
Hexachlorobutadiene
Encyclopedia
Hexachlorobutadiene, Cl2C=C(Cl)C(Cl)=CCl2, is a colorless liquid at room temperature
that has an odor similar to that of turpentine
. It is a chlorinated aliphatic diene
with niche applications but is most commonly used as a solvent
for other chlorine-containing compounds.
and tetrachloroethene. Chlorinolysis is a radical chain reaction that occurs when hydrocarbon
s are exposed to chlorine
gas under pyrolytic conditions. The hydrocarbon is chlorinated and the resulting chlorocarbons are broken down. This process is analogous to combustion, but with chlorine instead of oxygen.
Hexachlorobutadiene occurs as a by-product during the chlorinolysis of butane
derivatives in the production of both carbon tetrachloride and tetrachloroethene. These two commodities are manufactured on such a large scale, that enough HCBD can generally be obtained to meet the industrial demand. Alternatively, hexachlorobutadiene can be directly synthesized via the chlorination
of butane
or butadiene.

Just like chlorine, many other chlorine-containing compounds can be readily dissolved in a solution of hexachlorobutadiene. As a solvent, it is unreactive toward common acids and select non-nucleophilic bases. An illustrative application HCBD as a solvent is the FeCl3
-catalyzed chlorination of toluene
to give pentachloromethylbenzene. Hexachlorobutadiene is used exclusively over carbon tetrachloride in this reaction because ferric chloride (FeCl3) is insoluble in CCl4.
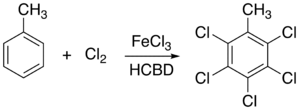 Given its affinity for chlorinated compounds, liquid HCBD is used as a scrubber in order to remove chlorine containing contaminants from gas streams. An example of this application is its use in the production of HCl gas
Given its affinity for chlorinated compounds, liquid HCBD is used as a scrubber in order to remove chlorine containing contaminants from gas streams. An example of this application is its use in the production of HCl gas
as the primary contaminants, especially Cl2, are more soluble in hexachlorobutadiene than the gaseous hydrogen chloride.
In IR spectroscopy, hexachlorobutadiene is occasionally used as a mull in order to analyze the stretching frequencies of C-H stretching bands. The usual mulling agent, Nujol, is a hydrocarbon and thus exhibits C-H stretching bands that can interfere with the signal from the sample. Since HCBD contains no C-H bonds, it can be used instead to obtain this portion of the IR spectrum. Unfortunately, some organometallic
compounds react with HCBD, and therefore, care must be taken when selecting it as a mulling agent so as not to destroy the sample.
Hexachlorobutadiene has yet another, albeit somewhat dated, application as an algicide in industrial cooling systems. Although HCBD is a potent herbicide, in recent years, this particular application has been discouraged due to the high toxicity of the compound at low concentrations.
The carcinogenicity of Hexachlorobutadiene has been classified by the United States Environmental Protection Agency has classified hexachlorobutadiene as a group C Possible Human Carcinogen. The American Conference of Governmental and Industrial Hygienists has classified Hexachlorobutadiene as an A3 Confirmed Animal Carcinogen with Unknown Relevance to Humans.
Room temperature
-Comfort levels:The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers has listings for suggested temperatures and air flow rates in different types of buildings and different environmental circumstances. For example, a single office in a building has an occupancy ratio per...
that has an odor similar to that of turpentine
Turpentine
Turpentine is a fluid obtained by the distillation of resin obtained from trees, mainly pine trees. It is composed of terpenes, mainly the monoterpenes alpha-pinene and beta-pinene...
. It is a chlorinated aliphatic diene
Diene
In organic chemistry a diene or diolefin is a hydrocarbon that contains two carbon double bonds.Conjugated dienes are functional groups, with a general formula of CnH2n-2. Dienes and alkynes are functional isomers...
with niche applications but is most commonly used as a solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
for other chlorine-containing compounds.
Synthesis
Hexachlorobutadiene, or HCBD, is primarily produced in chlorinolysis plants as a by-product in the production of carbon tetrachlorideCarbon tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names is the organic compound with the formula CCl4. It was formerly widely used in fire extinguishers, as a precursor to refrigerants, and as a cleaning agent...
and tetrachloroethene. Chlorinolysis is a radical chain reaction that occurs when hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls....
s are exposed to chlorine
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
gas under pyrolytic conditions. The hydrocarbon is chlorinated and the resulting chlorocarbons are broken down. This process is analogous to combustion, but with chlorine instead of oxygen.
