
History of Sudan (1884-1898)
Encyclopedia
Developments in Sudan
during the late 19th century cannot be understood without reference to the British position in Egypt
. In 1869, the Suez Canal
opened and quickly became Britain's economic lifeline to India and the Far East. To defend this waterway, Britain sought a greater role in Egyptian affairs. In 1873, the British government therefore supported a programme whereby an Anglo-French debt commission assumed responsibility for managing Egypt's fiscal affairs. This commission eventually forced khedive
Ismail
to abdicate in favor of his more politically acceptable son, Tawfiq
(1877–1892).
After the removal in 1877 of Ismail, who had appointed him to the post, Charles George Gordon
resigned as governor general of Sudan in 1880. His successors lacked direction from Cairo
and feared the political turmoil that had engulfed Egypt. As a result, they failed to continue the policies Gordon had put in place. The illegal slave trade revived, although not enough to satisfy the merchants whom Gordon had put out of business. The Sudanese army suffered from a lack of resources, and unemployed soldiers from disbanded units troubled garrison towns. Tax collectors arbitrarily increased taxation.
 In this troubled atmosphere, Muhammad Ahmad ibn as Sayyid Abd Allah, a fakir
In this troubled atmosphere, Muhammad Ahmad ibn as Sayyid Abd Allah, a fakir
, or holy man, who combined personal magnetism with religious zealotry, emerged, determined to expel the Turks
and restore Islam
to its primitive purity. The son of a Dunqulah boatbuilder, Muhammad Ahmad had become the disciple of Muhammad ash Sharif, the head of the Sammaniyah order. Later, as a shaykh of the order, Muhammad Ahmad spent several years in seclusion and gained a reputation as a mystic and teacher. In 1880, he became a Sammaniyah.
Even after the Mahdi proclaimed a jihad
, or holy war, against the Turkiyah
, Khartoum
dismissed him as a religious fanatic. The government paid more attention when his religious zeal turned to denunciation of tax collectors. To avoid arrest, the Mahdi and a party of his followers, the Ansar
, made a long march to Kurdufan
, where he gained a large number of recruits, especially from the Baqqara. From a refuge in the area, he wrote appeals to the shaykhs of the religious orders and won active support or assurances of neutrality from all except the pro-Egyptian Khatmiyyah. Merchants and Arab tribes that had depended on the slave trade responded as well, along with the Hadendowa
Beja
, who were rallied to the Mahdi by an Ansar captain, Usman Digna
.
and seized their rifles, field guns and ammunition. The Mahdi followed up this victory by laying siege to Al Ubayyid and starving it into submission after four months. The Ansar, 30,000 men strong, then defeated an 8,000-man Egyptian relief force at Sheikan. Next the Mahdi captured Darfur and imprisoned Rudolf Carl von Slatin
, an Austria
n in the khedive's service, who later became the first Egyptian-appointed governor of Darfur
Province.
The advance of the Ansar and the Hadendowa rising in the east imperiled communications with Egypt and threatened to cut off garrisons at Khartoum, Kassala, Sennar
, and Sawakin and in the south. To avoid being drawn into a costly military intervention, the British government ordered an Egyptian withdrawal from Sudan. Gordon, who had received a reappointment as governor general, arranged to supervise the evacuation of Egyptian troops and officials and all foreigners from Sudan.
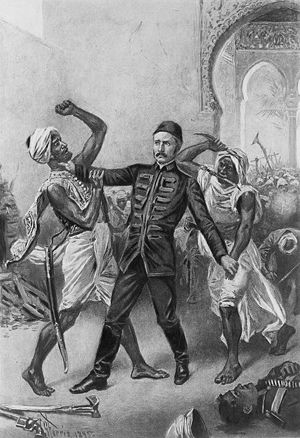
 After reaching Khartoum in February 1884, Gordon soon realized that he could not extricate the garrisons. As a result, he called for reinforcements from Egypt to relieve Khartoum. Gordon also recommended that Zubayr
After reaching Khartoum in February 1884, Gordon soon realized that he could not extricate the garrisons. As a result, he called for reinforcements from Egypt to relieve Khartoum. Gordon also recommended that Zubayr
, an old enemy whom he recognized as an excellent military commander, be named to succeed him to give disaffected Sudanese a leader other than the Mahdi to rally behind. London rejected this plan. As the situation deteriorated, Gordon argued that Sudan was essential to Egypt's security and that to allow the Ansar a victory there would invite the movement to spread elsewhere.
