HLA-DQ6
Encyclopedia
HLA-DQ6 is a human leukocyte antigen
serotype
within HLA-DQ
(DQ) serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of β6 subset of DQ β-chains. The β-chain of DQ isoforms are encoded by HLA-DQB1
locus and DQ6 are encoded by the HLA-DQB1*06 allele group. This group currently contains many common alleles, DQB1*0602 is the most common. HLA-DQ6 and DQB1*06 are almost synonymous in meaning. DQ6 β-chains combine with α-chains, encoded by genetically linked HLA-DQA1
alleles, to form the cis-haplotype isoforms. For DQ6, however, cis-isoform pairing only occurs with DQ1
α-chains. There are many haplotypes of DQ6.
infection was found associated with undifferentiated DQ6. Whereas DQ6 was protective against death (or need for liver transplantion) in primary sclerosing cholangitis
.
absent in Western Europe. It confers protection from narcolepsy
, juvenile diabetes, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) syndrome, pemphigus vulgaris
, multiple sclerosis
, myasthenia gravis
.
haplotype. This haplotype is considered to be the longest multigene haplotype known within the human genome as it covers over 4.7 million nucleotides. The DR15-DQ6.2 haplotype is the most common DR-DQ haplotype in Europe, and approximately 30% of Americans carry at least DQ6.2. The haplotype is even more common in Central Asia.
, recognition α34-49 of AChR increased with DQ6.2. DQA1*0102 increases risk cervical cancer
. In multiple sclerosis
DQA1*0102 was the most frequent allele and DQB1*0602 increased significantly in the MS patients.
DQ6.2 appears to have a negative association with disease. DQ6.2 also appears to have a protective effect in juvenile diabetes. DQ6.2 is also protective against infantile spasms in mestizos.
Human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen system is the name of the major histocompatibility complex in humans. The super locus contains a large number of genes related to immune system function in humans. This group of genes resides on chromosome 6, and encodes cell-surface antigen-presenting proteins and...
serotype
Serotype
Serotype or serovar refers to distinct variations within a subspecies of bacteria or viruses. These microorganisms, viruses, or cells are classified together based on their cell surface antigens...
within HLA-DQ
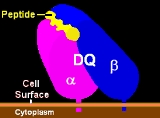
HLA-DQ
HLA-DQ is a cell surface receptor type protein found on antigen presenting cells. DQ is an αβ heterodimer of the MHC Class II type. The α and β chains are encoded by HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1, respectively. These two loci are adjacent to each other on chromosome 6p21.3. Both the α-chain and β-chain...
(DQ) serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of β6 subset of DQ β-chains. The β-chain of DQ isoforms are encoded by HLA-DQB1
HLA-DQB1
Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ beta 1, also known as HLA-DQB1, is a human gene and also denotes the genetic locus that contains this gene...
locus and DQ6 are encoded by the HLA-DQB1*06 allele group. This group currently contains many common alleles, DQB1*0602 is the most common. HLA-DQ6 and DQB1*06 are almost synonymous in meaning. DQ6 β-chains combine with α-chains, encoded by genetically linked HLA-DQA1
HLA-DQA1
Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ alpha 1, also known as HLA-DQA1, is a human gene present on short arm of chromosome 6 and also denotes the genetic locus which contains this gene...
alleles, to form the cis-haplotype isoforms. For DQ6, however, cis-isoform pairing only occurs with DQ1
HLA-DQ1
HLA-DQ1 is a serotype that covers a broad range of HLA-DQ haplotypes. Historically it was identified as a DR-like alpha chain called DC1, later, it was among 3 types DQw1 , DQw2 and DQw3. Of these three serotyping specificities only DQw1 recognized DQ alpha chain. The serotype is positive in...
α-chains. There are many haplotypes of DQ6.
