
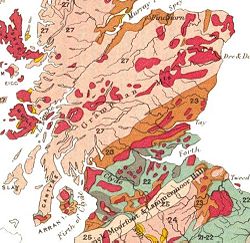
Highland Boundary Fault
Encyclopedia

Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
from Arran
Isle of Arran
Arran or the Isle of Arran is the largest island in the Firth of Clyde, Scotland, and with an area of is the seventh largest Scottish island. It is in the unitary council area of North Ayrshire and the 2001 census had a resident population of 5,058...
and Helensburgh
Helensburgh
Helensburgh is a town in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It lies on the north shore of the Firth of Clyde and the eastern shore of the entrance to the Gareloch....
on the west coast to Stonehaven
Stonehaven
Stonehaven is a town in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It lies on Scotland's northeast coast and had a population of 9,577 in 2001 census.Stonehaven, county town of Kincardineshire, grew around an Iron Age fishing village, now the "Auld Toon" , and expanded inland from the seaside...
in the east. It separates two distinctly different physiographic regions: the Highlands
Scottish Highlands
The Highlands is an historic region of Scotland. The area is sometimes referred to as the "Scottish Highlands". It was culturally distinguishable from the Lowlands from the later Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Scots replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands...
from the Lowlands
Scottish Lowlands
The Scottish Lowlands is a name given to the Southern half of Scotland.The area is called a' Ghalldachd in Scottish Gaelic, and the Lawlands ....
, but in most places it is only recognisable as a change in topography
Topography
Topography is the study of Earth's surface shape and features or those ofplanets, moons, and asteroids...
.
Aligned southwest to northeast, from Lochranza
Lochranza
Lochranza is a village located on the Isle of Arran in the Firth of Clyde, Scotland. The population, somewhat in decline, is around 200 people....
on Arran it bisects the Isle of Bute
Isle of Bute
Bute is an island in the Firth of Clyde in Scotland. Formerly part of the county of Buteshire, it now constitutes part of the council area of Argyll and Bute. Its resident population was 7,228 in April 2001.-Geography:...
, and crosses the south eastern parts of the Cowal
Cowal
thumb|Cowal shown within ArgyllCowal is a peninsula in Argyll and Bute in the Scottish Highlands.-Description:The northern part of Cowal is mostly the mountainous Argyll Forest Park. Cowal is separated from the Kintyre peninsula to the west by Loch Fyne, and from Inverclyde and North Ayrshire to...
and Rosneath
Rosneath
Rosneath is a village in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It sits on the western shore of the Gare Loch near to the tip of the Rosneath peninsula which projects south to the Firth of Clyde between the Gare Loch and Loch Long to the west, and about 2 miles from the village of Kilcreggan which is sited...
Peninsulas as it passes up the Firth of Clyde
Firth of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde forms a large area of coastal water, sheltered from the Atlantic Ocean by the Kintyre peninsula which encloses the outer firth in Argyll and Ayrshire, Scotland. The Kilbrannan Sound is a large arm of the Firth of Clyde, separating the Kintyre Peninsula from the Isle of Arran.At...
. It comes ashore near Helensburgh
Helensburgh
Helensburgh is a town in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It lies on the north shore of the Firth of Clyde and the eastern shore of the entrance to the Gareloch....
then continues through Loch Lomond
Loch Lomond
Loch Lomond is a freshwater Scottish loch, lying on the Highland Boundary Fault. It is the largest lake in Great Britain by surface area. The lake contains many islands, including Inchmurrin, the largest fresh-water island in the British Isles, although the lake itself is smaller than many Irish...
. The loch islands of Inchmurrin
Inchmurrin
Inchmurrin is an island in Loch Lomond in Scotland. It is the largest fresh water island in the British Isles.- Geography and geology :...
, Creinch
Creinch
Creinch is an island on the Highland boundary fault in Loch Lomond.-History:Formerly Inchcroin , Creinch lies a little north of Inchmurrin. Inchcailloch, Torrinch, Creinch and Inchmurrin form part of the Highland boundary fault...
, Torrinch
Torrinch
Torrinch or Inchtore is an island in Loch Lomond in Scotland. The name Torremach is also recorded for it. It is wooded.- Geography :It is one of the smaller islands in the loch. Torrinch, along with Inchmurrin, Creinch, and Inchcailloch, forms part of the Highland Boundary Fault...
, and Inchcailloch
Inchcailloch
Inchcailloch is an island on Loch Lomond in Scotland. It is 85 m at its highest point. It is also known to some as Inchebroida....
all form part of the Highland Boundary Fault.
From Loch Lomond it continues to Aberfoyle, then Callander
Callander
Callander is a burgh in the region of Stirling, Scotland, situated on the River Teith. The town is located in the former county of Perthshire and is a popular tourist stop to and from the Highlands....
, Comrie
Comrie
Comrie is an affluent village and parish in the southern highlands of Scotland, towards the western end of the Strathearn district of Perth and Kinross, seven miles west of Crieff. The village has won the Royal Horticultural Society "Large Village Britain in Bloom Winner" in 2007 and 2010...
and Crieff
Crieff
Crieff is a market town in Perth and Kinross, Scotland. It lies on the A85 road between Perth and Crianlarich and also lies on the A822 between Greenloaning and Aberfeldy. The A822 joins onto the A823 which leads to Dunfermline....