Increasing British popular support for Gordon eventually forced Prime Minister
William Gladstone
to mobilize a relief force under the command of Lord Garnet Joseph Wolseley. A "flying column" sent overland from Wadi Halfa
across the Bayuda Desert
bogged down at Abu Tulayh (commonly called Abu Klea), where the Hadendowa broke the British line. An advance unit that had gone ahead by river when the column reached Al Matammah arrived at Khartoum on 28 January 1885, to find the town had fallen
two days earlier. The Ansar had waited for the Nile
flood to recede before attacking the poorly defended river approach to Khartoum in boats, slaughtering the garrison, killing Gordon, and delivering his head to the Mahdi's tent. Kassala and Sennar fell soon after, and by the end of 1885, the Ansar had begun to move into the southern region. In all Sudan, only Sawakin, reinforced by Indian army troops, and Wadi Halfa on the northern frontier remained in Anglo-Egyptian hands.
s. Sudan's new ruler also authorized the burning of lists of pedigrees and books of law and theology because of their association with the old order and because he believed that the former accentuated tribalism at the expense of religious unity.
The Mahdiyah has become known as the first genuine Sudanese nationalist government. The Mahdi maintained that his movement was not a religious order that could be accepted or rejected at will, but that it was a universal regime, which challenged man to join or to be destroyed. The Mahdi modified Islam's five pillars to support the dogma that loyalty to him was essential to true belief. The Mahdi also added the declaration "and Muhammad Ahmad is the Mahdi of God and the representative of His Prophet" to the recitation of the creed, the shahada
. Moreover, service in the jihad replaced the hajj
, or pilgrimage to Mecca
, as a duty incumbent on the faithful. Zakat
(almsgiving) became the tax paid to the state. The Mahdi justified these and other innovations and reforms as responses to instructions conveyed to him by God in visions.
The Mahdist regime was also known for its severe persecution of Christians in Sudan, including Copts.
. The task of establishing and maintaining a government fell to his deputies—three caliphs chosen by the Mahdi in emulation of the Prophet Muhammad
. Rivalry among the three, each supported by people of his native region, continued until 1891, when Abdallahi ibn Muhammad
, with the help primarily of the Baqqara Arabs, overcame the opposition of the others and emerged as unchallenged leader of the Mahdiyah. Abdallahi—called the Khalifa
(successor)—purged the Mahdiyah of members of the Mahdi's family and many of his early religious disciples.
Originally, the Mahdiyah was a jihad state, run like a military camp. Sharia
courts enforced Islamic law and the Mahdi's precepts, which had the force of law. After consolidating his power, the Khalifa instituted an administration and appointed Ansar (who were usually Baqqara) as amirs over each of the several provinces. The Khalifa also ruled over rich Al Jazirah
. Although he failed to restore this region's commercial wellbeing, the Khalifa organized workshops to manufacture ammunition and to maintain river steamboats.
Regional relations remained tense throughout much of the Mahdiyah period, largely because of the Khalifa's commitment to using the jihad to extend his version of Islam throughout the world. For example, the Khalifa rejected an offer of an alliance against the Europeans by Emperor
Yohannes IV of Ethiopia
. In 1887, a 60,000-man Ansar army invaded Ethiopia, penetrated as far as Gondar
, and captured prisoners and booty. The Khalifa then refused to conclude peace with Ethiopia. In March 1889, an Ethiopian force, commanded by the emperor, marched on Metemma
; however, after Yohannes fell in the ensuing Battle of Gallabat
, the Ethiopians withdrew. Abd ar Rahman an Nujumi, the Khalifa's best general, invaded Egypt in 1889, but British-led Egyptian troops defeated the Ansar at Tushkah
. The failure of the Egyptian invasion ended the Ansars' invincibility. The Belgians prevented the Mahdi's men from conquering Equatoria
, and in 1893, the Italians repulsed an Ansar attack at Akordat (in Eritrea
) and forced the Ansar to withdraw from Ethiopia.
, or commander, of the Egyptian army and started preparations for the reconquest of Sudan. The British thought they needed to occupy Sudan in part because of international developments. By the early 1890s, British, French, and Belgian claims had converged at the Nile headwaters. Britain feared that the other colonial powers would take advantage of Sudan's instability to acquire territory previously annexed to Egypt. Apart from these political considerations, Britain wanted to establish control over the Nile to safeguard a planned irrigation dam at Aswan.