Serology
| DQ6 | DQ1 | DQ5 | N | |
| allele | % | % | % | size (N) |
| 64 | 23 | 675 | ||
| 67 | 30 | 1 | 5151 | |
| 62 | 23 | 2 | 2807 | |
| 59 | 27 | 2 | 1592 | |
| 76 | 13 | 358 | ||
| 48 | 32 | 3 | 149 | |
Alleles
| freq | ||
| ref. | Population | (%) |
| Indig. Australian Cape York | 31.3 | |
| Indig. Australian Kimberly | 30.5 | |
| Nauru | 28.4 | |
| Fiji Viti Levu | 26.3 | |
| India Bombay | 26.3 | |
| Papua New Guinea Lowland | 26.0 | |
| China Guizhou Prov. Miao | 25.9 | |
| Papua New Guinea Madang | 23.1 | |
| Kiribati | 22.6 | |
| Japan | 22.0 | |
| Indonesia Nusa Tenggara | 19.2 | |
| India North Hindus | 18.7 | |
| Japan Hokkaido Wajin | 17.0 | |
| Uttar Pradesh Hindu | 15.1 | |
| PNG Lowland Wosera | 14.1 | |
| Western Samoa & Tokelau | 13.7 | |
| Pakistan Kalash | 13.0 | |
| India Lucknow | 12.9 | |
| China Wuhan | 12.8 | |
| South Korea (4) | 11.4 | |
| PNG Highland | 10.9 | |
| India Delhi | 9.0 | |
| Iran Baloch | 8.0 | |
| Mongolia Khalkha | 5.5 | |
| Lebanon Yuhmur | 4.3 | |
| Tunisia Ghannouch | 4.3 | |
| Poland Wielkopolska | 4.0 | |
| Mexico Mazatecans | 3.5 | |
| Spain E. Andalusia | 2.0 | |
| Italy Central | 1.9 | |
| France South East | 1.6 | |
| England Caucasoid | 1.1 | |
| Ireland South | 0.2 | |
| Italy Sardinia | 0.1 | |
| Brazil Guarani Kaiowa | 0.0 | |
| Cameroon Saa | 0.0 | |
DQB1*0601
DQB1*0601 is generally linked to DQA1*0103 as 6.1 haplotype. This haplotype is more common in Japan and other parts of East Asa.| freq | ||
| ref. | Population | (%) |
| Spain Pas Valley | 31.5 | |
| Cameroon Saa | 30.8 | |
| Congo Kinshasa Bantu | 30.0 | |
| PNG E. Highlands Goroka | 29.8 | |
| Siberia Ket Lower Yenisey | 29.4 | |
| Spain North Cabuernigo | 28.9 | |
| Russia Arkhangelsk Pomors | 24.7 | |
| Spain North Cantabrian | 24.7 | |
| Ireland South | 19.6 | |
| Belgian (2) | 19.4 | |
| Siberia Kushun Buryat | 18.0 | |
| Finland | 17.1 | |
| Siberia Kets Sulamai Village | 17.0 | |
| Poland Wielkopolska | 16.9 | |
| German Essen | 16.7 | |
| Sp. Basque Arratia Valley | 16.7 | |
| Denmark | 16.6 | |
| France Ceph | 15.7 | |
| Kenya | 14.6 | |
| England Caucasoid | 14.4 | |
| Sweden | 14.1 | |
| France Rennes | 13.8 | |
| Tunisia Matmata Berber | 11.7 | |
| Jordan Amman | 10.7 | |
| Japan Hokkaido Wajin | 10.0 | |
| Saudi A. Guraiat & Hail | 8.4 | |
| Japan Central | 8.2 | |
| Nauru | 8.2 | |
| Georgia Svaneti Svans | 8.1 | |
| France South East | 8.0 | |
| Ethiopia Amhara | 7.7 | |
| Algeria Oran | 7.6 | |
| Slovenia | 7.5 | |
| South Korea (1) | 7.4 | |
| Japan Fukuoka | 6.4 | |
| Pakistan Kalash | 5.8 | |
| China Xinjiang Uygur | 5.4 | |
| Papua New Guinea Lowland | 5.2 | |
| Mongolia Khalkh Ulaanbaatar | 4.9 | |
| Spain Murcia | 4.8 | |
| India Bombay | 4.2 | |
| Japan | 4.0 | |
| Greece (2) | 3.3 | |
| Israel Arabs | 2.3 | |
| Vietnam Hanoi Kinh | 2.0 | |
| Israel Jews | 1.5 | |
| Mongolia Khoton Tarialan | 1.2 | |
| USA Alaska Yupik Natives | 0.8 | |
| Mexico Mixtec Oaxaca | 0.5 | |
| Italy Sardinia pop2 | 0.1 | |
DQB1*0602
DQB1*0602 is commonly linked to DQA1*0102 to form 6.2 haplotype. DQ6.2 and is common from Central Asia into Western Europe, *0602 is also linked to DQA1*0103 in parts of Asia.| freq | ||
