from the Ancient Greek: Seirios . The star has the Bayer designation Alpha Canis Majoris...
, Procyon
Procyon
Procyon is the brightest star in the constellation Canis Minor. To the naked eye, it appears to be a single star, the seventh brightest in the night sky with a visual apparent magnitude of 0.34...
, and Aldebaran
Aldebaran
Aldebaran is a red giant star located about 65 light years away in the zodiac constellation of Taurus. With an average apparent magnitude of 0.87 it is the brightest star in the constellation and is one of the brightest stars in the nighttime sky...
.
Characteristics
HD 2039 is a stable G-type star, meaning it shines with white light that can be seen in the SunSun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
. In terms of mass, the star exhibits almost identical properties. HD 2039 exhibits a radius approximately six-fifth times the size of the Sun's. The star is slightly hotter than the Sun; while HD 2039 has a temperature of 5984 K, the Sun's surface temperature lies nearly 200 kelvins lower at 5778 K. HD 2039 is unusually metal-rich, which has attracted the attention of astrophysicists.

Distance and visibility
The star's magnitudeApparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
as observed from Earth is 9; this signifies that the body is not visible with the naked eye
Naked eye
The naked eye is a figure of speech referring to human visual perception unaided by a magnifying or light-collecting optical device, such as a telescope or microscope. Vision corrected to normal acuity using corrective lenses is considered "naked"...
, but can be seen with a telescope. HD 2039 lies roughly 330 light years from the Sun, which is about as far from the Sun as the second brightest star in the night sky, Canopus
Canopus
Canopus |Alpha]] Carinae) is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Carina and Argo Navis, and the second brightest star in the night-time sky, after Sirius. Canopus's visual magnitude is −0.72, and it has an absolute magnitude of −5.53.Canopus is a supergiant of spectral...
.
Planetary system
In 2002, a planetExtrasolar planet
An extrasolar planet, or exoplanet, is a planet outside the Solar System. A total of such planets have been identified as of . It is now known that a substantial fraction of stars have planets, including perhaps half of all Sun-like stars...
was found by the Anglo-Australian Planet Search
Anglo-Australian Planet Search
The Anglo-Australian Planet Search or AAPS is a long-term astronomical survey started in 1998 and continuing to the present. It is being carried out on the 3.9m Anglo-Australian Telescope, AAT, of the Anglo-Australian Observatory in Australia. The purpose of this survey is to catalog planets around...
team to be orbiting the star in a very eccentric
Orbital eccentricity
The orbital eccentricity of an astronomical body is the amount by which its orbit deviates from a perfect circle, where 0 is perfectly circular, and 1.0 is a parabola, and no longer a closed orbit...
orbit
Orbit
In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in space, for example the orbit of a planet around the center of a star system, such as the Solar System...
. It has a minimum mass
Minimum mass
In astronomy, minimum mass is the lower-bound calculated mass of observed objects such as planets, stars and binary systems, nebulae, and black holes. Minimum mass is a widely cited statistic for extrasolar planets...
more than three times that of Jupiter
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
and has a orbital period
Orbital period
The orbital period is the time taken for a given object to make one complete orbit about another object.When mentioned without further qualification in astronomy this refers to the sidereal period of an astronomical object, which is calculated with respect to the stars.There are several kinds of...
of over three years. The planet orbits its star at a distance of approximately two AU
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
away; the planet Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
, in comparison, orbits at a distance of one AU away from the Sun. HD 2039 b's discovery was reported quietly; no press release was provided by the observatory that discovered the star's planet, and no formal announcement of the planet's existence was made. The entity was the 100th exoplanet to have been verified by the scientific community.

