
Herod Archelaus
Encyclopedia

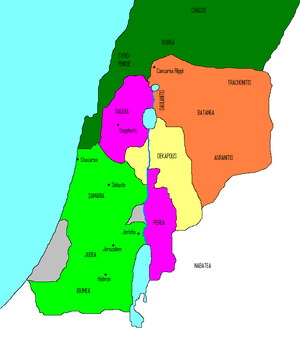
Herod Archelaus was the ethnarch
Ethnarch
Ethnarch, pronounced , the anglicized form of ethnarches refers generally to political leadership over a common ethnic group or homogeneous kingdom. The word is derived from the Greek words and ....
of Samaria
Samaria
Samaria, or the Shomron is a term used for a mountainous region roughly corresponding to the northern part of the West Bank.- Etymology :...
, Judea
Judea
Judea or Judæa was the name of the mountainous southern part of the historic Land of Israel from the 8th century BCE to the 2nd century CE, when Roman Judea was renamed Syria Palaestina following the Jewish Bar Kokhba revolt.-Etymology:The...
, and Idumea (biblical Edom
Edom
Edom or Idumea was a historical region of the Southern Levant located south of Judea and the Dead Sea. It is mentioned in biblical records as a 1st millennium BC Iron Age kingdom of Edom, and in classical antiquity the cognate name Idumea was used to refer to a smaller area in the same region...
) from 4 BC to 6 AD. He was the son of Herod the Great
Herod the Great
Herod , also known as Herod the Great , was a Roman client king of Judea. His epithet of "the Great" is widely disputed as he is described as "a madman who murdered his own family and a great many rabbis." He is also known for his colossal building projects in Jerusalem and elsewhere, including his...
and Malthace
Malthace
Malthace was a Samaritan woman who lived in the latter half of the 1st century BC. She was one of the wives of Herod the Great and the mother by Herod of Herod Antipas, Archelaus and a daughter Olympias....
the Samaritan, the brother of Herod Antipas
Herod Antipas
Herod Antipater , known by the nickname Antipas, was a 1st-century AD ruler of Galilee and Perea, who bore the title of tetrarch...
, and the half-brother of Herod Philip I.
Archelaus received the Tetrarchy of Judea
Tetrarchy (Judea)
The Tetrarchy of Judea was formed following the death of Herod the Great in 4 BCE, when his kingdom was divided between his sons as an inheritance...
by the last will of his father, though a previous will had bequeathed it to his brother Antipas. He was proclaimed king by the army, but declined to assume the title until he had submitted his claims to Caesar Augustus in Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
. Before setting out, he quelled with the utmost cruelty a sedition of the Pharisees
Pharisees
The Pharisees were at various times a political party, a social movement, and a school of thought among Jews during the Second Temple period beginning under the Hasmonean dynasty in the wake of...
, slaying nearly three thousand of them. In Rome he was opposed by Antipas and by many of the Jews, who feared his cruelty; but in 4 BC Augustus allotted to him the greater part of the kingdom (Samaria, Judea, and Idumea) with the title of ethnarch (not king) until 6 AD when Judaea province
Iudaea Province
Judaea or Iudaea are terms used by historians to refer to the Roman province that extended over parts of the former regions of the Hasmonean and Herodian kingdoms of Israel...
was formed, under direct Roman rule, at the time of the Census of Quirinius
Census of Quirinius
The Census of Quirinius refers to the enrollment of the Roman Provinces of Syria and Iudaea for tax purposes taken in the year 6/7 during the reign of Emperor Augustus , when Publius Sulpicius Quirinius was appointed governor of Syria, after the banishment of Herod Archelaus from the Tetrarchy of...
.
The first wife of Archelaus is given by Josephus simply as Mariamne, perhaps Mariamne III
Mariamne III
Mariamne III was a daughter of Aristobulus IV and Berenice. She had three brothers, Herod of Chalcis, Herod Agrippa I, and Aristobulus V, and one sister, Herodias...
(Mariamne bint Aristobulus), whom he divorced to marry Glaphyra
Glaphyra
Glaphyra was an Anatolian Princess from Cappadocia and through marriage was related to the Herodian Dynasty. -Family and early life:Glaphyra was a royal princess of Greek, Armenian and Persian descent. Her father was the Roman ally king Archelaus of Cappadocia, her only natural sibling was her...
. She was the widow of Archelaus' brother Alexander, though her second husband, Juba
Juba II
Juba II or Juba II of Numidia was a king of Numidia and then later moved to Mauretania. His first wife was Cleopatra Selene II, daughter to Greek Ptolemaic Queen Cleopatra VII of Egypt and Roman triumvir Mark Antony.-Early life:Juba II was a prince of Berber descent from North Africa...
