
Havildar Ishar Singh
Encyclopedia
Tirah Campaign
The Tirah Campaign, often referred to in contemporary British accounts as the Tirah Expedition, was an Indian frontier war in 1897–98. Tirah is a mountainous tract of country.-Rebellion:...
on 12 September 1897 between twenty-one Sikh
Sikh
A Sikh is a follower of Sikhism. It primarily originated in the 15th century in the Punjab region of South Asia. The term "Sikh" has its origin in Sanskrit term शिष्य , meaning "disciple, student" or शिक्ष , meaning "instruction"...
s of the 4th Battalion (then 36th Sikhs
36th Sikhs
The 36th Sikhs was an infantry regiment in the British Indian Army. They could trace their origins to 1887, when they were the 36th Bengal Infantry. They had one other change in title in 1901, when they became the 36th Sikh Infantry. They finally became the 36th Sikhs in 1903, after the...
) of the Sikh Regiment
The Sikh Regiment
The Sikh Regiment is an 19 battalion strong, infantry regiment of the Indian Army, drawing a bulk of its recruits from the Sikh community. The regiment was officially raised just before the annexation of the Sikh Empire on August 1, 1846, by the British Empire...
of British India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, defending an army post, and 10,000 Afghan
Pashtun people
Pashtuns or Pathans , also known as ethnic Afghans , are an Eastern Iranic ethnic group with populations primarily between the Hindu Kush mountains in Afghanistan and the Indus River in Pakistan...
and Orakzai
Orakzai
Orakzai is a Pashtun tribe settled in the Orakzai Agency of Pakistan. It consists of eighteen clans. Most of the members are situated in the North West Frontier Province of Pakistan.-Location:...
tribesmen. The battle occurred in the Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, now part of Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, which then formed part of British India.
The contingent of the twenty-one Sikhs from the 36th Sikhs was led by Havildar
Havildar
Havildar ) was the Military 'In Charge' of a Fort during the times of Maratha Empire. In the British Indian Army it was equivalent rank to Sergeant, next above Naik, and is still used in the modern Indian Army and Pakistan Army. The cavalry equivalent is Daffadar...
Ishar Singh. They all chose to fight to the death.
Sikh military personnel and Sikh civilians commemorate the battle every year on 12 September, as Saragarhi Day.
Situation
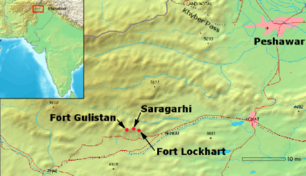
Saragarhi is a small village in the border district of KohatKohat District
Kohat is a district of the Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan, Kohat city is the capital of the district. It is inhabited by various Pashtun tribes such as Afridi,Khattaks, Bangash and the Orakzaies. The main language of the district is Pashto....
, situated on the Samana Range
Samana Range
The Samana Range is a mountain ridge in the Kohat District of the North-West Frontier Province of Pakistan, commanding the southern boundary of Tirah. The ridge lies between the Khanki Valley on the north and the Miranzai Valley on the south, and extends for some 30 m. west from Hangu to the Samana...
, in present day Pakistan. On the 20th April 1894, the 36th Sikh Regiment of the British Army was created, under the command of Colonel J. Cook.
In August 1897, five companies of the 36th Sikhs under Lt. Col. John Haughton, were sent to the Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, stationed at Samana Hills, Kurag, Sangar, Sahtop Dhar and Saragarhi.
The British had partially succeeded in getting control of this volatile area, however tribal Pashtuns attacked British personnel from time to time. Thus a series of forts, originally constructed by Maharaja Ranjit Singh
Ranjit Singh
Maharaja Ranjit Singh Ji was the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire.-Early life:...
, Ruler of the Sikh Empire, were consolidated. Two of the forts were Fort Lockhart, (on the Samana Range of the Hindu Kush
Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range that stretches between central Afghanistan and northern Pakistan. The highest point in the Hindu Kush is Tirich Mir in the Chitral region of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.It is the westernmost extension of the Pamir Mountains, the Karakoram Range, and is a...
mountains), and Fort Gulistan (Sulaiman Range), situated a few miles apart. Due to the forts not being visible to each other, Saragarhi was created midway, as a heliograph
Heliograph
A heliograph is a wireless solar telegraph that signals by flashes of sunlight reflected by a mirror. The flashes are produced by momentarily pivoting the mirror, or by interrupting the beam with a shutter...
ic communication post. The Saragarhi post, situated on a rocky ridge, consisted of a small block house with loop-holed ramparts and a signalling tower.
