Home energy rating
Encyclopedia
A Home Energy Rating is a measurement of a home’s energy efficiency
, used primarily in the United States. Home energy ratings can be used for either existing homes or new homes. A home energy rating of an existing home allows a homeowner to receive a report listing options for upgrading a home’s energy efficiency. The homeowners may then use the report to determine the most effective ways in which to upgrade the home’s energy efficiency. A home energy rating of a new home allows buyers to compare the energy efficiency of homes they are considering buying.
 A home energy rating can be used to gauge the current energy efficiency of a home or estimate the efficiency of a home that is being constructed or improved. A home energy rating of a home prior to construction or improvement is called a “projected rating.” A home energy rating that is used to determine a home’s current efficiency is referred to as a “confirmed rating.”
A home energy rating can be used to gauge the current energy efficiency of a home or estimate the efficiency of a home that is being constructed or improved. A home energy rating of a home prior to construction or improvement is called a “projected rating.” A home energy rating that is used to determine a home’s current efficiency is referred to as a “confirmed rating.”
Energy assessments take into account different climatic conditions in different parts of the country and are benchmarked according to average household energy consumption
particular to a given climatic region.
For capitalizing a building’s energy performance
in the mortgage loan, certification of “White Tags
” for private financial investors, and by the US government for verification of building energy performance for such programs as federal tax incentives, the United States Environmental Protection Agency
’s Energy Star
program and the U.S. Department of Energy’s Building America Program.
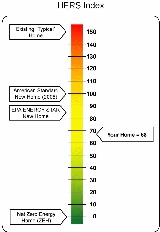
The HERS Index was introduced in 2006 and replaced the earlier "HERS Score", which ran in the opposite direction: The higher the value, the better.http://www.energystar.gov/index.cfm?c=bldrs_lenders_raters.nh_HERS In 2009, the U.S. Department of Energy presented a new scale, the "EnergySmart Home Scale (E-Scale)", "based on" the HERS Index, apparently simply by subtracting the HERS Index from 100. In this new scale, higher values correspond again to better performance.http://www1.eere.energy.gov/buildings/challenge/printable_versions/energysmart.html
A confirmed rating, which indicates the home’s current efficiency, requires an inspection of the home from an energy rater. The home energy rater reviews the home to identify its energy characteristics, such as insulation
levels, window efficiency, wall-to-window ratios, the heating and cooling system
efficiency, the solar orientation
of the home, and the water heating
system. Performance testing, such as a blower door
test for air leakage and duct
leakage, is usually part of the rating.
There are no prerequisites for individuals who wish to obtain HERS Training and take the national rater test. However, HERS subject matter is difficult and the learning curve may be quicker for individuals who have a background in the construction or home inspection industry. The test is open book and open note but students may not use web resources to answer questions.
Efficient energy use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal of efforts to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a home allows a building to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a comfortable temperature...
, used primarily in the United States. Home energy ratings can be used for either existing homes or new homes. A home energy rating of an existing home allows a homeowner to receive a report listing options for upgrading a home’s energy efficiency. The homeowners may then use the report to determine the most effective ways in which to upgrade the home’s energy efficiency. A home energy rating of a new home allows buyers to compare the energy efficiency of homes they are considering buying.
Usage

Energy assessments take into account different climatic conditions in different parts of the country and are benchmarked according to average household energy consumption
Domestic Energy Consumption
Domestic energy consumption is the amount of energy that is spent on the different appliances used within housing. The amount of energy used per household varies widely depending on the standard of living of the country, climate, and the age and type of residence...
particular to a given climatic region.
HERS Index and related scales
Ratings provide a relative energy use index called the HERS Index – a HERS Index of 100 represents the energy use of the “American Standard Building” and an Index of 0 (zero) indicates that the building uses no net purchased energy (a Zero Energy Building). The lower the value, the better.For capitalizing a building’s energy performance
Building performance
Building performance or home performance is a comprehensive whole-house approach to identifying and fixing comfort and energy efficiency problems in a home....
in the mortgage loan, certification of “White Tags
White certificates
In environmental policy, white certificates are documents certifying that a certain reduction of energy consumption has been attained. In most applications, the white certificates are tradable and combined with an obligation to achieve a certain target of energy savings...
