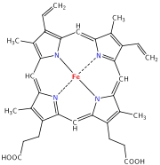
Heme b
Encyclopedia
Heme B or haem B is the most abundant heme
, both hemoglobin
and myoglobin
are examples of oxygen
transport proteins that contain heme B. The peroxidase
family of enzymes also contain heme B. The COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes (cyclooxygenase) of recent fame, also contain heme B at one of two active sites.
Generally, heme B is attached to the surrounding protein matrix (known as the apoprotein
) through a single coordination bond between the heme iron and an amino-acid side-chain.
Both hemoglobin
and myoglobin
have a coordination bond to an evolutionarily-conserved histidine
, while nitric oxide synthase
and cytochrome P450 have a coordination bond to an evolutionarily-conserved cysteine
bound to the iron center of heme B.
Since the iron in heme B containing proteins is bound to the four nitrogen
s of the porphyrin
(forming a plane) and a single electron donating atom of the protein, the iron is often in a pentacoordinate state. When oxygen or the toxic carbon monoxide
is bound the iron is hexacoordinated.
Heme
A heme or haem is a prosthetic group that consists of an iron atom contained in the center of a large heterocyclic organic ring called a porphyrin. Not all porphyrins contain iron, but a substantial fraction of porphyrin-containing metalloproteins have heme as their prosthetic group; these are...
, both hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of all vertebrates, with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae, as well as the tissues of some invertebrates...
and myoglobin
Myoglobin
Myoglobin is an iron- and oxygen-binding protein found in the muscle tissue of vertebrates in general and in almost all mammals. It is related to hemoglobin, which is the iron- and oxygen-binding protein in blood, specifically in the red blood cells. The only time myoglobin is found in the...
are examples of oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
transport proteins that contain heme B. The peroxidase
Peroxidase
Peroxidases are a large family of enzymes that typically catalyze a reaction of the form:For many of these enzymes the optimal substrate is hydrogen peroxide, but others are more active with organic hydroperoxides such as lipid peroxides...
family of enzymes also contain heme B. The COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes (cyclooxygenase) of recent fame, also contain heme B at one of two active sites.
Generally, heme B is attached to the surrounding protein matrix (known as the apoprotein
Apoprotein
Apoprotein can refer to:*Apoenzyme, the protein part of an enzyme without its characteristic prosthetic group.*Apolipoprotein, a lipid-binding protein that is a constituent of the plasma lipoprotein....
) through a single coordination bond between the heme iron and an amino-acid side-chain.
Both hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of all vertebrates, with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae, as well as the tissues of some invertebrates...
and myoglobin
Myoglobin
Myoglobin is an iron- and oxygen-binding protein found in the muscle tissue of vertebrates in general and in almost all mammals. It is related to hemoglobin, which is the iron- and oxygen-binding protein in blood, specifically in the red blood cells. The only time myoglobin is found in the...
have a coordination bond to an evolutionarily-conserved histidine
Histidine
Histidine Histidine, an essential amino acid, has a positively charged imidazole functional group. It is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are CAU and CAC. Histidine was first isolated by German physician Albrecht Kossel in 1896. Histidine is an essential amino acid in humans...
, while nitric oxide synthase
Nitric oxide synthase
Nitric oxide synthases are a family of enzymes that catalyze the production of nitric oxide from L-arginine. NO is an important cellular signaling molecule, having a vital role in many biological processes...
and cytochrome P450 have a coordination bond to an evolutionarily-conserved cysteine
Cysteine
Cysteine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2SH. It is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans. Its codons are UGU and UGC. The side chain on cysteine is thiol, which is polar and thus cysteine is usually classified as a hydrophilic amino acid...
bound to the iron center of heme B.
Since the iron in heme B containing proteins is bound to the four nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
s of the porphyrin
Porphyrin
Porphyrins are a group of organic compounds, many naturally occurring. One of the best-known porphyrins is heme, the pigment in red blood cells; heme is a cofactor of the protein hemoglobin. Porphyrins are heterocyclic macrocycles composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at...
(forming a plane) and a single electron donating atom of the protein, the iron is often in a pentacoordinate state. When oxygen or the toxic carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide , also called carbonous oxide, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly lighter than air. It is highly toxic to humans and animals in higher quantities, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal...
is bound the iron is hexacoordinated.

