
Hasty Pudding Cipher
Encyclopedia
The Hasty Pudding Cipher (HPC) is a variable-block-size block cipher
designed by Richard Schroeppel
, which was an unsuccessful candidate in the competition for selecting the U.S.
Advanced Encryption Standard
(AES). It has a number of unusual properties for a block cipher: its input block size and key length are variable, and it includes an additional input parameter called the "spice" that is meant to be used as a secondary, non-secret key. The Hasty Pudding cipher was the only AES candidate designed exclusively by U.S. cryptographers.
The Hasty Pudding cipher is in the public domain
.
The Hasty Pudding cipher algorithms all use 64-bit words internally. The cipher is designed to run on 64-bit machines
, which can easily perform simple operations on 64-bit words.
Decryption involves undoing the steps of encryption one by one. Many operations are easily undone (e.g. s0 = s0 + s1 is undone by computing s0 = s0 − s1). Other operations are more complex to undo. Some of the ideas involved include:
The Hasty Pudding cipher can also be used to encrypt values in a range that do not translate to strings with an integral number of bits; for instance, it can encrypt a number from 0 to N by producing another number from 0 to N. It does this by using the smallest subcipher that can handle the input as a bit string, and applying it to the input as a bit string, repeatedly, until the output is in the proper range.
, and three times as fast as the other candidates, and that its performance on a 32-bit machine was adequate. Comments from others did not support this view; for instance, Schneier
et al.'s analysis ranked the Hasty Pudding cipher 4th best (376 cycles) on a 64-bit machine, although for Rijndael and Twofish
, the performance was only estimated. On a 32-bit Pentium, Hasty Pudding encryption was rated by Schneier et al. at 1600 clock cycles, 10th best out of the 15 candidates. Schneier et al., and Schroeppel, noted that the speed of the cipher would be significantly impacted on a 32-bit machine because of its heavy use of 64-bit operations, particularly bit shifts.
The Hasty Pudding cipher's key setup was rated as relatively slow; 120000 cycles on a Pentium..
The cipher was criticized for its performance on smartcards. Specifically, some comments pointed out the difficulty of keeping over 2KB of RAM for the key table.
Despite the relative lack of cryptanalysis, the Hasty Pudding cipher was criticized for its hard-to-understand design and its lack of grounding in research results. Schroeppel has offered a bottle of Dom Pérignon champagne
to the best paper presenting progress on the Hasty Pudding cipher. It did not make the second round of consideration for AES.
The Hasty Pudding cipher is regarded to be the first tweakable block cipher.
Block cipher
In cryptography, a block cipher is a symmetric key cipher operating on fixed-length groups of bits, called blocks, with an unvarying transformation. A block cipher encryption algorithm might take a 128-bit block of plaintext as input, and output a corresponding 128-bit block of ciphertext...
designed by Richard Schroeppel
Richard Schroeppel
Richard C. Schroeppel is an American mathematician born in Illinois. His research has included magic squares, elliptic curves, and cryptography...
, which was an unsuccessful candidate in the competition for selecting the U.S.
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
Advanced Encryption Standard
Advanced Encryption Standard
Advanced Encryption Standard is a specification for the encryption of electronic data. It has been adopted by the U.S. government and is now used worldwide. It supersedes DES...
(AES). It has a number of unusual properties for a block cipher: its input block size and key length are variable, and it includes an additional input parameter called the "spice" that is meant to be used as a secondary, non-secret key. The Hasty Pudding cipher was the only AES candidate designed exclusively by U.S. cryptographers.
The Hasty Pudding cipher is in the public domain
Public domain
Works are in the public domain if the intellectual property rights have expired, if the intellectual property rights are forfeited, or if they are not covered by intellectual property rights at all...
.
The cipher
The Hasty Pudding cipher consists of 5 different sub-ciphers:| HPC-Tiny | 0–35 bits |
| HPC-Short | 36–64 bits |
| HPC-Medium | 65-128 bits |
| HPC-Long | 129–512 bits |
| HPC-Extended | 513+ bits |
The Hasty Pudding cipher algorithms all use 64-bit words internally. The cipher is designed to run on 64-bit machines
Computer architecture
In computer science and engineering, computer architecture is the practical art of selecting and interconnecting hardware components to create computers that meet functional, performance and cost goals and the formal modelling of those systems....
, which can easily perform simple operations on 64-bit words.
Key expansion
The Hasty Pudding cipher can take a key of any number of bits for any one of the five subciphers. The cipher itself uses a key table of 16,384 bits (256 64-bit words). In order to derive the key table from the key, the key expansion function uses the following algorithm:- The first three words, KX[0], KX[1], KX[2] are set based on constants, the sub-cipher, and the length of the key. KX[1] is computed with a multiplication; the other operations involved are an addition and a bit shift.
- Each successive word, KX[i] is determined from the three previous words by an efficient recursive formula.
- The key bits are XORed into the bits of the key table, starting at KX[0], until all the key bits are used. (Keys longer than 8,192 bits use a more complicated procedure.)
