HLA-DQ4
Encyclopedia
HLA-DQ4 is a serotype
subgroup within HLA-DQ
(DQ) serotypes. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of β4 subset of DQ β-chains. The β-chain of DQ is encoded by HLA-DQB1
locus and DQ4 are encoded by the HLA-DQB1*04 allele group. This group currently contains 2 common alleles, DQB1*0401 and DQB1*0402. HLA-DQ4 and HLA-DQB1*04 are almost synonymous in meaning. DQ4 β-chains combine with α-chains, encoded by genetically linked HLA-DQA1
alleles, to form the cis-haplotype isoforms. These isoforms, nicknamed DQ4.3 and DQ4.4, are also encoded by the DQA1*0303 and DQA1*0401 genes, respectively.
to Japan
and inland areas of Eastern Asia. In Japan it confers susceptibility to juvenile diabetes likely via the DR4 gene.
DQA1*0303:DQB1*0402 is primarily found in Northeastern Asia and the west pacific rim.
It is similar to DQA1*0303:DQB1*0402.
are found in the highland regions of the new world, peaking in NW Mexico
and in the Andes
. It is also found at high levels in Namibia
and Botswana
. Between these two population it is moderatedly high in the Ainu of northern Japan.
The DR8-DQ4 haplotype is associated with
DR4-DQ4(DRB1*0405:DQB1*0401) is associated with:
The DQA1*0303:DQB1*04 haplotype is associated with:
Other diseases mentioned are high altitude pulmonary edema
, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome
(DRB1*0405, see above table for Japanese), HIV resistance in the US, and haemophilia A
(anti-FVIII inhibitor response).
The table to the left shows the values of Japanese(values converted from phenotype frequencies to haplotype frequencies for sake of consistency) DR-DQ types. This table is presented here because of the diversity of DQ4 types in the Japanese population not seen elsewhere.
DQ4 is typically rare most of the world but where it appears more frequently is something of interest. The node of DQ4 is with the DQA1*0401:DQB1*0402 (DQ4.24 for this page) haplotype in Northwestern Mexico and the highland region of western South America reaching 40% haplotype frequencies in that area. Outside of the Indigenous American population DQ4.24 is elevated
at 10% in the Ainu of Hokkaidō, Japan. There are a number of other A-B haplotypes that suggest a connection between the Ainu and the Meso-American and Andean populations as well as Lakota Souix all have DQ4 levels higher than the Ainu. The linkage of DQ4 in Asia appears to be heaviest with DR8 (DR*0801, DR*0802, DR*0804) for DQ4.24 and the frequency is elevated from
the Ryukyu Islands
to Okhotsk, Ulchi, Negidal, Tofalar at approximately 10% falling off in the Mansi at 4% and punctate levels in between. Haplotype diversity of DQB1*0402 appears to be centered around the Amur River/Japanese Island Chain, and diversity of DQB1*0401 very roughly follows a similar pattern. DQ4.24 is also high in the Swedes however this may be due to east to west gene flow tracable at other HLA loci.
Since DQA1*0401:DQB1*0402 is found in the !Kung, one reasonably assumes it evolved in Africa and migrated with one of several potential waves, probably the earliest. Tracing the migration route is excessively difficult, but it appears that a possible second node of expansion in Central Asia and not the West Pacific Rim/Austro-Indic route postulated as the early human distribution. The most common haplotypes in the !Kung (for example Cw-B) that also appear in Eurasia appear to have been associated with the earliest migration, and is suggestive of a coastal migration; however the relatively high frequencies in the Ainu and Amur basin suggest a migration through the Transbaikal that is consistent with archaeology from about 18 kya. One expects with such a route that Korean would be higher than Japanese and Japanese higher the Ryukuans still higher than Taiwan aboriginals. From the west gene frequencies in the Levant and Black Sea region are at 'diffusive' levels whereas there are pockets of increased frequency in the Zoroastrians of Yadz region (DQA1*0401 and DQB1*0402). Thus the DR8-DQ4.24 haplotype is probably one of western origin.
The DR4-DQA1*0303:DQB1*040X can be found at high frequencies in PNG highland groups but not DQ4.24. The DR*0405 and DR*410 are found specifically associated with these DQ types and there is some haplotype diversity. So that it appears the presence of the DQA1*03:DQB1*04 is of West Pacific Rim origins in Japanese and proximal Siberians, but unfortunately there is no current typing of these haplotypes in the Taiwan aboriginal population. The presence in Indonesia may be the result of retrograde gene flow that can be established by other HLA types as well as mtDNA.
