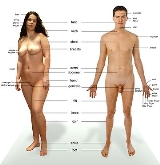
Human body
Encyclopedia
The human body is the entire structure of a human
organism
, and consists of a head
, neck
, torso
, two arm
s and two leg
s.
By the time the human reaches adulthood, the body consists of close to 100 trillion cells
, the basic unit of life
. These cells are organised biologically to eventually form the whole body.
The average height of an adult male human (in developed countries) is about 1.7–1.8 m (5'7" to 5'11") tall and the adult female about 1.6–1.7 m (5'2" to 5'7") tall. This size is firstly determined by gene
s and secondly by diet. Body type and body composition
are influenced by postnatal factors such as diet
and exercise.
, cardiovascular system, digestive system, endocrine system
, integumentary system
, urinary system
, lymphatic system
, immune system
, respiratory system
, nervous system
and reproductive system
.
.svg.png)
, vein
s, arteries
and capillaries. The primary function of the heart is to circulate the blood
, and through the blood, oxygen and vital minerals are transferred to the tissues and organs that comprise the body.
The left side of the main organ (left ventricle
and left atrium
) is responsible for pumping blood to all parts of the body, while the right side (right ventricle
and right atrium
) pumps only to the lungs for re-oxygenation of the blood. The heart itself is divided into three layers called the endocardium
, myocardium and epicardium
, which vary in thickness and function.
and transforming nutrient
s into energy
.
The digestive system consists of the - buccal cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine ending in the rectum and anus. These parts together are called the alimentary canal (digestive tract).
. The integument also includes appendages
, primarily the sweat
and sebaceous
glands, hair
, nail
s and arrectores pili (tiny muscles at the root of each hair that cause goose bumps
).
, the fluid found in between cells. The lymphatic system is very similar to the circulatory system in terms of both its structure and its most basic function (to carry a body fluid).
, made by bone
s attached to other bones with joint
s, and skeletal muscle attached to the skeleton by tendon
s.
penis
of the male
is inserted into the female
's vagina
until the male ejaculates semen, which contains sperm
, into the female's vagina. The sperm then travels through the vagina and cervix into the uterus
or fallopian tube
s for fertilization of the ovum
.
The human male reproductive system is a series of organs located outside the body and around the pelvic region of a male that contribute towards the reproductive process. The primary direct function of the male reproductive system is to provide the male gamete
or spermatozoa for fertilization of the ovum.
The major reproductive organs of the male can be grouped into three categories. The first category is sperm production and storage. Production takes place in the testes which are housed in the temperature regulating scrotum
, immature sperm then travel to the epididymis
for development and storage. The second category are the ejaculatory fluid producing glands which include the seminal vesicles, prostate
, and the vas deferens
. The final category are those used for copulation, and deposition of the spermatozoa (sperm
) within the female, these include the penis
, urethra
, vas deferens
and Cowper's gland.
The human female reproductive system is a series of organs primarily located inside of the body and around the pelvic region of a female
that contribute towards the reproductive process. The human female reproductive system contains three main parts: the vagina
, which acts as the receptacle for the male's sperm, the uterus
, which holds the developing fetus, and the ovaries
, which produce the female's ova. The breasts are also an important reproductive organ during the parenting stage of reproduction.
The vagina meets the outside at the vulva
, which also includes the labia, clitoris
and urethra
; during intercourse this area is lubricated by mucus secreted by the Bartholin's glands. The vagina is attached to the uterus through the cervix
, while the uterus is attached to the ovaries via the fallopian tube
s. At certain intervals, typically approximately every 28 days, the ovaries release an ovum
, which passes through the fallopian tube into the uterus. The lining of the uterus, called the endometrium
, and unfertilized ova are shed each cycle through a process known as menstruation
.
Human
Humans are the only living species in the Homo genus...
organism
Organism
In biology, an organism is any contiguous living system . In at least some form, all organisms are capable of response to stimuli, reproduction, growth and development, and maintenance of homoeostasis as a stable whole.An organism may either be unicellular or, as in the case of humans, comprise...