| ref. | Population | (%) |
| Georgia Svaneti Svans | 14.4 | |
| France West | 11.0 | |
| Netherlands | 10.6 | |
| German Essen | 9.2 | |
| Czech Republic | 9.0 | |
| Spain Murcia | 8.7 | |
| Slovakia | 8.4 | |
| Denmark | 8.3 | |
| India Lucknow | 8.3 | |
| Jordan Amman | 8.3 | |
| France Rennes | 8.1 | |
| Poland Wielkopolska | 8.0 | |
| Saudi Arabia Guraiat & Hail | 8.0 | |
| Tunisia Jerba Berber | 7.8 | |
| Uganda Muganda Baganda | 7.4 | |
| Spain North Cantabrian | 7.2 | |
| Finland | 7.1 | |
| France South | 6.9 | |
| China Xinjiang Uygur | 6.5 | |
| Russia Northwest Slavic | 6.0 | |
| Ireland Donegal | 5.3 | |
| Greece (3) | 5.2 | |
| Ireland Northern (2) | 4.9 | |
| Italy Rome | 4.0 | |
| CAR Aka Pygmies | 3.6 | |
| Lebanon Kafar Zubian | 3.2 | |
| Sweden | 2.5 | |
| Thailand | 2.1 | |
| China Wuhan | 1.7 | |
| Japan (2) | 1.0 | |
| South Korea (3) | 0.9 | |
| Malaysia | 0.6 | |
DQB1*0603
DQB1*0603 is commonly linked to DQA1*0103 as 6.3 and is common from Central Asia into Western Europe, *0603 is also linked to DQA1*0102 in parts of Asia. In Europe it is most common in the Netherlands.| freq | ||
| ref. | Population | (%) |
| Ethiopia Amhara | 10.7 | |
| Rwanda Kigali Hutu and Tutsi | 10.7 | |
| Ethiopia Oromo | 10.2 | |
| Japan | 8.0 | |
| Saudi Arabia Guraiat & Hail | 8.0 | |
| Iran Yazd Zoroastrians | 6.9 | |
| CAR Aka Pygmies | 6.5 | |
| South Korea (2) | 6.5 | |
| Sweden | 6.1 | |
| Netherlands | 5.6 | |
| Uganda Muganda Baganda | 5.3 | |
| Lebanon Niha el Shouff | 4.9 | |
| Denmark | 4.6 | |
| France Rennes | 4.6 | |
| Israel Gaza Palestinians | 3.9 | |
| China Xinjiang Uygur | 3.8 | |
| Algeria1 | 3.5 | |
| Russia Northwest Slavic | 3.5 | |
| England Caucasoid | 3.1 | |
| German Essen | 2.6 | |
| Czech Republic | 2.4 | |
| Greece | 2.0 | |
| India Delhi | 1.8 | |
| Nauru | 1.5 | |
| Finland | 1.4 | |
| Gambia | 0.7 | |
DQB1*0604
DQB1*0604 is found at higher frequencies in parts Africa and Asia and is linked almost exclusively to DQA1*0102 as 6.4. This haplotype is found at its highest Eurasian frequencies in Japan.| freq | ||
| ref. | Population | (%) |
| Rwanda Kigali Hutu & Tutsi | 5.7 | |
| Kenya | 5.3 | |
| Uganda Muganda Baganda | 5.3 | |
| Congo Kinshasa Bantu | 4.4 | |
| Gambia | 4.4 | |
| Mongolia Tsaatan | 4.2 | |
| South Korea (3) | 3.7 | |
| Cameroon Saa | 3.5 | |
| Slovenia | 3.0 | |
| Tunisia | 3.0 | |
| Zimbabwe Harare Shona | 2.2 | |
| Vietnam Hanoi Kinh | 2.0 | |
| Netherlands | 1.7 | |
| Saudi Arabia Guraiat & Hail | 1.6 | |
| Algeria Oran | 1.5 | |
| Greece (2) | 1.2 | |
| Thailand (2) | 1.2 | |
| Tunisia Matmata Berber | 1.2 | |
| Italy Rome | 1.0 | |
| Spain Granada | 0.7 | |
| Italy Bergamo | 0.6 | |
| Ireland South | 0.2 | |
| China Urumqi Uygur | 0.0 | |
| USA Alaska Yupik Natives | 0.0 | |
Haplotypes and disease
Susceptibility to LeptospirosisLeptospirosis
Leptospirosis is caused by infection with bacteria of the genus Leptospira, and affects humans as well as other mammals, birds, amphibians, and reptiles.The...