” for private financial investors, and by the US government for verification of building energy performance for such programs as federal tax incentives, the United States Environmental Protection Agency
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is an agency of the federal government of the United States charged with protecting human health and the environment, by writing and enforcing regulations based on laws passed by Congress...
’s Energy Star
Energy Star
Energy Star is an international standard for energy efficient consumer products originated in the United States of America. It was first created as a United States government program during the early 1990s, but Australia, Canada, Japan, New Zealand, Taiwan and the European Union have also adopted...
program and the U.S. Department of Energy’s Building America Program.
The HERS Index was introduced in 2006 and replaced the earlier "HERS Score", which ran in the opposite direction: The higher the value, the better.http://www.energystar.gov/index.cfm?c=bldrs_lenders_raters.nh_HERS In 2009, the U.S. Department of Energy presented a new scale, the "EnergySmart Home Scale (E-Scale)", "based on" the HERS Index, apparently simply by subtracting the HERS Index from 100. In this new scale, higher values correspond again to better performance.http://www1.eere.energy.gov/buildings/challenge/printable_versions/energysmart.html
Projected and Confirmed Ratings
Projected ratings give home owners and builders an estimate of what a home’s efficiency will be like after construction or improvements, so that they may determine the most cost-effective route to improve a building’s efficiency.A confirmed rating, which indicates the home’s current efficiency, requires an inspection of the home from an energy rater. The home energy rater reviews the home to identify its energy characteristics, such as insulation
Building insulation
building insulation refers broadly to any object in a building used as insulation for any purpose. While the majority of insulation in buildings is for thermal purposes, the term also applies to acoustic insulation, fire insulation, and impact insulation...
levels, window efficiency, wall-to-window ratios, the heating and cooling system
HVAC
HVAC refers to technology of indoor or automotive environmental comfort. HVAC system design is a major subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer...
efficiency, the solar orientation
Passive solar building design
In passive solar building design, windows, walls, and floors are made to collect, store, and distribute solar energy in the form of heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer...
of the home, and the water heating
Water heating
Water heating is a thermodynamic process using an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water are for cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating...
system. Performance testing, such as a blower door
Blower Door
A blower door is a piece of equipment primarily used to measure the airtightness of small to medium size buildings. It can also be used to measure airflow between building zones, to test ductwork airtightness and to help physically locate air leakage sites in the building envelope.There are three...
test for air leakage and duct
Duct (HVAC)
Ducts are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning to deliver and remove air. These needed airflows include, for example, supply air, return air, and exhaust air. Ducts also deliver, most commonly as part of the supply air, ventilation air...
leakage, is usually part of the rating.
HERS Training
To provide Home Energy Ratings, individuals must attend a HERS Rater training program and pass the national rater test. The industry standard for HERS training is a 40 hour course that spans between 5 and 10 days although some trainers offer self paced online programs. Students learn the basics of building science, proper use of duct blaster and blower door equipment, RESNET standards, and mortgage and white tag related information.There are no prerequisites for individuals who wish to obtain HERS Training and take the national rater test. However, HERS subject matter is difficult and the learning curve may be quicker for individuals who have a background in the construction or home inspection industry. The test is open book and open note but students may not use web resources to answer questions.
See also
- Australia - House Energy RatingHouse Energy RatingA House Energy Rating is an index of a building's thermal performance for residential homes in Australia....
- UK - National Home Energy RatingNational Home Energy RatingThe National Home Energy Rating Scheme is both a UK accreditation scheme for energy assessors and a rating scale for the energy efficiency of housing.The NHER is owned and operated by National Energy Services...
- Canada - EnerGuideEnerGuideEnerGuide is the official Government of Canada mark associated with the labelling and rating of the energy consumption or energy efficiency of specific products...
- Building Information ModelingBuilding Information ModelingBuilding information modeling is the process of generating and managing building data during its life cycle.BIM involves representing a design as objects – vague and undefined, generic or product-specific, solid shapes or void-space oriented , that carry their geometry, relations and attributes...
- Energy auditEnergy auditAn energy audit is an inspection, survey and analysis of energy flows for energy conservation in a building, process or system to reduce the amount of energy input into the system without negatively affecting the output.-Principle:...
- Low-energy houseLow-energy houseA low-energy house is any type of house that from design, technologies and building products uses less energy, from any source, than a traditional or average contemporary house...