, and consists of a head
Human head
In human anatomy, the head is the upper portion of the human body. It supports the face and is maintained by the skull, which itself encloses the brain.-Cultural importance:...
, neck
Neck
The neck is the part of the body, on many terrestrial or secondarily aquatic vertebrates, that distinguishes the head from the torso or trunk. The adjective signifying "of the neck" is cervical .-Boner anatomy: The cervical spine:The cervical portion of the human spine comprises seven boney...
, torso
Torso
Trunk or torso is an anatomical term for the central part of the many animal bodies from which extend the neck and limbs. The trunk includes the thorax and abdomen.-Major organs:...
, two arm
Arm
In human anatomy, the arm is the part of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow joints. In other animals, the term arm can also be used for analogous structures, such as one of the paired forelimbs of a four-legged animal or the arms of cephalopods...
s and two leg
Human leg
The human leg is the entire lower extremity or limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh and even the hip or gluteal region; however, the precise definition in human anatomy refers only to the section of the lower limb extending from the knee to the ankle.Legs are used for standing,...
s.
By the time the human reaches adulthood, the body consists of close to 100 trillion cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
, the basic unit of life
Life
Life is a characteristic that distinguishes objects that have signaling and self-sustaining processes from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased , or else because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate...
. These cells are organised biologically to eventually form the whole body.
Size, type and proportion
| Constituent | Weight | Percent of atoms |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Oxygen Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition... |
38.8 kg | 25.5 % |
| Carbon Carbon Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds... |
10.9 kg | 9.5 % |
| Hydrogen Hydrogen Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly... |
6.0 kg | 63 % |
| Nitrogen Nitrogen Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere... |
1.9 kg | 1.4 % |
| Calcium Calcium Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust... |
1.2 kg | 0.3 % |
| Phosphorus Phosphorus Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks... |
0.6 kg | 0.2 % |
| Potassium Potassium Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are... |
0.2 kg | 0.06 % |
The average height of an adult male human (in developed countries) is about 1.7–1.8 m (5'7" to 5'11") tall and the adult female about 1.6–1.7 m (5'2" to 5'7") tall. This size is firstly determined by gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
s and secondly by diet. Body type and body composition
Body composition
In physical fitness, body composition is used to describe the percentages of fat, bone and muscle in human bodies. Because muscular tissue takes up less space in our body than fat tissue, our body composition, as well as our weight, determines leanness...
are influenced by postnatal factors such as diet
Diet (nutrition)
In nutrition, diet is the sum of food consumed by a person or other organism. Dietary habits are the habitual decisions an individual or culture makes when choosing what foods to eat. With the word diet, it is often implied the use of specific intake of nutrition for health or weight-management...
and exercise.
Systems
The organ systems of the body include the musculoskeletal systemMusculoskeletal system
A musculoskeletal system is an organ system that gives animals the ability to move using the muscular and skeletal systems...
, cardiovascular system, digestive system, endocrine system
Endocrine system
In physiology, the endocrine system is a system of glands, each of which secretes a type of hormone directly into the bloodstream to regulate the body. The endocrine system is in contrast to the exocrine system, which secretes its chemicals using ducts. It derives from the Greek words "endo"...
, integumentary system
Integumentary system
The integumentary system is the organ system that protects the body from damage, comprising the skin and its appendages...
, urinary system
Urinary system
The urinary system is the organ system that produces, stores, and eliminates urine. In humans it includes two kidneys, two ureters, the bladder and the urethra.-Kidney:...
, lymphatic system
Lymphatic system
The lymphoid system is the part of the immune system comprising a network of conduits called lymphatic vessels that carry a clear fluid called lymph unidirectionally toward the heart. Lymphoid tissue is found in many organs, particularly the lymph nodes, and in the lymphoid follicles associated...
, immune system
Immune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
, respiratory system
Respiratory system
The respiratory system is the anatomical system of an organism that introduces respiratory gases to the interior and performs gas exchange. In humans and other mammals, the anatomical features of the respiratory system include airways, lungs, and the respiratory muscles...