In 1895, the British government authorized Kitchener to launch a campaign to reconquer Sudan. Britain provided men and matériel while Egypt financed the expedition. The Anglo-Egyptian Nile Expeditionary Force included 25,800 men, 8,600 of whom were British. The remainder were troops belonging to Egyptian units that included six battalions recruited in southern Sudan. An armed river flotilla escorted the force, which also had artillery support. In preparation for the attack, the British established army headquarters at Wadi Halfa, and extended and reinforced the perimeter defenses around Sawakin. In March 1896, the campaign started; in September, Kitchener captured Dunqulah
. The British then constructed a rail line from Wadi Halfa
to Abu Hamad
and an extension parallel to the Nile to transport troops and supplies to Berber
. Anglo-Egyptian units fought a sharp action at Abu Hamad, but there was little other significant resistance until Kitchener reached Atbarah
and defeated the Ansar. After this engagement, Kitchener's soldiers marched and sailed toward Omdurman
, where the Khalifa made his last stand
.
On 2 September 1898, the Khalifa committed his 52,000-man army to a frontal assault against the Anglo-Egyptian force, which was massed on the plain outside Omdurman. The outcome never was in doubt, largely because of superior British firepower. During the five-hour battle, about 11,000 Mahdists died, whereas Anglo-Egyptian losses amounted to 48 dead and fewer than 400 wounded.
Mopping-up operations required several years, but organized resistance ended when the Khalifa, who had escaped to Kurdufan
, died in fighting at Umm Diwaykarat
in November 1899. Many areas welcomed the downfall of his regime. Sudan's economy had been all but destroyed during his reign and the population had declined by approximately one-half because of famine, disease, persecution, and warfare. Moreover, none of the country's traditional institutions or loyalties remained intact. Tribes had been divided in their attitudes toward Mahdism, religious brotherhoods had been weakened, and orthodox religious leaders had vanished.
Sudan
Sudan , officially the Republic of the Sudan , is a country in North Africa, sometimes considered part of the Middle East politically. It is bordered by Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the northeast, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the east, South Sudan to the south, the Central African Republic to the...
during the late 19th century cannot be understood without reference to the British position in Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
. In 1869, the Suez Canal
Suez Canal
The Suez Canal , also known by the nickname "The Highway to India", is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea. Opened in November 1869 after 10 years of construction work, it allows water transportation between Europe and Asia without navigation...
opened and quickly became Britain's economic lifeline to India and the Far East. To defend this waterway, Britain sought a greater role in Egyptian affairs. In 1873, the British government therefore supported a programme whereby an Anglo-French debt commission assumed responsibility for managing Egypt's fiscal affairs. This commission eventually forced khedive
Khedive
The term Khedive is a title largely equivalent to the English word viceroy. It was first used, without official recognition, by Muhammad Ali Pasha , the Wāli of Egypt and Sudan, and vassal of the Ottoman Empire...
Ismail
Isma'il Pasha
Isma'il Pasha , known as Ismail the Magnificent , was the Khedive of Egypt and Sudan from 1863 to 1879, when he was removed at the behest of the United Kingdom...
to abdicate in favor of his more politically acceptable son, Tawfiq
Tewfik Pasha
HH Muhammed Tewfik Pasha ' was Khedive of Egypt and Sudan between 1879 and 1892, and the sixth ruler from the Muhammad Ali Dynasty.-Early life:...
(1877–1892).
After the removal in 1877 of Ismail, who had appointed him to the post, Charles George Gordon
Charles George Gordon
Major-General Charles George Gordon, CB , known as "Chinese" Gordon, Gordon Pasha, and Gordon of Khartoum, was a British army officer and administrator....
resigned as governor general of Sudan in 1880. His successors lacked direction from Cairo
Cairo
Cairo , is the capital of Egypt and the largest city in the Arab world and Africa, and the 16th largest metropolitan area in the world. Nicknamed "The City of a Thousand Minarets" for its preponderance of Islamic architecture, Cairo has long been a centre of the region's political and cultural life...
and feared the political turmoil that had engulfed Egypt. As a result, they failed to continue the policies Gordon had put in place. The illegal slave trade revived, although not enough to satisfy the merchants whom Gordon had put out of business. The Sudanese army suffered from a lack of resources, and unemployed soldiers from disbanded units troubled garrison towns. Tax collectors arbitrarily increased taxation.