Serotype
Serotype or serovar refers to distinct variations within a subspecies of bacteria or viruses. These microorganisms, viruses, or cells are classified together based on their cell surface antigens...
subgroup within HLA-DQ
HLA-DQ
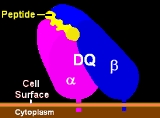
HLA-DQ is a cell surface receptor type protein found on antigen presenting cells. DQ is an αβ heterodimer of the MHC Class II type. The α and β chains are encoded by HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1, respectively. These two loci are adjacent to each other on chromosome 6p21.3. Both the α-chain and β-chain...
(DQ) serotypes. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of β4 subset of DQ β-chains. The β-chain of DQ is encoded by HLA-DQB1
HLA-DQB1
Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ beta 1, also known as HLA-DQB1, is a human gene and also denotes the genetic locus that contains this gene...
locus and DQ4 are encoded by the HLA-DQB1*04 allele group. This group currently contains 2 common alleles, DQB1*0401 and DQB1*0402. HLA-DQ4 and HLA-DQB1*04 are almost synonymous in meaning. DQ4 β-chains combine with α-chains, encoded by genetically linked HLA-DQA1
HLA-DQA1
Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ alpha 1, also known as HLA-DQA1, is a human gene present on short arm of chromosome 6 and also denotes the genetic locus which contains this gene...
alleles, to form the cis-haplotype isoforms. These isoforms, nicknamed DQ4.3 and DQ4.4, are also encoded by the DQA1*0303 and DQA1*0401 genes, respectively.
Serotype
| DQB1* | DQ4 | DQ3 | Sample |
| allele | % | % | size (N) |
| 71 | 10 | 176 | |
| 86 | 2 | 1085 | |
| Red indicates the level of 'false' reaction in non-DQ4 serotypes | |||
DQ4.3
DQA1*0303:DQB1*0401 is linked to DRB1*0405 and is common on the west pacific rim, from IndonesiaIndonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
to Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
and inland areas of Eastern Asia. In Japan it confers susceptibility to juvenile diabetes likely via the DR4 gene.
DQA1*0303:DQB1*0402 is primarily found in Northeastern Asia and the west pacific rim.
It is similar to DQA1*0303:DQB1*0402.
DQ4.2
DQB1*0401:DQB1*0402 has a trimodal global distribution. The highest frequenciesare found in the highland regions of the new world, peaking in NW Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
and in the Andes
Andes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
. It is also found at high levels in Namibia
Namibia
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia , is a country in southern Africa whose western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and east. It gained independence from South Africa on 21 March...
and Botswana
Botswana
Botswana, officially the Republic of Botswana , is a landlocked country located in Southern Africa. The citizens are referred to as "Batswana" . Formerly the British protectorate of Bechuanaland, Botswana adopted its new name after becoming independent within the Commonwealth on 30 September 1966...
. Between these two population it is moderatedly high in the Ainu of northern Japan.
DQ4 and Disease
DQ4 is associated with:- juvenile diabetic retinopathy
The DR8-DQ4 haplotype is associated with
- papillary thyroid carcinomas
- juvenile idiopathic arthritisJuvenile idiopathic arthritisJuvenile idiopathic arthritis is the most common form of persistent arthritis in children. JIA is a subset of arthritis seen in childhood, which may be transient and...
via DR8 allele , - chronic chlamydia infection,
- possibly pemphigus
DR4-DQ4(DRB1*0405:DQB1*0401) is associated with:
- autoimmune pancreatitis ,
- juvenile type 1 diabetesDiabetes mellitus type 1Diabetes mellitus type 1 is a form of diabetes mellitus that results from autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. The subsequent lack of insulin leads to increased blood and urine glucose...
, - rheumatoid arthritis in Japanese.
The DQA1*0303:DQB1*04 haplotype is associated with:
- Crohn's disease in Japanese.
Other diseases mentioned are high altitude pulmonary edema
High Altitude Pulmonary Edema
High altitude pulmonary edema is a life-threatening form of non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema that occurs in otherwise healthy mountaineers at altitudes typically above ....
, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome
Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada syndrome is a condition seen in humans and dogs involving various melanocyte-containing organs, characterized by uveitis , poliosis , vitiligo , and meningitis, although dogs with this syndrome rarely develop meningitis...
(DRB1*0405, see above table for Japanese), HIV resistance in the US, and haemophilia A
Haemophilia A
Haemophilia A is a deficiency in clotting factor VIII.Haemophilia A is inherited as an X-linked recessive trait, and thus occurs in males and in homozygous females. However, mild haemophilia A has been described in heterozygous females, presumably due to extremely unfavourable lyonization...
(anti-FVIII inhibitor response).
