Hallirhoidae
Encyclopedia
Hallirhoidae is an extinct family of lithistid demosponge
s found throughout the world from the Cretaceous
to the Eocene
, whereupon they became extinct. The highest concentration of species occurred in the Tethys Ocean
during the upper Cretaceous
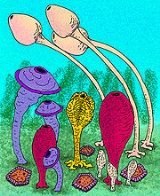
. The hallirhoid demosponges were very distinctive-looking, largely pear-shaped sponges that were attached to the seafloor by a long stem-like stalk.
Demosponge
The Demospongiae are the largest class in the phylum Porifera. Their "skeletons" are made of spicules consisting of fibers of the protein spongin, the mineral silica, or both. Where spicules of silica are present, they have a different shape from those in the otherwise similar glass sponges...
s found throughout the world from the Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
to the Eocene
Eocene
The Eocene Epoch, lasting from about 56 to 34 million years ago , is a major division of the geologic timescale and the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Palaeocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the...
, whereupon they became extinct. The highest concentration of species occurred in the Tethys Ocean
Tethys Ocean
The Tethys Ocean was an ocean that existed between the continents of Gondwana and Laurasia during the Mesozoic era before the opening of the Indian Ocean.-Modern theory:...
during the upper Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
. The hallirhoid demosponges were very distinctive-looking, largely pear-shaped sponges that were attached to the seafloor by a long stem-like stalk.