Muhammad Ahmad

Fakir
The fakir or faqir ; ) Derived from faqr is a Muslim Sufi ascetic in Middle East and South Asia. The Faqirs were wandering Dervishes teaching Islam and living on alms....
, or holy man, who combined personal magnetism with religious zealotry, emerged, determined to expel the Turks
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are peoples residing in northern, central and western Asia, southern Siberia and northwestern China and parts of eastern Europe. They speak languages belonging to the Turkic language family. They share, to varying degrees, certain cultural traits and historical backgrounds...
and restore Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
to its primitive purity. The son of a Dunqulah boatbuilder, Muhammad Ahmad had become the disciple of Muhammad ash Sharif, the head of the Sammaniyah order. Later, as a shaykh of the order, Muhammad Ahmad spent several years in seclusion and gained a reputation as a mystic and teacher. In 1880, he became a Sammaniyah.
Even after the Mahdi proclaimed a jihad
Jihad
Jihad , an Islamic term, is a religious duty of Muslims. In Arabic, the word jihād translates as a noun meaning "struggle". Jihad appears 41 times in the Quran and frequently in the idiomatic expression "striving in the way of God ". A person engaged in jihad is called a mujahid; the plural is...
, or holy war, against the Turkiyah
Turkiyah
The History of Sudan under Muhammad Ali and his successors traces the period from Muhammad Ali Pasha's invasion of Sudan in 1820 until the fall of Khartoum in 1885 to Muhammad Ahmad, the self-proclaimed Mahdi...
, Khartoum
Khartoum
Khartoum is the capital and largest city of Sudan and of Khartoum State. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile flowing north from Lake Victoria, and the Blue Nile flowing west from Ethiopia. The location where the two Niles meet is known as "al-Mogran"...
dismissed him as a religious fanatic. The government paid more attention when his religious zeal turned to denunciation of tax collectors. To avoid arrest, the Mahdi and a party of his followers, the Ansar
Ansar (Sudan)
The Ansar , or followers of the Mahdi, is a Sufi religious movement in the Sudan whose followers are disciples of Muhammad Ahmad , the self-proclaimed Mahdi....
, made a long march to Kurdufan
Kurdufan
Kurdufan , also spelled Kordofan, is a former province of central Sudan. In 1994 it was divided into three new federal states: North Kurdufan, South Kurdufan, and West Kurdufan...
, where he gained a large number of recruits, especially from the Baqqara. From a refuge in the area, he wrote appeals to the shaykhs of the religious orders and won active support or assurances of neutrality from all except the pro-Egyptian Khatmiyyah. Merchants and Arab tribes that had depended on the slave trade responded as well, along with the Hadendowa
Hadendoa
Hadendoa is the name of a nomadic subdivision of the Beja people. Other Beja tribes include the Bisharin and Ababda. The area inhabited by the Hadendoa is today parts of Sudan, Egypt and Eritrea.-Overview:...
Beja
Beja people
The Beja people are an ethnic group dwelling in parts of North Africa and the Horn of Africa.-Geography:The Beja are found mostly in Sudan, but also in parts of Eritrea, and Egypt...
, who were rallied to the Mahdi by an Ansar captain, Usman Digna
Osman Digna
Osman Digna was a follower of the Mahdi in Sudan, and hailed from the Hadendoa tribe of the Beja people. His birthplace is unknown; Suakin was said to be the town where he was born. When he was called Osman Ali, Osman Digna lived in Alexandria, Egypt, where he dealt in the selling of slaves...
.
Advancing attacks
Early in 1882, the Ansar, armed with spears and swords, overwhelmed a British-led 7,000-man Egyptian force not far from Al UbayyidAl-Ubayyid
Al-Ubayyid , also spelled El Obeid, is the capital of the state of North Kurdufan in central Sudan. In 2008, its population was 340,940. It is an important transportation hub: the terminus of a rail line, the junction of various roads and camel caravan routes, and the end of a pilgrim route from...
and seized their rifles, field guns and ammunition. The Mahdi followed up this victory by laying siege to Al Ubayyid and starving it into submission after four months. The Ansar, 30,000 men strong, then defeated an 8,000-man Egyptian relief force at Sheikan. Next the Mahdi captured Darfur and imprisoned Rudolf Carl von Slatin
Rudolf Carl von Slatin
Major-General Rudolf Anton Carl Freiherr von Slatin, Geh. Rat, GCVO, KCMG, CB was an Anglo-Austrian soldier and administrator in the Sudan.- Early life :...