, nervous system
Nervous system
The nervous system is an organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of an animal and transmit signals between different parts of its body. In most animals the nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. The central nervous...
and reproductive system
Reproductive system
The reproductive system or genital system is a system of organs within an organism which work together for the purpose of reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ systems, the sexes...
.
.svg.png)
Cardiovascular system
The cardiovascular system comprises the heartHuman heart
The human heart is a muscular organ that provides a continuous blood circulation through the cardiac cycle and is one of the most vital organs in the human body...
, vein
Vein
In the circulatory system, veins are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart...
s, arteries
Artery
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. This blood is normally oxygenated, exceptions made for the pulmonary and umbilical arteries....
and capillaries. The primary function of the heart is to circulate the blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
, and through the blood, oxygen and vital minerals are transferred to the tissues and organs that comprise the body.
The left side of the main organ (left ventricle
Left ventricle
The left ventricle is one of four chambers in the human heart. It receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium via the mitral valve, and pumps it into the aorta via the aortic valve.-Shape:...
and left atrium
Left atrium
The left atrium is one of the four chambers in the human heart. It receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins, and pumps it into the left ventricle, via the mitral valve.-Foramen ovale:...
) is responsible for pumping blood to all parts of the body, while the right side (right ventricle
Right ventricle
The right ventricle is one of four chambers in the human heart. It receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium via the tricuspid valve, and pumps it into the pulmonary artery via the pulmonary valve and pulmonary trunk....
and right atrium
Right atrium
The right atrium is one of four chambers in the hearts of mammals and archosaurs...
) pumps only to the lungs for re-oxygenation of the blood. The heart itself is divided into three layers called the endocardium
Endocardium
The endocardium is the innermost layer of tissue that lines the chambers of the heart. Its cells are embryologically and biologically similar to the endothelial cells that line blood vessels....
, myocardium and epicardium
Epicardium
Epicardium describes the outer layer of heart tissue . When considered as a part of the pericardium, it is the inner layer, or visceral pericardium, continuous with the serous layer....
, which vary in thickness and function.
Digestive system
The digestive system provides the body's means of processing foodFood
Food is any substance consumed to provide nutritional support for the body. It is usually of plant or animal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals...
and transforming nutrient
Nutrient
A nutrient is a chemical that an organism needs to live and grow or a substance used in an organism's metabolism which must be taken in from its environment. They are used to build and repair tissues, regulate body processes and are converted to and used as energy...
s into energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
.
The digestive system consists of the - buccal cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine ending in the rectum and anus. These parts together are called the alimentary canal (digestive tract).
Integumentary system
The integumentary system is the largest organ system in the human body, and is responsible for protecting the body from most physical and environmental factors. The largest organ in the body, is the skinHuman skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body. In humans, it is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to that of most other mammals,...
. The integument also includes appendages
Skin appendage
Skin appendages are appendages that are associated with the skin and serve a particular function. In humans some of the more common skin appendages are hairs , arrector pilli , sebaceous glands , sweat glands Skin appendages are appendages that are associated with the skin and serve a particular...
, primarily the sweat
Sweat gland
Sweat glands, or sudoriferous glands, are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. There are two kinds of sweat glands:...
and sebaceous
Sebaceous gland
The sebaceous glands are microscopic glands in the skin that secrete an oily/waxy matter, called sebum, to lubricate and waterproof the skin and hair of mammals...
glands, hair
Hair
Hair is a filamentous biomaterial, that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Found exclusively in mammals, hair is one of the defining characteristics of the mammalian class....
, nail
Nail (anatomy)
A nail is a horn-like envelope covering the dorsal aspect of the terminal phalanges of fingers and toes in humans, most non-human primates, and a few other mammals. Nails are similar to claws, which are found on numerous other animals....
s and arrectores pili (tiny muscles at the root of each hair that cause goose bumps
Goose bumps
Goose bumps, also called goose flesh, goose pimples, chill bumps, chicken skin, funky spots, Dasler Bumps, chicken bumps or the medical term cutis anserina, are the bumps on a person's skin at the base of body hairs which may involuntarily develop when a person is cold or experiences strong...
