Hesperocyon
Encyclopedia
Hesperocyon is an extinct genus of canids, family of Canidae
and subfamily Hesperocyoninae
which was endemic to North America
from southern Canada to appearing during the Uintan age
-Bridgerian age (NALMA) of the Mid-Eocene
42.5 mya—31.0 Ma. (AEO
). Hesperocyon existed for approximately .
 Hesperocyon was assigned to Borophagini by Wang et al. in 1999 the and the earliest of the canids to evolve after the Caniformia
Hesperocyon was assigned to Borophagini by Wang et al. in 1999 the and the earliest of the canids to evolve after the Caniformia
-Feliformia
split some 42 million year ago. Fossil evidence dates Hesperocyon gregarius to be at least 37 million years old, but the oldest Hesperocyon has been dated at 39.74 mya from the Duchesnean
North American Land Mammal Age.
The Canidae subfamily Hesperocyoninae probably arose out of Hesperocyon to become the first of the three great dogs groups: Hesperocyoninae (~40-30 Ma), Borophaginae (~36-2 Ma), and the Caninae
lineage that led to present-day Canidae, inclusive of modern-day wolves, foxes, coyotes, jackals and dogs (Canis familiaris). At least twenty eight known species of Hesperocyoninae evolved out of Hesperocyon, including Ectopocynus
(32-19 mya), Osbornodon
(32-18 mya), Paraenhydrocyon
(20-25 mya), and Mesocyon
-Enhydrocyon
(31-15 mya).
or a small raccoon
than a canine. Its body and tail
were long and flexible, while its limbs were weak and short. Still, the build of its ossicles
and distribution of its teeth showed it was a canid. Although it was definitely a carnivore
, it may also have been an omnivore
- unlike the hypercarnivore
Borophaginae
that later split from this canid lineage.
dating from 42.5 mya—31.0 Ma. The youngest fossil was recovered from the Dog Jaw Butte site, Goshen County, Wyoming dating to the Arikareean age
(NALMA) of the Oligocene
and Miocene
42.5 mya—31.0 Ma. (AEO).
Canidae
Canidae is the biological family of carnivorous and omnivorous mammals that includes wolves, foxes, jackals, coyotes, and domestic dogs. A member of this family is called a canid . The Canidae family is divided into two tribes: Canini and Vulpini...
and subfamily Hesperocyoninae
Hesperocyoninae
Hesperocyoninae is a subfamily of extinct canids.-Taxonomic history:Hesperocyoninae was named by Martin . The members of this subfamily were reassigned to the family Canidae by Xiaoming Wang in 1999....
which was endemic to North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
from southern Canada to appearing during the Uintan age
Uintan
The Uintan North American Stage on the geologic timescale is the North American faunal stage according to the North American Land Mammal Ages chronology , typically set from 46,200,000 to 42,000,000 years BP lasting . It is usually considered to fall within the Eocene epoch...
-Bridgerian age (NALMA) of the Mid-Eocene
Eocene
The Eocene Epoch, lasting from about 56 to 34 million years ago , is a major division of the geologic timescale and the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Palaeocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the...
42.5 mya—31.0 Ma. (AEO
Appearance Event Ordination
Appearance Event Ordination or AEO is a scientific method for biochronology through the ordering of the appearance of fossil mammal genera by multivariate analysis, using conjunctional and disconjunctional range distributions in large sets of data.-Process:AEO is based on faunal overlap and...
). Hesperocyon existed for approximately .
Taxonomy

Caniformia
Caniformia, or Canoidea , is a suborder within the order Carnivora. They typically possess a long snout and non-retractile claws . The Pinnipedia evolved from caniform ancestors and are accordingly assigned to this group...
-Feliformia
Feliformia
The Feliformia are a suborder within the order Carnivora and includes cats , hyenas, mongooses, civets and related taxa. The other suborder of Carnivora is Caniformia...
split some 42 million year ago. Fossil evidence dates Hesperocyon gregarius to be at least 37 million years old, but the oldest Hesperocyon has been dated at 39.74 mya from the Duchesnean
Duchesnean
The Duchesnean North American Stage on the geologic timescale is a North American Land Mammal Age , with an age from 42 to 38 million years BP, representing . It falls within the Eocene epoch. The Duchesnean is preceded by the Uintan and followed by the Chadronian NALMA.The Duchesnean falls within...
North American Land Mammal Age.