, an Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
n in the khedive's service, who later became the first Egyptian-appointed governor of Darfur
Darfur
Darfur is a region in western Sudan. An independent sultanate for several hundred years, it was incorporated into Sudan by Anglo-Egyptian forces in 1916. The region is divided into three federal states: West Darfur, South Darfur, and North Darfur...
Province.
The advance of the Ansar and the Hadendowa rising in the east imperiled communications with Egypt and threatened to cut off garrisons at Khartoum, Kassala, Sennar
Sennar
Sennar is a town on the Blue Nile in Sudan and capital of the state of Sennar. For several centuries it was the capital of the Funj Kingdom of Sennar. It had an estimated population of 100,000 inhabitants in the early 19th century. The modern town lies 17km SSE of the ruins of the ancient capital...
, and Sawakin and in the south. To avoid being drawn into a costly military intervention, the British government ordered an Egyptian withdrawal from Sudan. Gordon, who had received a reappointment as governor general, arranged to supervise the evacuation of Egyptian troops and officials and all foreigners from Sudan.
British response
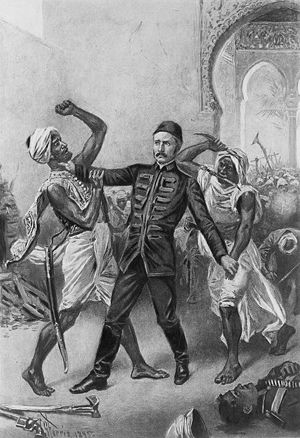

Al-Zubayr Rahma
A Sudanese Arab slave trader in the late 19th-century, Al-Zubayr Rahma Mansur later became a pasha and Sudanese governor....
, an old enemy whom he recognized as an excellent military commander, be named to succeed him to give disaffected Sudanese a leader other than the Mahdi to rally behind. London rejected this plan. As the situation deteriorated, Gordon argued that Sudan was essential to Egypt's security and that to allow the Ansar a victory there would invite the movement to spread elsewhere.
Increasing British popular support for Gordon eventually forced Prime Minister
Prime Minister of the United Kingdom
The Prime Minister of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the Head of Her Majesty's Government in the United Kingdom. The Prime Minister and Cabinet are collectively accountable for their policies and actions to the Sovereign, to Parliament, to their political party and...
William Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone FRS FSS was a British Liberal statesman. In a career lasting over sixty years, he served as Prime Minister four separate times , more than any other person. Gladstone was also Britain's oldest Prime Minister, 84 years old when he resigned for the last time...
to mobilize a relief force under the command of Lord Garnet Joseph Wolseley. A "flying column" sent overland from Wadi Halfa
Wadi Halfa
Wadi Halfa is a city in the state of Northern, in northern Sudan, on the shores of Lake Nubia . It is the terminus of a rail line from Khartoum and the point where goods are transferred from rail to ferries going down the Lake Nasser...
across the Bayuda Desert
Bayuda Desert
The Bayuda Desert is located north of modern Khartoum, Sudan, west of Kadabas, and south of the Nubian Desert, together making up part of the Sahara's eastern flank. It is located at . Within the desert can be found the Bayuda Volcanic Field....
bogged down at Abu Tulayh (commonly called Abu Klea), where the Hadendowa broke the British line. An advance unit that had gone ahead by river when the column reached Al Matammah arrived at Khartoum on 28 January 1885, to find the town had fallen
Battle of Khartoum
The Battle of Khartoum or Siege of Khartoum lasted from March 13, 1884 to January 26, 1885. It was fought in and around Khartoum between Egyptian forces led by British General Charles George Gordon and a Mahdist Sudanese army led by the self-proclaimed Mahdi Muhammad Ahmad...
two days earlier. The Ansar had waited for the Nile
Nile
The Nile is a major north-flowing river in North Africa, generally regarded as the longest river in the world. It is long. It runs through the ten countries of Sudan, South Sudan, Burundi, Rwanda, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Kenya, Ethiopia, Uganda and Egypt.The Nile has two major...
flood to recede before attacking the poorly defended river approach to Khartoum in boats, slaughtering the garrison, killing Gordon, and delivering his head to the Mahdi's tent. Kassala and Sennar fell soon after, and by the end of 1885, the Ansar had begun to move into the southern region. In all Sudan, only Sawakin, reinforced by Indian army troops, and Wadi Halfa on the northern frontier remained in Anglo-Egyptian hands.
