HLA-DP
Encyclopedia
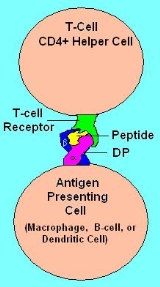
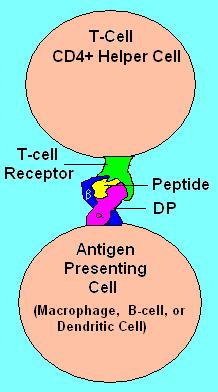
HLA-DP is a protein/peptide-antigen receptor
and graft-versus-host disease
antigen that is composed of 2 subunits, DPα and DPβ. DPα and DPβ are encoded by two loci, HLA-DPA1 and HLA-DPB1
, that are found in the MHC
Class II (or HLA-D) region in the Human Leukocyte Antigen
complex on human chromosome 6 (see protein boxes on right for links).
Less is known about HLA-DP relative to HLA-DQ
and HLA-DR but the sequencing of DP types and determination of more frequent haplotype
s has progressed greatly within the last few years.
category of the major histocompatibility complex
of humans, however this antigen is an artifact of the era of organ transplantation. HLA DQ functions as a cell surface receptor for foreign or self antigens. The immune system surveys antigens for foreign pathogens when presented by MHC receptors (like HLA-DP). The MHC Class II antigens are found on antigen presenting cells (APC)(macrophages, dendritic cells, and B-lymphocytes). Normally, these APC 'present' class II receptor/antigens to a great many T-cells, each with unique T-cell receptor (TCR) variants. A few TCR variants that recognize these DQ/antigen complexes are on CD4 positive T-cells. These T-cells, called T-helper (Th) cells, can promote the amplification of B-cells that recognize a different portion of the same antigen. Alternatively, macrophages and other cytotoxic lymphocytes consume or destroy cells by apoptotic signaling and present self-antigens. Self antigens, in the right context, form a suppressor T-cell population that protects self tissues from immune attack or autoimmunity.
encoding loci and therefore is much more equilibrated with respect to other HLA loci. In the Super B8
complex DP locus is more frequently substituted, either as a result of its distance from other loci, or because it was not as actively selected in the evolution of Super B8.
Each combination of DPA1 allele gene product with each combination of DPB1 'gene' product can potentially recombine to produce one isoform. DP genes are highly variable
in the human population. In a typical population there are many DP alpha and beta. Most isoforms are not common.
These 'cis'-isoforms will account for at least 50% of the DP isoforms. The other, trans isoforms are typically more rare, isoforms result from random 'trans' combinations of haplotypes in individuals as a result of 'trans' paternal/maternal gene product isoforms.
HLA-DPB1 Alleles
and DPB1*0203 becomes DPB1*101:01.
All renamed alleles are listed in the HLA-DPB1 Nomenclature Conversion Chart below.
To aid in migration of data to the new nomenclature the WHO Nomenclature Committee for Factors of the HLA System has provided the IMGT/HLA Nomenclature Conversion Tool. This tool allows you to enter an HLA allele name and will provide you with both the current and new versions of the allele name. New alleles that have never been assigned with a name prior to the April 2010 update are:
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a receptor is a molecule found on the surface of a cell, which receives specific chemical signals from neighbouring cells or the wider environment within an organism...
and graft-versus-host disease
Graft-versus-host disease
Graft-versus-host disease is a common complication after a stem cell transplant or bone marrow transplant from another person . Immune cells in the donated marrow or stem cells recognize the recipient as "foreign". The transplanted immune cells then attack the host's body cells...
antigen that is composed of 2 subunits, DPα and DPβ. DPα and DPβ are encoded by two loci, HLA-DPA1 and HLA-DPB1
HLA-DPB1
HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DP beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DPB1 gene.-Further reading:...
, that are found in the MHC
MHC
-Biology:*Myosin heavy chain - part of the motor protein myosin's quaternary protein structure*Major histocompatibility complex - a highly polymorphic region on chromosome 6 with genes particularly involved in immune functions-Colleges:...
Class II (or HLA-D) region in the Human Leukocyte Antigen
Human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen system is the name of the major histocompatibility complex in humans. The super locus contains a large number of genes related to immune system function in humans. This group of genes resides on chromosome 6, and encodes cell-surface antigen-presenting proteins and...
complex on human chromosome 6 (see protein boxes on right for links).