- Several passes over the key table are made. Each time, a "stirring function" is applied to each word of the key table, in sequence. The stirring function uses eight internal variables, and uses 14 logical bit operations, 5 bit shifts, and 14 additions / subtractions. Each use of the stirring function will modify one word in the key table, based on its previous value, the values of certain other words, and the internal variables of the stirring function. (3 total passes is the default.)
Encryption and decryption
Each of the subciphers uses a different algorithm, but there are certain similarities. Three inputs are used to determine the ciphertext: the plaintext (in several 64-bit words plus one "fragment"), the spice (eight 64-bit words, with default value 0), and the key table. The operations within the cipher consist of "stirring", in which internal variables are combined in various ways, with values from the key table and spice being included at regular intervals. HPC-Short uses two fixed permutations in addition, and HPC-Tiny consists of many special sub-cases.Decryption involves undoing the steps of encryption one by one. Many operations are easily undone (e.g. s0 = s0 + s1 is undone by computing s0 = s0 − s1). Other operations are more complex to undo. Some of the ideas involved include:
- An operation like x = x
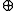 (x >> 17 ) is undone by a two-step process: (1) x = x
(x >> 17 ) is undone by a two-step process: (1) x = x 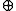 (x >> 17 ), followed by (2) x = x
(x >> 17 ), followed by (2) x = x 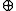 (x >> 34 ).
(x >> 34 ). - The cipher uses value-dependent lookups into the key table. These can be undone, since the lookup depends only on the last 8 bits of a variable, and when it becomes necessary to look up the value from the key table in decryption, the last 8 bits of the value at a certain earlier point in the computation are predictable, even when those operations cannot all be undone without the key table value. For instance, if the lookup of k is based on the last 8 bits of x, then when we want to undo a step like x = x
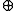 (k << 8), we can look up k by noting that the last 8 bits of x are unchanged by this operation.
(k << 8), we can look up k by noting that the last 8 bits of x are unchanged by this operation.
The Hasty Pudding cipher can also be used to encrypt values in a range that do not translate to strings with an integral number of bits; for instance, it can encrypt a number from 0 to N by producing another number from 0 to N. It does this by using the smallest subcipher that can handle the input as a bit string, and applying it to the input as a bit string, repeatedly, until the output is in the proper range.
Performance
The Hasty Pudding cipher was claimed by Schroeppel to be the fastest AES candidate on a 64-bit architecture; Schroeppel claimed it to be twice as fast as its nearest competitor, DFCDFC (cipher)
In cryptography, DFC is a block cipher which wascreated in 1998 by a group of researchers from École Normale Supérieure, CNRS, and France Télécom and submitted to the AES competition.Like other AES candidates, DFC operates on blocks of 128 bits, using a key of 128, 192, or 256 bits...
, and three times as fast as the other candidates, and that its performance on a 32-bit machine was adequate. Comments from others did not support this view; for instance, Schneier
Bruce Schneier
Bruce Schneier is an American cryptographer, computer security specialist, and writer. He is the author of several books on general security topics, computer security and cryptography, and is the founder and chief technology officer of BT Managed Security Solutions, formerly Counterpane Internet...
et al.'s analysis ranked the Hasty Pudding cipher 4th best (376 cycles) on a 64-bit machine, although for Rijndael and Twofish
Twofish
In cryptography, Twofish is a symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 128 bits and key sizes up to 256 bits. It was one of the five finalists of the Advanced Encryption Standard contest, but was not selected for standardisation...
, the performance was only estimated. On a 32-bit Pentium, Hasty Pudding encryption was rated by Schneier et al. at 1600 clock cycles, 10th best out of the 15 candidates. Schneier et al., and Schroeppel, noted that the speed of the cipher would be significantly impacted on a 32-bit machine because of its heavy use of 64-bit operations, particularly bit shifts.
The Hasty Pudding cipher's key setup was rated as relatively slow; 120000 cycles on a Pentium..
The cipher was criticized for its performance on smartcards. Specifically, some comments pointed out the difficulty of keeping over 2KB of RAM for the key table.
Further work
There have been relatively few results on attacking the Hasty Pudding cipher. Early in the AES process, David Wagner noted that relatively large classes of Hasty Pudding keys were equivalent in that they led to the same key table. This was expanded upon by D'Halluin et al., who noted that for 128-bit keys, approximately 2120 keys are "weak keys" which each have 230 equivalent keys each. In response to this attack, Schroeppel modified the key expansion algorithm to include one additional step.Despite the relative lack of cryptanalysis, the Hasty Pudding cipher was criticized for its hard-to-understand design and its lack of grounding in research results. Schroeppel has offered a bottle of Dom Pérignon champagne
Dom Pérignon (wine)
Dom Pérignon is a brand of vintage Champagne produced by the Champagne house Moët & Chandon and serves as that house's prestige champagne. It is named after Dom Pérignon, a Benedictine monk who was an important quality pioneer for Champagne wine but who, contrary to popular myths, did not discover...
to the best paper presenting progress on the Hasty Pudding cipher. It did not make the second round of consideration for AES.
The Hasty Pudding cipher is regarded to be the first tweakable block cipher.