Mahdiyah
The Mahdiyah (Mahdist regime) imposed traditional Islamic lawSharia
Sharia law, is the moral code and religious law of Islam. Sharia is derived from two primary sources of Islamic law: the precepts set forth in the Quran, and the example set by the Islamic prophet Muhammad in the Sunnah. Fiqh jurisprudence interprets and extends the application of sharia to...
s. Sudan's new ruler also authorized the burning of lists of pedigrees and books of law and theology because of their association with the old order and because he believed that the former accentuated tribalism at the expense of religious unity.
The Mahdiyah has become known as the first genuine Sudanese nationalist government. The Mahdi maintained that his movement was not a religious order that could be accepted or rejected at will, but that it was a universal regime, which challenged man to join or to be destroyed. The Mahdi modified Islam's five pillars to support the dogma that loyalty to him was essential to true belief. The Mahdi also added the declaration "and Muhammad Ahmad is the Mahdi of God and the representative of His Prophet" to the recitation of the creed, the shahada
Shahada
The Shahada , means "to know and believe without suspicion, as if witnessed"/testification; it is the name of the Islamic creed. The shahada is the Muslim declaration of belief in the oneness of God and acceptance of Muhammad as God's prophet...
. Moreover, service in the jihad replaced the hajj
Hajj
The Hajj is the pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia. It is one of the largest pilgrimages in the world, and is the fifth pillar of Islam, a religious duty that must be carried out at least once in their lifetime by every able-bodied Muslim who can afford to do so...
, or pilgrimage to Mecca
Mecca
Mecca is a city in the Hijaz and the capital of Makkah province in Saudi Arabia. The city is located inland from Jeddah in a narrow valley at a height of above sea level...
, as a duty incumbent on the faithful. Zakat
Zakat
Zakāt , one of the Five Pillars of Islam, is the giving of a fixed portion of one's wealth to charity, generally to the poor and needy.-History:Zakat, a practice initiated by Muhammed himself, has played an important role throughout Islamic history...
(almsgiving) became the tax paid to the state. The Mahdi justified these and other innovations and reforms as responses to instructions conveyed to him by God in visions.
The Mahdist regime was also known for its severe persecution of Christians in Sudan, including Copts.
Khalifa
Six months after the capture of Khartoum, the Mahdi died of typhusTyphus
Epidemic typhus is a form of typhus so named because the disease often causes epidemics following wars and natural disasters...
. The task of establishing and maintaining a government fell to his deputies—three caliphs chosen by the Mahdi in emulation of the Prophet Muhammad
Muhammad
Muhammad |ligature]] at U+FDF4 ;Arabic pronunciation varies regionally; the first vowel ranges from ~~; the second and the last vowel: ~~~. There are dialects which have no stress. In Egypt, it is pronounced not in religious contexts...
. Rivalry among the three, each supported by people of his native region, continued until 1891, when Abdallahi ibn Muhammad
Abdallahi ibn Muhammad
Abdullah Ibn-Mohammed or Abdullah al-Taaisha, also known as "The Khalifa" was a Sudanese Ansar General and ruler.-Early years:Abdullah was born into the Ta'aisha Baqqara tribe in Darfur around 1846 and was trained and educated as a preacher and holy man.He became a follower of Mohammed Ahmed "the...
, with the help primarily of the Baqqara Arabs, overcame the opposition of the others and emerged as unchallenged leader of the Mahdiyah. Abdallahi—called the Khalifa
Caliph
The Caliph is the head of state in a Caliphate, and the title for the ruler of the Islamic Ummah, an Islamic community ruled by the Shari'ah. It is a transcribed version of the Arabic word which means "successor" or "representative"...
(successor)—purged the Mahdiyah of members of the Mahdi's family and many of his early religious disciples.