Less is known about HLA-DP relative to HLA-DQ
HLA-DQ
HLA-DQ is a cell surface receptor type protein found on antigen presenting cells. DQ is an αβ heterodimer of the MHC Class II type. The α and β chains are encoded by HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1, respectively. These two loci are adjacent to each other on chromosome 6p21.3. Both the α-chain and β-chain...
and HLA-DR but the sequencing of DP types and determination of more frequent haplotype
Haplotype
A haplotype in genetics is a combination of alleles at adjacent locations on the chromosome that are transmitted together...
s has progressed greatly within the last few years.
Structure, Functions, Genetics

Structure
HLA-DP is an αβ-heterodimer cell-surface receptor. Each DP subunit (α-subunit, β-subunit) is composed of a α-helical N-terminal domain, a IgG-like β-sheet, a membrane spanning domain, and a cytoplasmic domain. The α-helical domain forms the sides of the peptide binding groove. The β-sheet regions form the base of the binding groove and the bulk of the molecule as well as the inter-subunit (non-covalent) binding region.Function
The name 'HLA-DP' originally describes a transplantation antigen of MHC class IIMHC class II
MHC Class II molecules are found only on a few specialized cell types, including macrophages, dendritic cells and B cells, all of which are professional antigen-presenting cells ....
category of the major histocompatibility complex
Major histocompatibility complex
Major histocompatibility complex is a cell surface molecule encoded by a large gene family in all vertebrates. MHC molecules mediate interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells , which are immune cells, with other leukocytes or body cells...
of humans, however this antigen is an artifact of the era of organ transplantation. HLA DQ functions as a cell surface receptor for foreign or self antigens. The immune system surveys antigens for foreign pathogens when presented by MHC receptors (like HLA-DP). The MHC Class II antigens are found on antigen presenting cells (APC)(macrophages, dendritic cells, and B-lymphocytes). Normally, these APC 'present' class II receptor/antigens to a great many T-cells, each with unique T-cell receptor (TCR) variants. A few TCR variants that recognize these DQ/antigen complexes are on CD4 positive T-cells. These T-cells, called T-helper (Th) cells, can promote the amplification of B-cells that recognize a different portion of the same antigen. Alternatively, macrophages and other cytotoxic lymphocytes consume or destroy cells by apoptotic signaling and present self-antigens. Self antigens, in the right context, form a suppressor T-cell population that protects self tissues from immune attack or autoimmunity.
Genetics
The α-chain and β- of DP is encoded by the HLA-DPA1 locus and HLA-DPB1 loci, respectively. This cluster is located at the proximal (centromeric) end of the HLA superlocus in human chromosome 6p21.31. It is distal from HLA-DR and HLA-DQHLA-DQ
HLA-DQ is a cell surface receptor type protein found on antigen presenting cells. DQ is an αβ heterodimer of the MHC Class II type. The α and β chains are encoded by HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1, respectively. These two loci are adjacent to each other on chromosome 6p21.3. Both the α-chain and β-chain...
encoding loci and therefore is much more equilibrated with respect to other HLA loci. In the Super B8
HLA DR3-DQ2
HLA DR3-DQ2 is double serotype that specifically recognizes cells from individuals who carry a multigene HLA DR, DQ haplotype.Certain HLA DR and DQ genes have known involvementin autoimmune diseases. DR3-DQ2, a multigene...
complex DP locus is more frequently substituted, either as a result of its distance from other loci, or because it was not as actively selected in the evolution of Super B8.
Understanding the Heterodimeric DP Isoforms
| HLA | DPB1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| allele | (m) | (p) | |
| DPA1 | |(m) | αmβm (Cis m) | αmβp (Trans) |
| (p) | αpβm (Trans) | αpβp (Cis p) | |
| Result: 2 Cis, αmβm & αpβp, isoforms and 2 trans,αmβp & αpβm. | |||
Each combination of DPA1 allele gene product with each combination of DPB1 'gene' product can potentially recombine to produce one isoform. DP genes are highly variable
Human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen system is the name of the major histocompatibility complex in humans. The super locus contains a large number of genes related to immune system function in humans. This group of genes resides on chromosome 6, and encodes cell-surface antigen-presenting proteins and...
in the human population. In a typical population there are many DP alpha and beta. Most isoforms are not common.