, king of Mauretania
Mauretania
Mauretania is a part of the historical Ancient Libyan land in North Africa. It corresponds to present day Morocco and a part of western Algeria...
, was alive. This violation of the Mosaic law
Torah
Torah- A scroll containing the first five books of the BibleThe Torah , is name given by Jews to the first five books of the bible—Genesis , Exodus , Leviticus , Numbers and Deuteronomy Torah- A scroll containing the first five books of the BibleThe Torah , is name given by Jews to the first five...
along with Archelaus' continued cruelty roused the ire of the Jews, who complained to Augustus. Archelaus was deposed in the year 6 and banished to Vienne
Vienne, Isère
Vienne is a commune in south-eastern France, located south of Lyon, on the Rhône River. It is the second largest city after Grenoble in the Isère department, of which it is a subprefecture. The city's population was of 29,400 as of the 2001 census....
in Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
; Samaria, Judea proper, and Idumea became the Roman province
Roman province
In Ancient Rome, a province was the basic, and, until the Tetrarchy , largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside of Italy...
of Iudaea
Iudaea Province
Judaea or Iudaea are terms used by historians to refer to the Roman province that extended over parts of the former regions of the Hasmonean and Herodian kingdoms of Israel...
.
In the Bible, Archelaus is mentioned in the Gospel of Matthew
Gospel of Matthew
The Gospel According to Matthew is one of the four canonical gospels, one of the three synoptic gospels, and the first book of the New Testament. It tells of the life, ministry, death, and resurrection of Jesus of Nazareth...
. According to , Joseph, Mary and Jesus fled to Egypt to avoid the Massacre of the Innocents
Massacre of the Innocents
The Massacre of the Innocents is an episode of infanticide by the King of Judea, Herod the Great. According to the Gospel of Matthew Herod orders the execution of all young male children in the village of Bethlehem, so as to avoid the loss of his throne to a newborn King of the Jews whose birth...
. When Herod the Great died, Joseph was told by an angel in a dream to return to Israel (presumably to Bethlehem
Bethlehem
Bethlehem is a Palestinian city in the central West Bank of the Jordan River, near Israel and approximately south of Jerusalem, with a population of about 30,000 people. It is the capital of the Bethlehem Governorate of the Palestinian National Authority and a hub of Palestinian culture and tourism...
). However, upon hearing that Archelaus had succeeded his father as ruler of Judaea he "was afraid to go thither" , and was again notified in a dream to go to Galilee
Galilee
Galilee , is a large region in northern Israel which overlaps with much of the administrative North District of the country. Traditionally divided into Upper Galilee , Lower Galilee , and Western Galilee , extending from Dan to the north, at the base of Mount Hermon, along Mount Lebanon to the...
. This is Matthew's explanation of why Jesus was born in Bethlehem
Bethlehem
Bethlehem is a Palestinian city in the central West Bank of the Jordan River, near Israel and approximately south of Jerusalem, with a population of about 30,000 people. It is the capital of the Bethlehem Governorate of the Palestinian National Authority and a hub of Palestinian culture and tourism...
in Judea
Judea
Judea or Judæa was the name of the mountainous southern part of the historic Land of Israel from the 8th century BCE to the 2nd century CE, when Roman Judea was renamed Syria Palaestina following the Jewish Bar Kokhba revolt.-Etymology:The...
but grew up in Nazareth
Nazareth
Nazareth is the largest city in the North District of Israel. Known as "the Arab capital of Israel," the population is made up predominantly of Palestinian Arab citizens of Israel...
.
The beginning and conclusion of Christ's Parable of the minas in the Gospel of Luke
Gospel of Luke
The Gospel According to Luke , commonly shortened to the Gospel of Luke or simply Luke, is the third and longest of the four canonical Gospels. This synoptic gospel is an account of the life and ministry of Jesus of Nazareth. It details his story from the events of his birth to his Ascension.The...
may refer to Archelaus's journey to Rome. Some interpreters conclude from this that Jesus' parables and preaching made use of events familiar to the people as examples for bringing his spiritual lessons to life. Others read the allusion as arising from later adaptation of Jesus' parable in the oral tradition, before the parables were recorded in the gospels.
"A nobleman went into a far country to receive for himself a kingdom and then return…But his citizens hated him and sent a delegation after him, saying, 'We do not want this man to reign over us.'… 'But as for these enemies of mine,' [said the nobleman] 'who did not want me to reign over them, bring them here and slaughter them before me.'"
External links
- Resources > Second Temple and Talmudic Era > Herod and the Herodian Dynasty: The Jewish History Resource Center - Project of the Dinur Center for Research in Jewish History, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
- King Herod Archelaus
- Jewish Encyclopedia: Archelaus