).
Lymphatic system
The main function of the lymphatic system is to extract, transport and metabolise lymphLymph
Lymph is considered a part of the interstitial fluid, the fluid which lies in the interstices of all body tissues. Interstitial fluid becomes lymph when it enters a lymph capillary...
, the fluid found in between cells. The lymphatic system is very similar to the circulatory system in terms of both its structure and its most basic function (to carry a body fluid).
Musculoskeletal system
The human musculoskeletal system consists of the human skeletonHuman skeleton
The human skeleton consists of both fused and individual bones supported and supplemented by ligaments, tendons, muscles and cartilage. It serves as a scaffold which supports organs, anchors muscles, and protects organs such as the brain, lungs and heart....
, made by bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
s attached to other bones with joint
Joint
A joint is the location at which two or more bones make contact. They are constructed to allow movement and provide mechanical support, and are classified structurally and functionally.-Classification:...
s, and skeletal muscle attached to the skeleton by tendon
Tendon
A tendon is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that usually connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding tension. Tendons are similar to ligaments and fasciae as they are all made of collagen except that ligaments join one bone to another bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other...
s.
Bones
An adult human has approximately 206 distinct bones:- Spine and vertebral column (26)
- CraniumHuman skullThe human skull is a bony structure, skeleton, that is in the human head and which supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.In humans, the adult skull is normally made up of 22 bones...
(8) - FaceFaceThe face is a central sense organ complex, for those animals that have one, normally on the ventral surface of the head, and can, depending on the definition in the human case, include the hair, forehead, eyebrow, eyelashes, eyes, nose, ears, cheeks, mouth, lips, philtrum, temple, teeth, skin, and...
(14) - Hyoid boneHyoid boneThe hyoid bone is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies at the level of the base of the mandible in the front and the third cervical vertebra behind.Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly...
, sternum and ribs (26) - Upper extremities (70)
- Lower extremities (62)
Nervous system
The nervous system consists of cells that communicate information about an organism's surroundings and itself.Reproductive system
Human reproduction takes place as internal fertilization by sexual intercourse. During this process, the erectErectile tissue
Erectile tissue is tissue in the body that can become erect, usually by becoming engorged with blood.-Erectile tissue in the clitoris and penis:...
penis
Penis
The penis is a biological feature of male animals including both vertebrates and invertebrates...
of the male
Male
Male refers to the biological sex of an organism, or part of an organism, which produces small mobile gametes, called spermatozoa. Each spermatozoon can fuse with a larger female gamete or ovum, in the process of fertilization...
is inserted into the female
Female
Female is the sex of an organism, or a part of an organism, which produces non-mobile ova .- Defining characteristics :The ova are defined as the larger gametes in a heterogamous reproduction system, while the smaller, usually motile gamete, the spermatozoon, is produced by the male...
's vagina
Vagina
The vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the...
until the male ejaculates semen, which contains sperm
Sperm
The term sperm is derived from the Greek word sperma and refers to the male reproductive cells. In the types of sexual reproduction known as anisogamy and oogamy, there is a marked difference in the size of the gametes with the smaller one being termed the "male" or sperm cell...
, into the female's vagina. The sperm then travels through the vagina and cervix into the uterus
Uterus
The uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
or fallopian tube
Fallopian tube
The Fallopian tubes, also known as oviducts, uterine tubes, and salpinges are two very fine tubes lined with ciliated epithelia, leading from the ovaries of female mammals into the uterus, via the utero-tubal junction...
s for fertilization of the ovum
Ovum
An ovum is a haploid female reproductive cell or gamete. Both animals and embryophytes have ova. The term ovule is used for the young ovum of an animal, as well as the plant structure that carries the female gametophyte and egg cell and develops into a seed after fertilization...