infection was found associated with undifferentiated DQ6. Whereas DQ6 was protective against death (or need for liver transplantion) in primary sclerosing cholangitis
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a chronic liver disease caused by progressive inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts of the liver. The inflammation impedes the flow of bile to the gut, which can ultimately lead to liver cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer...
.
DQ6.1
DQA1*0103:DQB1*0601 (DQ6.1) is found at increased freqeuncies in Asia and is almostabsent in Western Europe. It confers protection from narcolepsy
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a chronic sleep disorder, or dyssomnia, characterized by excessive sleepiness and sleep attacks at inappropriate times, such as while at work. People with narcolepsy often experience disturbed nocturnal sleep and an abnormal daytime sleep pattern, which often is confused with insomnia...
, juvenile diabetes, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) syndrome, pemphigus vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris is a chronic blistering skin disease with skin lesions that are rarely pruritic, but which are often painful.-Pathophysiology:...
, multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory disease in which the fatty myelin sheaths around the axons of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to demyelination and scarring as well as a broad spectrum of signs and symptoms...
, myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune neuromuscular disease leading to fluctuating muscle weakness and fatiguability...
.
DQ6.2
DQ6.2 (DQA1*0102 : DQB1*0602) is commonly linked to DR15 and as such is part of the HLA B7-DR15-DQ6HLA B7-DR15-DQ6
HLA B7-DR15-DQ6 is a multigene haplotype that covers a majority of the human major histocompatibility complex on chromosome 6. A multigene haplotype is set of inherited alleles covering several genes, or gene-alleles, common multigene haplotypes are generally the result of descent by common ancestry...
haplotype. This haplotype is considered to be the longest multigene haplotype known within the human genome as it covers over 4.7 million nucleotides. The DR15-DQ6.2 haplotype is the most common DR-DQ haplotype in Europe, and approximately 30% of Americans carry at least DQ6.2. The haplotype is even more common in Central Asia.
DQ6.2 associations with disease
For myasthenia gravisMyasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune neuromuscular disease leading to fluctuating muscle weakness and fatiguability...
, recognition α34-49 of AChR increased with DQ6.2. DQA1*0102 increases risk cervical cancer
Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is malignant neoplasm of the cervix uteri or cervical area. One of the most common symptoms is abnormal vaginal bleeding, but in some cases there may be no obvious symptoms until the cancer is in its advanced stages...
. In multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory disease in which the fatty myelin sheaths around the axons of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to demyelination and scarring as well as a broad spectrum of signs and symptoms...
DQA1*0102 was the most frequent allele and DQB1*0602 increased significantly in the MS patients.
Protective effects of DQ6.2
In primary biliary cirrhosisPrimary biliary cirrhosis
Primary biliary cirrhosis, often abbreviated PBC, is an autoimmune disease of the liver marked by the slow progressive destruction of the small bile ducts within the liver. When these ducts are damaged, bile builds up in the liver and over time damages the tissue. This can lead to scarring,...
DQ6.2 appears to have a negative association with disease. DQ6.2 also appears to have a protective effect in juvenile diabetes. DQ6.2 is also protective against infantile spasms in mestizos.