A general uprising by the Afghans began there in 1897, and between 27 August - 11 September, many vigorous efforts by Pashtuns to capture the forts were thwarted by 36th Sikh regiment. In 1897, insurgent and inimical activities had increased, and on 3rd and 9 September Afridi tribes, with allegiance to Afghans, attacked Fort Gulistan. Both the attacks were repulsed, and a relief column from Fort Lockhart, on its return trip, reinforced the signalling detachment positioned at Saragarhi, increasing its strength to one Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) and twenty troops of Other Ranks (ORs).
On September 12, 1897, 10,000 Pashtuns attacked the signalling post at Saragarhi, so that communication would be lost between the two forts.
The battle
Details of the Battle of Saragarhi are considered fairly accurate, due to Gurmukh Singh signalling events to Fort Lockhart as they occurred.- Around 9:00am, around 10,000 Afghans reach the signaling post at Saragarhi.
- Sardar Gurmukh Singh signals to Col. Haughton, situated in Fort Lockhart, that they are under attack.
- Colonel Haughton states he cannot send immediate help to Saragarhi.
- The soldiers decide to fight to the last to prevent the enemy from reaching the forts.
- Bhagwan Singh becomes the first injured and Lal Singh is seriously wounded.
- Soldiers Lal Singh and Jiwa Singh reportedly carry the dead body of Bhagwan Singh back to the inner layer of the post.
- The enemy breaks a portion of the wall of the picket.
- Colonel Haughton signals that he has estimated between 10,000 and 14,000 Pashtuns attacking Saragarhi.
- The leaders of the Afghan forces reportedly make promises to the soldiers to entice them to surrender.
- Reportedly two determined attempts are made to rush the open gate, but are unsuccessful.
- Later, the wall is breached.
- Thereafter, some of the fiercest hand-to-hand fighting occurs.
- In an act of outstanding bravery, Ishar Singh orders his men to fall back into the inner layer, whilst he remains to fight. However, this is breached and all but one of the defending soldiers are killed, along with many of the Pashtuns.
- Gurmukh Singh, who communicated the battle with Col. Haughton, was the last Sikh defender. He is stated to have killed 20 Afghans, the Pashtuns having to set fire to the post to kill him. As he was dying he was said to have yelled repeatedly the Sikh battle-cry "Bole So Nihal, Sat Sri Akal" (Victory belongs to those who recite the name of God with a true heart).
Having destroyed Saragarhi, the Afghans turned their attention to Fort Gulistan, but they had been delayed too long, and reinforcements arrived there in the night of 13–14 September, before the fort could be conquered. The Pashtuns later admitted that they had lost about 180 killed and many more wounded during the engagement against the 21 Sikh soldiers, but some 600 bodies are said to have been seen around the ruined post when the relief party arrived (however, the fort had been retaken, on 14 September, by the use of intensive artillery fire, which may have caused many casualties). The total casualties in the entire campaign, including the Battle of Saragarhi, numbered at around 4,800.
British parliament
When the gallantry of Saragarhi was recounted to the Parliament of the United KingdomParliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body in the United Kingdom, British Crown dependencies and British overseas territories, located in London...
, the recitation drew a standing ovation
Standing ovation
A standing ovation is a form of applause where members of a seated audience stand up while applauding after extraordinary performances of particularly high acclaim...
from the members. The saga of Saragarhi was also brought to the notice of Queen Victoria
Victoria of the United Kingdom
Victoria was the monarch of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death. From 1 May 1876, she used the additional title of Empress of India....
.