The Canidae subfamily Hesperocyoninae probably arose out of Hesperocyon to become the first of the three great dogs groups: Hesperocyoninae (~40-30 Ma), Borophaginae (~36-2 Ma), and the Caninae
Caninae
Caninae is the only living subfamily of Canidae. Many extinct species of Caninae were endemic to North America, living from 34 Ma—11,000 years ago. Some members of the endemic North American canines survived to the present time. This subfamily was recently revised by Tedford, Wang, and Taylor...
lineage that led to present-day Canidae, inclusive of modern-day wolves, foxes, coyotes, jackals and dogs (Canis familiaris). At least twenty eight known species of Hesperocyoninae evolved out of Hesperocyon, including Ectopocynus
Ectopocynus
Ectopocynus is an extinct genus of small bone crushing carnivorous mammal similar to a dog of the family Canidae) which inhabited North America during the Oligocene living from 33.3—16.0 Ma and existed for approximately ....
(32-19 mya), Osbornodon
Osbornodon
Osbornodon is an extinct genus of bone-crushing canid that were endemic to North America and which lived from the Orellan age of the Early Oligocene to Early Miocene epoch 33.9—15.97 Ma and existed for approximately ....
(32-18 mya), Paraenhydrocyon
Paraenhydrocyon
Paraenhydrocyon is an extinct genus of bone crushing omnivorous mammal similar to a dog of the family Canidae which inhabited North America during the Oligocene living from 33.3—20.6 Ma and existed for approximately ....
(20-25 mya), and Mesocyon
Mesocyon
Mesocyon is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivore within the family Canidae, subfamily Hesperocyoninae, which inhabited North America from the Early Oligocene 33.9—20.6 Ma, existing for approximately ....
-Enhydrocyon
Enhydrocyon
Enhydrocyon is an extinct genus of bone crushing dog which inhabited North America exclusively during the Oligocene living from around 28.7—22.0 Ma and existed for approximately ....
(31-15 mya).
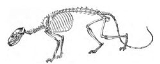
Morphology
This early, 80 cm (2 ft 8 in) long canine looked more like a civetCivet
The family Viverridae is made up of around 30 species of medium-sized mammal, including all of the genets, the binturong, most of the civets, and the two African linsangs....
or a small raccoon
Raccoon
Procyon is a genus of nocturnal mammals, comprising three species commonly known as raccoons, in the family Procyonidae. The most familiar species, the common raccoon , is often known simply as "the" raccoon, as the two other raccoon species in the genus are native only to the tropics and are...
than a canine. Its body and tail
Tail
The tail is the section at the rear end of an animal's body; in general, the term refers to a distinct, flexible appendage to the torso. It is the part of the body that corresponds roughly to the sacrum and coccyx in mammals, reptiles, and birds...
were long and flexible, while its limbs were weak and short. Still, the build of its ossicles
Ossicles
The ossicles are the three smallest bones in the human body. They are contained within the middle ear space and serve to transmit sounds from the air to the fluid-filled labyrinth . The absence of the auditory ossicles would constitute a moderate-to-severe hearing loss...
and distribution of its teeth showed it was a canid. Although it was definitely a carnivore
Carnivore
A carnivore meaning 'meat eater' is an organism that derives its energy and nutrient requirements from a diet consisting mainly or exclusively of animal tissue, whether through predation or scavenging...
, it may also have been an omnivore
Omnivore
Omnivores are species that eat both plants and animals as their primary food source...
- unlike the hypercarnivore
Hypercarnivore
A hypercarnivore is an animal which has a diet that is more than 70% meat, with the balance consisting of non-animal foods such as fungi, fruits or other plant material. Some examples include the big cats, dolphins, eagles, snakes, marlin, most sharks, and such invertebrates as octopuses and sea...
Borophaginae
Borophaginae
The subfamily Borophaginae is an extinct group of canids called "bone crushing dogs" that were endemic to North America during the Oligocene to Pliocene and lived roughly 36—2.5 million years ago and existing for approximately .-Origin:...
that later split from this canid lineage.
Body mass
Two specimens were examined by Legendre and Roth for body mass. One specimen was estimated to weigh 1.67 kg (3.7 lb). A second was estimated to weigh 1.73 kg (3.8 lb).Fossil record
The oldest fossil evidence was recovered from SaskatchewanSaskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a prairie province in Canada, which has an area of . Saskatchewan is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota....
dating from 42.5 mya—31.0 Ma. The youngest fossil was recovered from the Dog Jaw Butte site, Goshen County, Wyoming dating to the Arikareean age
Arikareean
The Arikareean North American Stage on the geologic timescale is the North American faunal stage according to the North American Land Mammal Ages chronology , typically set from 30,600,000 to 20,800,000 years BP, a period of . It is usually considered to overlap the Oligocene and Miocene epochs...
(NALMA) of the Oligocene
Oligocene
The Oligocene is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 34 million to 23 million years before the present . As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the period are slightly...
and Miocene
Miocene
The Miocene is a geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about . The Miocene was named by Sir Charles Lyell. Its name comes from the Greek words and and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern sea invertebrates than the Pliocene. The Miocene follows the Oligocene...
42.5 mya—31.0 Ma. (AEO).