DQ4 distribution
| DQ | DR-DQ | DR | DQ | Freq | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serotype | haplotype | B1 | A1 | B1 | % | rank | ||
| DQ4 | DR4-DQ4 | 0405 | 0303 | 0401 | 14. | 3 | ² | |
| 0410 | 0303 | 0402 | 1. | 9 | 11 | |||
| DR8-DQ4 | 0802 | 0401 | 0402 | 1. | 3 | 15 | ||
| DQ5 | DR1-DQ5 | 0101 | 0101 | 0501 | 6. | 4 | 5 | |
| DR14-DQ5 | 1401 | 0104 | 0502 | 1. | 1 | 17 | ||
| 1401 | 0104 | 0503 | 0. | 8 | 18 | |||
| 1405 | 0104 | 0503 | 1. | 6 | 13 | |||
| DQ6 | DR8-DQ6 | 0803 | 0103 | 0601 | 9. | 3 | 4 | |
| DR13-DQ6 | 1302 | 0102 | 0604 | 6. | 0 | 6 | ||
| DR15-DQ6 | 1502 | 0103 | 0601 | 12. | 9 | ³ | ||
| 1501 | 0102 | 0602 | 6. | 0 | 7 | |||
| DQ7 | DR11-DQ7 | 1101 | 0505 | 0301 | 1. | 8 | 12 | |
| DR12-DQ7 | 1201 | 0505 | 0301 | 2. | 7 | 9 | ||
| 1202 | 0601 | 0301 | 1. | 3 | 15 | |||
| DR14-DQ7 | 1403 | 0503 | 0301 | 1. | 4 | 14 | ||
| DQ8 | DR4-DQ8 | 0403 | 0301 | 0302 | 1. | 9 | 10 | |
| 0406 | 0301 | 0302 | 3. | 4 | 8 | |||
| DR8-DQ8 | 0802 | 0401 | 0302 | 0. | 7 | 19 | ||
| DQ9 | DR9-DQ9 | 0901 | 0302 | 0303 | 16. | 0 | 1 | |
The table to the left shows the values of Japanese(values converted from phenotype frequencies to haplotype frequencies for sake of consistency) DR-DQ types. This table is presented here because of the diversity of DQ4 types in the Japanese population not seen elsewhere.
DQ4 is typically rare most of the world but where it appears more frequently is something of interest. The node of DQ4 is with the DQA1*0401:DQB1*0402 (DQ4.24 for this page) haplotype in Northwestern Mexico and the highland region of western South America reaching 40% haplotype frequencies in that area. Outside of the Indigenous American population DQ4.24 is elevated
at 10% in the Ainu of Hokkaidō, Japan. There are a number of other A-B haplotypes that suggest a connection between the Ainu and the Meso-American and Andean populations as well as Lakota Souix all have DQ4 levels higher than the Ainu. The linkage of DQ4 in Asia appears to be heaviest with DR8 (DR*0801, DR*0802, DR*0804) for DQ4.24 and the frequency is elevated from
the Ryukyu Islands
Ryukyu Islands
The , also known as the , is a chain of islands in the western Pacific, on the eastern limit of the East China Sea and to the southwest of the island of Kyushu in Japan. From about 1829 until the mid 20th century, they were alternately called Luchu, Loochoo, or Lewchew, akin to the Mandarin...
to Okhotsk, Ulchi, Negidal, Tofalar at approximately 10% falling off in the Mansi at 4% and punctate levels in between. Haplotype diversity of DQB1*0402 appears to be centered around the Amur River/Japanese Island Chain, and diversity of DQB1*0401 very roughly follows a similar pattern. DQ4.24 is also high in the Swedes however this may be due to east to west gene flow tracable at other HLA loci.
Since DQA1*0401:DQB1*0402 is found in the !Kung, one reasonably assumes it evolved in Africa and migrated with one of several potential waves, probably the earliest. Tracing the migration route is excessively difficult, but it appears that a possible second node of expansion in Central Asia and not the West Pacific Rim/Austro-Indic route postulated as the early human distribution. The most common haplotypes in the !Kung (for example Cw-B) that also appear in Eurasia appear to have been associated with the earliest migration, and is suggestive of a coastal migration; however the relatively high frequencies in the Ainu and Amur basin suggest a migration through the Transbaikal that is consistent with archaeology from about 18 kya. One expects with such a route that Korean would be higher than Japanese and Japanese higher the Ryukuans still higher than Taiwan aboriginals. From the west gene frequencies in the Levant and Black Sea region are at 'diffusive' levels whereas there are pockets of increased frequency in the Zoroastrians of Yadz region (DQA1*0401 and DQB1*0402). Thus the DR8-DQ4.24 haplotype is probably one of western origin.
The DR4-DQA1*0303:DQB1*040X can be found at high frequencies in PNG highland groups but not DQ4.24. The DR*0405 and DR*410 are found specifically associated with these DQ types and there is some haplotype diversity. So that it appears the presence of the DQA1*03:DQB1*04 is of West Pacific Rim origins in Japanese and proximal Siberians, but unfortunately there is no current typing of these haplotypes in the Taiwan aboriginal population. The presence in Indonesia may be the result of retrograde gene flow that can be established by other HLA types as well as mtDNA.