These 'cis'-isoforms will account for at least 50% of the DP isoforms. The other, trans isoforms are typically more rare, isoforms result from random 'trans' combinations of haplotypes in individuals as a result of 'trans' paternal/maternal gene product isoforms.
Alleles
HLA-DPA1 Alleles| HLA-DPA1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| *01 | *02 | *03 | *04 |
| *01:03 *01:04 *01:05 *01:06 *01:07 *01:08 *01:09 *01:10 |
*02:01 *02:02 *02:03 *02:04 |
*03:01 *03:02 *03:03 |
*04:01 |
HLA-DPB1 Alleles
| HLA-DPB1 | |
|---|---|
| *01 | *01:01 |
| *02 | *02:01 |
| *02:02 | |
| *03 | *03:01 |
| *04 | *04:01 |
| *04:02 | |
| *05 | *05:01 |
| *06 | *06:01 |
| *07 | *07:01 |
| *08 | *08:01 |
| *09 | *09:01 |
| *10 | *10:01 |
| DPB1*11:01 - DPB1*129:01 |
|
HLA-DPB1 Allele Nomenclature Change
Before the April 2010 HLA nomenclature update, new HLA-DPB1 allele names were assigned within the existing nomenclature system. For example the allele discovered after HLA-DPB1*9901 was assigned as DPB1*0102, the subsequent allele was named DPB1*0202, then *0302 and so on. This name assignment was decided because of the complex genetic characteristics of DPB1 alleles compared to alleles of other HLA loci. The majority of the HLA-DPB1 alleles cannot be simply grouped together by their nucleotide sequences. This name assignment has been the most confusing system within the HLA nomenclature. In the 2010 HLA nomenclature update, all DPB1 alleles, except DPB1*0202 and *0402, discovered after DPB1*9901 were reassigned with new numbers. For example DPB1*0102 becomes DPB1*100:01and DPB1*0203 becomes DPB1*101:01.
All renamed alleles are listed in the HLA-DPB1 Nomenclature Conversion Chart below.
| Previous Names | Current Names |
|---|---|
| DPB1*0102 | DPB1*100:01 |
| DPB1*0203 | DPB1*101:01 |
| DPB1*0302 | DPB1*102:01 |
| DPB1*0403 | DPB1*103:01 |
| DPB1*0502 | DPB1*104:01 |
| DPB1*0602 | DPB1*105:01 |
| DPB1*0802 | DPB1*106:01 |
| DPB1*0902 | DPB1*107:01 |
| DPB1*1002 | DPB1*108:01 |
| DPB1*1102 | DPB1*109:01 |
| DPB1*1302 | DPB1*110:01 |
| DPB1*1402 | DPB1*111:01 |
| DPB1*1502 | DPB1*112:01 |
| DPB1*1602 | DPB1*113:01 |
| DPB1*1702 | DPB1*114:01 |
| DPB1*1802 | DPB1*115:01 |
| DPB1*1902 | DPB1*116:01 |
| DPB1*2002 | DPB1*117:01 |
| DPB1*2102 | DPB1*118:01 |
| DPB1*2202 | DPB1*119:01 |
| DPB1*2302N | DPB1*120:01N |
| DPB1*2402 | DPB1*121:01 |
| DPB1*2502 | DPB1*122:01 |
| DPB1*2602 | DPB1*123:01 |
| DPB1*2702 | DPB1*124:01 |
| DPB1*2802 | DPB1*125:01 |
To aid in migration of data to the new nomenclature the WHO Nomenclature Committee for Factors of the HLA System has provided the IMGT/HLA Nomenclature Conversion Tool. This tool allows you to enter an HLA allele name and will provide you with both the current and new versions of the allele name. New alleles that have never been assigned with a name prior to the April 2010 update are:
| DPB1*126:01 DPB1*127:01 DPB1*128:01 DPB1*129:01 |
Common DP Haplotypes
| HLA-DPA1*01:03/DPB1*04:01 (DP401) |
| HLA-DPA1*01:03/DPB1*04:02 (DP402) |