Commemorative tablet
The tablet (pictured right), inscription reads;
Order of Merit
All the 21 Sikh non-commissioned officers and soldiers of other ranks who laid down their lives in the Battle of Saragarhi were posthumously awarded the Indian Order of Merit, the highest gallantry award of that time, which an Indian soldier could receive by the hands of the British crownBritish monarchy
The monarchy of the United Kingdom is the constitutional monarchy of the United Kingdom and its overseas territories. The present monarch, Queen Elizabeth II, has reigned since 6 February 1952. She and her immediate family undertake various official, ceremonial and representational duties...
, the corresponding gallantry award being Victoria Cross
Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross is the highest military decoration awarded for valour "in the face of the enemy" to members of the armed forces of various Commonwealth countries, and previous British Empire territories....
. This award is equivalent to today's Param Vir Chakra
Param Vir Chakra
The Param Vir Chakra is India's highest military decoration awarded for the highest degree of valour or self-sacrifice in the presence of the enemy. It can be, and often has been, awarded posthumously....
awarded by the President of India
President of India
The President of India is the head of state and first citizen of India, as well as the Supreme Commander of the Indian Armed Forces. President of India is also the formal head of all the three branches of Indian Democracy - Legislature, Executive and Judiciary...
.
The names of the 21 recipients of the gallantry award are:
- HavildarHavildarHavildar ) was the Military 'In Charge' of a Fort during the times of Maratha Empire. In the British Indian Army it was equivalent rank to Sergeant, next above Naik, and is still used in the modern Indian Army and Pakistan Army. The cavalry equivalent is Daffadar...
Ishar Singh (regimental number 165) - NaikNaik (military rank)Naik is the equivalent rank to Corporal in the Indian Army and Pakistan Army, and previously in the British Indian Army and the Camel Corps, ranking between Lance Naik and Havildar. In cavalry units the equivalent is Lance Daffadar. Like a British Corporal, a Naik wears two rank chevrons....
Lal Singh (332) - Lance NaikLance NaikLance Naik is the equivalent rank to Lance Corporal in the Pakistan and Indian Armies and before 1947, in the British Indian Army, ranking below Naik. In cavalry units the equivalent is Acting Lance Daffadar. Like a British Lance Corporal, he wore a single rank chevron....
Chanda Singh (546) - SepoySepoyA sepoy was formerly the designation given to an Indian soldier in the service of a European power. In the modern Indian Army, Pakistan Army and Bangladesh Army it remains in use for the rank of private soldier.-Etymology and Historical usage:...
Sundar Singh (1321) - Sepoy Ram Singh (287)
- Sepoy Uttar Singh (492)
- Sepoy Sahib Singh (182)
- Sepoy Hira Singh (359)
- Sepoy Daya Singh (687)
- Sepoy Jivan Singh (760)
- Sepoy Bhola Singh (791)
- Sepoy Narayan Singh (834)
- Sepoy Gurmukh Singh (814)
- Sepoy Jivan Singh (871)
- Sepoy Gurmukh Singh (1733)
- Sepoy Ram Singh (163)
- Sepoy Bhagwan Singh (1257)
- Sepoy Bhagwan Singh (1265)
- Sepoy Buta Singh (1556)
- Sepoy Jivan Singh (1651)
- Sepoy Nand Singh (1221)
Remembrance and legacy
In 1915, Chuhar Singh wrote the epic poem "Khalsa BahadurKhalsa Bahadur
Khalsa Bahadur is an epic poem written by Chuhar Singh describing the "chivalry and sacrifice" of Sikh soldiers at the Battle of Saragarhi. The poem is 55 pages long, written using the baint verse form, and written in the Punjabi language...
" in memory of the Sikhs who died at Sargarhi.
According to the Indian Express, Saragarhi is "one of the eight collective stories on bravery published by UNESCO for children" (bibliographical details not given) which also, according to other sources, include the heroic Battle of Thermopylae
Battle of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae was fought between an alliance of Greek city-states, led by King Leonidas of Sparta, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I over the course of three days, during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place simultaneously with the naval battle at Artemisium, in August...