Hexachlorobutadiene occurs as a by-product during the chlorinolysis of butane
Butane
Butane is a gas with the formula C4H10 that is an alkane with four carbon atoms. The term may refer to any of two structural isomers, or to a mixture of them: in the IUPAC nomenclature, however, butane refers only to the unbranched n-butane isomer; the other one being called "methylpropane" or...
derivatives in the production of both carbon tetrachloride and tetrachloroethene. These two commodities are manufactured on such a large scale, that enough HCBD can generally be obtained to meet the industrial demand. Alternatively, hexachlorobutadiene can be directly synthesized via the chlorination
Chlorination
Chlorination is the process of adding the element chlorine to water as a method of water purification to make it fit for human consumption as drinking water...
of butane
Butane
Butane is a gas with the formula C4H10 that is an alkane with four carbon atoms. The term may refer to any of two structural isomers, or to a mixture of them: in the IUPAC nomenclature, however, butane refers only to the unbranched n-butane isomer; the other one being called "methylpropane" or...
or butadiene.
Reactivity
The products of chlorinolysis reactions heavily depend upon both the temperature and pressure under which the reaction occurs. Thus, by adjusting these reaction conditions in the presence of chlorine gas, hexachlorobutadiene can be even further chlorinated to give tetrachloroethylene, hexachloroethane, octachlorobutene and even decachlorobutane. In general, increasing the number of chlorine substituents on a compound increases its toxicity but decreases its combustibility. Chlorination via carbon skeleton cleavage is thermodynamically preferred, whereas chlorinated C4 products are favored at lower temperatures and pressures. The three chlorinolysis products of hexachlorobutadiene are shown in the reactions below.
Applications
One of the primary applications of hexachlorobutadiene is as a solvent for chlorine, a good illustration of the common aphorism “like dissolves like.” The molar solubility of chlorine in HCBD at 0 °C is around 34% (2.17 mol/L). The solubility of another chlorine solvent, carbon tetrachloride, at 0 °C is about 30% (3.11 mol/L). One mole of C4Cl6 can dissolve more chlorine than one mole of CCl4, but the molecular weight difference between the two solvents is such that per liter of solvent, more chlorine can be dissolved in carbon tetrachloride. Shown below is the molar solubility of hexachlorobutadiene compared to carbon tetrachloride at various temperatures.| Temp (C) | Molar Solubility of HCBD |
Molar Solubility of CCl4 |
|---|---|---|
| -20 | 60 | 60 |
| 0 | 34 | 30 |
| 20 | 21 | 18 |
| 40 | 13 | 10 |
| 60 | 10 | 8 |
| 80 | 6 | 5 |
Just like chlorine, many other chlorine-containing compounds can be readily dissolved in a solution of hexachlorobutadiene. As a solvent, it is unreactive toward common acids and select non-nucleophilic bases. An illustrative application HCBD as a solvent is the FeCl3
Iron(III) chloride
Iron chloride, also called ferric chloride, is an industrial scale commodity chemical compound, with the formula FeCl3. The colour of iron chloride crystals depends on the viewing angle: by reflected light the crystals appear dark green, but by transmitted light they appear purple-red...
-catalyzed chlorination of toluene
Toluene
Toluene, formerly known as toluol, is a clear, water-insoluble liquid with the typical smell of paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, i.e., one in which a single hydrogen atom from the benzene molecule has been replaced by a univalent group, in this case CH3.It is an aromatic...
to give pentachloromethylbenzene. Hexachlorobutadiene is used exclusively over carbon tetrachloride in this reaction because ferric chloride (FeCl3) is insoluble in CCl4.
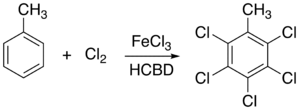
Hydrogen chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the formula HCl. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric humidity. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry...
as the primary contaminants, especially Cl2, are more soluble in hexachlorobutadiene than the gaseous hydrogen chloride.
In IR spectroscopy, hexachlorobutadiene is occasionally used as a mull in order to analyze the stretching frequencies of C-H stretching bands. The usual mulling agent, Nujol, is a hydrocarbon and thus exhibits C-H stretching bands that can interfere with the signal from the sample. Since HCBD contains no C-H bonds, it can be used instead to obtain this portion of the IR spectrum. Unfortunately, some organometallic
Organometallic chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of chemical compounds containing bonds between carbon and a metal. Since many compounds without such bonds are chemically similar, an alternative may be compounds containing metal-element bonds of a largely covalent character...
compounds react with HCBD, and therefore, care must be taken when selecting it as a mulling agent so as not to destroy the sample.
Hexachlorobutadiene has yet another, albeit somewhat dated, application as an algicide in industrial cooling systems. Although HCBD is a potent herbicide, in recent years, this particular application has been discouraged due to the high toxicity of the compound at low concentrations.
Toxicity
Hexachlorobutadiene has been observed to produce systemic toxicity following exposure via oral, inhalation, and dermal routes. Effects may included fatty liver degeneration, epithelial necrotizing nephritis, central nervous system depression and cyanosis.The carcinogenicity of Hexachlorobutadiene has been classified by the United States Environmental Protection Agency has classified hexachlorobutadiene as a group C Possible Human Carcinogen. The American Conference of Governmental and Industrial Hygienists has classified Hexachlorobutadiene as an A3 Confirmed Animal Carcinogen with Unknown Relevance to Humans.