Originally, the Mahdiyah was a jihad state, run like a military camp. Sharia
Sharia
Sharia law, is the moral code and religious law of Islam. Sharia is derived from two primary sources of Islamic law: the precepts set forth in the Quran, and the example set by the Islamic prophet Muhammad in the Sunnah. Fiqh jurisprudence interprets and extends the application of sharia to...
courts enforced Islamic law and the Mahdi's precepts, which had the force of law. After consolidating his power, the Khalifa instituted an administration and appointed Ansar (who were usually Baqqara) as amirs over each of the several provinces. The Khalifa also ruled over rich Al Jazirah
Al Jazirah (state)
Al Jazirah , also spelled Gezira, is one of the 15 states of Sudan. The state lies between the Blue Nile and the White Nile in the east-central region of the country. It has an area of 27,549 km². The name comes from the Arabic word for peninsula. Wad Madani is the capital of the state.It is...
. Although he failed to restore this region's commercial wellbeing, the Khalifa organized workshops to manufacture ammunition and to maintain river steamboats.
Regional relations remained tense throughout much of the Mahdiyah period, largely because of the Khalifa's commitment to using the jihad to extend his version of Islam throughout the world. For example, the Khalifa rejected an offer of an alliance against the Europeans by Emperor
Emperor of Ethiopia
The Emperor of Ethiopia was the hereditary ruler of Ethiopia until the abolition of the monarchy in 1974. The Emperor was the head of state and head of government, with ultimate executive, judicial and legislative power in that country...
Yohannes IV of Ethiopia
Yohannes IV of Ethiopia
Yohannes IV , born Lij Kassay Mercha Ge'ez, was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1872 until his death.-Early life:...
. In 1887, a 60,000-man Ansar army invaded Ethiopia, penetrated as far as Gondar
Gondar
Gondar or Gonder is a city in Ethiopia, which was once the old imperial capital and capital of the historic Begemder Province. As a result, the old province of Begemder is sometimes referred to as Gondar...
, and captured prisoners and booty. The Khalifa then refused to conclude peace with Ethiopia. In March 1889, an Ethiopian force, commanded by the emperor, marched on Metemma
Metemma
Metemma is a town in northwestern Ethiopia, on the border with Sudan. Located in the Semien Gondar Zone of the Amhara Region, Metemma has a latitude and longitude of with an elevation of 685 meters above sea level. Across the border is the corresponding Sudanese village of Gallabat...
; however, after Yohannes fell in the ensuing Battle of Gallabat
Battle of Gallabat
The Battle of Gallabat was fought 9–10 March 1889 between the Mahdist Sudanese and Ethiopian forces. It is a critical event in Ethiopian history because Nəgusä Nägäst Yohannes IV was killed in this battle...
, the Ethiopians withdrew. Abd ar Rahman an Nujumi, the Khalifa's best general, invaded Egypt in 1889, but British-led Egyptian troops defeated the Ansar at Tushkah
Battle of Toski
The battle of Toski took place on August 3rd, 1889 in Egypt between the Anglo-Egyptian forces and the Mahdist Sudanese.Since 1882, the British had taken control of Egypt and found themselves involved in the Sudan war. For this reason, they decided to reform and rearm the Egyptian Army...
. The failure of the Egyptian invasion ended the Ansars' invincibility. The Belgians prevented the Mahdi's men from conquering Equatoria
Equatoria
Equatoria is a region in the south of present-day South Sudan along the upper reaches of the White Nile. Originally a province of Egypt, it also contained most of Northern part of present day Uganda including Albert Lake...
, and in 1893, the Italians repulsed an Ansar attack at Akordat (in Eritrea
Eritrea
Eritrea , officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa. Eritrea derives it's name from the Greek word Erethria, meaning 'red land'. The capital is Asmara. It is bordered by Sudan in the west, Ethiopia in the south, and Djibouti in the southeast...
) and forced the Ansar to withdraw from Ethiopia.
Reconquest of Sudan
In 1892, Herbert Kitchener (later Lord Kitchener) became sirdarSirdar (Egypt)
Sirdar - a variant of Sardar, a long-standing of Indo-Aryan rank - was assigned to the British Commander-in-Chief of the nineteenth century Egyptian Army...
, or commander, of the Egyptian army and started preparations for the reconquest of Sudan. The British thought they needed to occupy Sudan in part because of international developments. By the early 1890s, British, French, and Belgian claims had converged at the Nile headwaters. Britain feared that the other colonial powers would take advantage of Sudan's instability to acquire territory previously annexed to Egypt. Apart from these political considerations, Britain wanted to establish control over the Nile to safeguard a planned irrigation dam at Aswan.