. It then forms the northern boundary of Strathmore
Strathmore, Angus and Perth & Kinross
Strathmore is a strath in east central Scotland running from northeast to southwest between the Grampian mountains and the Sidlaws....
and reaches the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
immediately north of Stonehaven
Stonehaven
Stonehaven is a town in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It lies on Scotland's northeast coast and had a population of 9,577 in 2001 census.Stonehaven, county town of Kincardineshire, grew around an Iron Age fishing village, now the "Auld Toon" , and expanded inland from the seaside...
near the ruined Chapel of St. Mary and St. Nathalan
Chapel of St. Mary and St. Nathalan
The Chapel of St. Mary and St. Nathalan is a ruined chapel overlooking the North Sea immediately north of Stonehaven, in the Mearns of Scotland, along the northern shoreline of Stonehaven Bay. The founding of this Catholic place of worship is associated with St. Nathalan. who lived circa 650 AD...
. To the north and west lie hard Precambrian
Precambrian
The Precambrian is the name which describes the large span of time in Earth's history before the current Phanerozoic Eon, and is a Supereon divided into several eons of the geologic time scale...
and Cambrian
Cambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock is the transformation of an existing rock type, the protolith, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". The protolith is subjected to heat and pressure causing profound physical and/or chemical change...
s: marine deposits metamorphosed to schist
Schist
The schists constitute a group of medium-grade metamorphic rocks, chiefly notable for the preponderance of lamellar minerals such as micas, chlorite, talc, hornblende, graphite, and others. Quartz often occurs in drawn-out grains to such an extent that a particular form called quartz schist is...
s, phyllite
Phyllite
Phyllite is a type of foliated metamorphic rock primarily composed of quartz, sericite mica, and chlorite; the rock represents a gradation in the degree of metamorphism between slate and mica schist. Minute crystals of graphite, sericite, or chlorite impart a silky, sometimes golden sheen to the...
s and slate
Slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. The result is a foliated rock in which the foliation may not correspond to the original sedimentary layering...
s. To the south and east are Old Red Sandstone
Old Red Sandstone
The Old Red Sandstone is a British rock formation of considerable importance to early paleontology. For convenience the short version of the term, 'ORS' is often used in literature on the subject.-Sedimentology:...
conglomerates
Conglomerate (geology)
A conglomerate is a rock consisting of individual clasts within a finer-grained matrix that have become cemented together. Conglomerates are sedimentary rocks consisting of rounded fragments and are thus differentiated from breccias, which consist of angular clasts...
and sandstone
Sandstone
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized minerals or rock grains.Most sandstone is composed of quartz and/or feldspar because these are the most common minerals in the Earth's crust. Like sand, sandstone may be any colour, but the most common colours are tan, brown, yellow,...
s: softer, sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rock are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution....
s of the Devonian
Devonian
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic Era spanning from the end of the Silurian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya , to the beginning of the Carboniferous Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya...
and Carboniferous
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Permian Period, about 299.0 ± 0.8 Mya . The name is derived from the Latin word for coal, carbo. Carboniferous means "coal-bearing"...
periods.
The Highland Boundary Fault was active during the Caledonian Orogeny
Caledonian orogeny
The Caledonian orogeny is a mountain building era recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Mountains, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that occurred from the Ordovician to Early Devonian, roughly...
, a plate tectonic
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that describes the large scale motions of Earth's lithosphere...
collision which took place from Mid Ordovician
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
to Mid Devonian
Devonian
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic Era spanning from the end of the Silurian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya , to the beginning of the Carboniferous Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya...
periods (520 to 400 million years ago), during the closure of the Iapetus Ocean
Iapetus Ocean
The Iapetus Ocean was an ocean that existed in the Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic eras of the geologic timescale . The Iapetus Ocean was situated in the southern hemisphere, between the paleocontinents of Laurentia, Baltica and Avalonia...
. The fault
Geologic fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock, across which there has been significant displacement along the fractures as a result of earth movement. Large faults within the Earth's crust result from the action of tectonic forces...
allowed the Midland Valley
Central Lowlands
The Central Lowlands or Midland Valley is a geologically defined area of relatively low-lying land in southern Scotland. It consists of a rift valley between the Highland Boundary Fault to the north and the Southern Uplands Fault to the south...
to descend as a major rift by up to 4000 metres and there was subsequently vertical movement. This earlier vertical movement was later replaced by a horizontal shear. A complementary fault, the Southern Uplands Fault
Southern Uplands Fault
The Southern Uplands Fault is a fault in Scotland that runs from Girvan to Dunbar on the East coast. It marks the southern boundary of the Scottish Midland Valley....
, forms the southern boundary for the Central Lowlands
Central Lowlands
The Central Lowlands or Midland Valley is a geologically defined area of relatively low-lying land in southern Scotland. It consists of a rift valley between the Highland Boundary Fault to the north and the Southern Uplands Fault to the south...
.

