
Hepatic fructokinase
Encyclopedia
Hepatic fructokinase is an enzyme
that catalyzes the phosphorylation
of fructose
to produce fructose-1-phosphate
.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes the phosphorylation
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation activates or deactivates many protein enzymes....
of fructose
Fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a simple monosaccharide found in many plants. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorbed directly into the bloodstream during digestion. Fructose was discovered by French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut in 1847...
to produce fructose-1-phosphate
Fructose-1-phosphate
Fructose-1-phosphate is a derivative of fructose. It is generated by hepatic fructokinase.It is converted by aldolase B into glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone phosphate ....
.
- ATP +
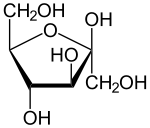
 ADP +
ADP + 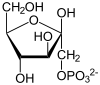
- ATPAdenosine triphosphateAdenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
+ D-fructose → ADPAdenosine diphosphateAdenosine diphosphate, abbreviated ADP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside adenosine. ADP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine....
+ D-fructose-1-phosphate