In 1895, the British government authorized Kitchener to launch a campaign to reconquer Sudan. Britain provided men and matériel while Egypt financed the expedition. The Anglo-Egyptian Nile Expeditionary Force included 25,800 men, 8,600 of whom were British. The remainder were troops belonging to Egyptian units that included six battalions recruited in southern Sudan. An armed river flotilla escorted the force, which also had artillery support. In preparation for the attack, the British established army headquarters at Wadi Halfa, and extended and reinforced the perimeter defenses around Sawakin. In March 1896, the campaign started; in September, Kitchener captured Dunqulah
Dongola
Dongola , also spelled Dunqulah, and formerly known as Al 'Urdi, is the capital of the state of Northern in Sudan, on the banks of the Nile. It should not be confused with Old Dongola, an ancient city located 80 km upstream on the opposite bank....
. The British then constructed a rail line from Wadi Halfa
Wadi Halfa
Wadi Halfa is a city in the state of Northern, in northern Sudan, on the shores of Lake Nubia . It is the terminus of a rail line from Khartoum and the point where goods are transferred from rail to ferries going down the Lake Nasser...
to Abu Hamad
Abu Hamad
Abu Hamad , also spelt 'Abu Hamed') is a town of Sudan on the right bank of the Nile, 345 mi by rail north of Khartoum. It stands at the centre of the great S-shaped bend of the Nile, and from it the railway to Wadi Halfa strikes straight across the Nubian desert, a little west of the old...
and an extension parallel to the Nile to transport troops and supplies to Berber
Berber people
Berbers are the indigenous peoples of North Africa west of the Nile Valley. They are continuously distributed from the Atlantic to the Siwa oasis, in Egypt, and from the Mediterranean to the Niger River. Historically they spoke the Berber language or varieties of it, which together form a branch...
. Anglo-Egyptian units fought a sharp action at Abu Hamad, but there was little other significant resistance until Kitchener reached Atbarah
Battle of Atbara
The Battle of Atbara took place during the Second Sudan War. Anglo-Egyptian forces defeated 15,000 Sudanese rebels, called Mahdists or Dervishes. The battle proved to be the turning point in the conquest of Sudan by a British and Egyptian coalition....
and defeated the Ansar. After this engagement, Kitchener's soldiers marched and sailed toward Omdurman
Omdurman
Omdurman is the second largest city in Sudan and Khartoum State, lying on the western banks of the River Nile, opposite the capital, Khartoum. Omdurman has a population of 2,395,159 and is the national centre of commerce...
, where the Khalifa made his last stand
Battle of Omdurman
At the Battle of Omdurman , an army commanded by the British Gen. Sir Herbert Kitchener defeated the army of Abdullah al-Taashi, the successor to the self-proclaimed Mahdi Muhammad Ahmad...
.
On 2 September 1898, the Khalifa committed his 52,000-man army to a frontal assault against the Anglo-Egyptian force, which was massed on the plain outside Omdurman. The outcome never was in doubt, largely because of superior British firepower. During the five-hour battle, about 11,000 Mahdists died, whereas Anglo-Egyptian losses amounted to 48 dead and fewer than 400 wounded.
Mopping-up operations required several years, but organized resistance ended when the Khalifa, who had escaped to Kurdufan
Kurdufan
Kurdufan , also spelled Kordofan, is a former province of central Sudan. In 1994 it was divided into three new federal states: North Kurdufan, South Kurdufan, and West Kurdufan...
, died in fighting at Umm Diwaykarat
Battle of Umm Diwaykarat
The Battle of Umm Diwaykarat on November 25, 1899 marked the final obliteration of Muhammad Ahmad's short-lived Sudanese empire, when Anglo-Egyptian forces under the command of Lord Kitchener wiped out what was left of the Mahdist armies under the command of the Abdallahi ibn Muhammad, known as the...
in November 1899. Many areas welcomed the downfall of his regime. Sudan's economy had been all but destroyed during his reign and the population had declined by approximately one-half because of famine, disease, persecution, and warfare. Moreover, none of the country's traditional institutions or loyalties remained intact. Tribes had been divided in their attitudes toward Mahdism, religious brotherhoods had been weakened, and orthodox religious leaders had vanished.