. The battle has become iconic
Cultural icon
A cultural icon can be a symbol, logo, picture, name, face, person, building or other image that is readily recognized and generally represents an object or concept with great cultural significance to a wide cultural group...
of eastern military civilization, British empire military history and Sikh history. The modern Sikh Regiment continues to celebrate the day of the Battle of Saragarhi each 12 September as the Regimental Battle Honours Day. To commemorate the men the British built two Saragarhi Gurudwaras: one in Amritsar
Amritsar
Amritsar is a city in the northern part of India and is the administrative headquarters of Amritsar district in the state of Punjab, India. The 2001 Indian census reported the population of the city to be over 1,500,000, with that of the entire district numbering 3,695,077...
very close to the main entrance of the Golden Temple
Harmandir Sahib
The Harmandir Sahib also Darbar Sahib , also referred to as the Golden Temple, is a prominent Sikh gurdwara located in the city of Amritsar, Punjab . Construction of the gurdwara was begun by Guru Ram Das, the fourth Sikh Guru, and completed by his successor, Guru Arjan Dev...
, and another in Ferozepur Cantonment, which was the district that most of the men hailed from.
In Indian Schools
The Indian military, in particular the Indian ArmyIndian Army
The Indian Army is the land based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. With about 1,100,000 soldiers in active service and about 1,150,000 reserve troops, the Indian Army is the world's largest standing volunteer army...
have been pushing for the battle to be taught in India's schools. They want it taught due to the heroism shown by the Indian soldiers to acts as inspiration for young children – in the field of bravery. There were articles like these, printed in the Punjab's longest-established newspaper, The Tribune in 1999: "the military action at Saragarhi is taught to students the world over and particularly to students in France." Although there seems to be no evidence for this claim (it is not, for example, on France's national school curriculum) the news was enough to provoke political debate, and the battle has been taught in schools in the Punjab since 2000:
Saragarhi Day
Saragarhi Day, is a SikhSikh
A Sikh is a follower of Sikhism. It primarily originated in the 15th century in the Punjab region of South Asia. The term "Sikh" has its origin in Sanskrit term शिष्य , meaning "disciple, student" or शिक्ष , meaning "instruction"...
military commemoration day celebrated on the 12th of September every year to commemorate The Battle of Saragarhi. Sikh military
Military
A military is an organization authorized by its greater society to use lethal force, usually including use of weapons, in defending its country by combating actual or perceived threats. The military may have additional functions of use to its greater society, such as advancing a political agenda e.g...
personnel and Sikh non-military people commemorate the battle around the World
World
World is a common name for the whole of human civilization, specifically human experience, history, or the human condition in general, worldwide, i.e. anywhere on Earth....
every year on September 12.
All units of the Sikh Regiment celebrate Saragarhi Day every year as the Regimental Battle Honours Day.
Saragarhi Memorial Gurudwara (temple) was built in memory of the 21 Sikh soldiers that fought at The Battle of Saragarhi.
Saragarhi and Thermopylae
The battle has frequently been compared to the Battle of ThermopylaeBattle of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae was fought between an alliance of Greek city-states, led by King Leonidas of Sparta, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I over the course of three days, during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place simultaneously with the naval battle at Artemisium, in August...
, where a small Greek
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
force faced a large Persian army of Xerxes
Xerxes I of Persia
Xerxes I of Persia , Ḫšayāršā, ), also known as Xerxes the Great, was the fifth king of kings of the Achaemenid Empire.-Youth and rise to power:...
(480 BC).
The comparison is made because of the overwhelming odds faced by a tiny defending force in each case, and the defenders' brave stand to their deaths, as well as the extremely disproportionate number of fatalities caused to the attacking force.
It is important to note that during the Battle of Saragarhi, the British did not manage to get a relief unit there until after the 21 had fought to their deaths. At Thermopylae, the 300 Spartans and their allies also stayed after their lines had been outflanked, to fight to their deaths.
Further reading
- Saragarhi Battalion: Ashes to Glory by Kanwaljit Singh and H.S. Ahluwalia, New Delhi : Lancer International, 1987 (ISBN 8170620228)
External links
- Battle of Saragarhi, britishempire.co.uk- accessed 2008-01-25
- Article on Saragarhi Day being celebrated by The Sikh Regiment, tribuneindia.com (4 October 1998)- accessed 2008-01-25