.
The human male reproductive system is a series of organs located outside the body and around the pelvic region of a male that contribute towards the reproductive process. The primary direct function of the male reproductive system is to provide the male gamete
Gamete
A gamete is a cell that fuses with another cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually...
or spermatozoa for fertilization of the ovum.
The major reproductive organs of the male can be grouped into three categories. The first category is sperm production and storage. Production takes place in the testes which are housed in the temperature regulating scrotum
Scrotum
In some male mammals the scrotum is a dual-chambered protuberance of skin and muscle containing the testicles and divided by a septum. It is an extension of the perineum, and is located between the penis and anus. In humans and some other mammals, the base of the scrotum becomes covered with curly...
, immature sperm then travel to the epididymis
Epididymis
The epididymis is part of the male reproductive system and is present in all male amniotes. It is a narrow, tightly-coiled tube connecting the efferent ducts from the rear of each testicle to its vas deferens. A similar, but probably non-homologous, structure is found in cartilaginous...
for development and storage. The second category are the ejaculatory fluid producing glands which include the seminal vesicles, prostate
Prostate
The prostate is a compound tubuloalveolar exocrine gland of the male reproductive system in most mammals....
, and the vas deferens
Vas deferens
The vas deferens , also called ductus deferens, , is part of the male anatomy of many vertebrates; they transport sperm from the epididymis in anticipation of ejaculation....
. The final category are those used for copulation, and deposition of the spermatozoa (sperm
Sperm
The term sperm is derived from the Greek word sperma and refers to the male reproductive cells. In the types of sexual reproduction known as anisogamy and oogamy, there is a marked difference in the size of the gametes with the smaller one being termed the "male" or sperm cell...
) within the female, these include the penis
Penis
The penis is a biological feature of male animals including both vertebrates and invertebrates...
, urethra
Urethra
In anatomy, the urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals for the removal of fluids out of the body. In males, the urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine...
, vas deferens
Vas deferens
The vas deferens , also called ductus deferens, , is part of the male anatomy of many vertebrates; they transport sperm from the epididymis in anticipation of ejaculation....
and Cowper's gland.
The human female reproductive system is a series of organs primarily located inside of the body and around the pelvic region of a female
Female
Female is the sex of an organism, or a part of an organism, which produces non-mobile ova .- Defining characteristics :The ova are defined as the larger gametes in a heterogamous reproduction system, while the smaller, usually motile gamete, the spermatozoon, is produced by the male...
that contribute towards the reproductive process. The human female reproductive system contains three main parts: the vagina
Vagina
The vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the...
, which acts as the receptacle for the male's sperm, the uterus
Uterus
The uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
, which holds the developing fetus, and the ovaries
Ovary
The ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ, often found in pairs as part of the vertebrate female reproductive system. Ovaries in anatomically female individuals are analogous to testes in anatomically male individuals, in that they are both gonads and endocrine glands.-Human anatomy:Ovaries...
, which produce the female's ova. The breasts are also an important reproductive organ during the parenting stage of reproduction.
The vagina meets the outside at the vulva
Vulva
The vulva consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals....
, which also includes the labia, clitoris
Clitoris
The clitoris is a sexual organ that is present only in female mammals. In humans, the visible button-like portion is located near the anterior junction of the labia minora, above the opening of the urethra and vagina. Unlike the penis, which is homologous to the clitoris, the clitoris does not...
and urethra
Urethra
In anatomy, the urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals for the removal of fluids out of the body. In males, the urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine...
; during intercourse this area is lubricated by mucus secreted by the Bartholin's glands. The vagina is attached to the uterus through the cervix
Cervix
The cervix is the lower, narrow portion of the uterus where it joins with the top end of the vagina. It is cylindrical or conical in shape and protrudes through the upper anterior vaginal wall...
, while the uterus is attached to the ovaries via the fallopian tube
Fallopian tube
The Fallopian tubes, also known as oviducts, uterine tubes, and salpinges are two very fine tubes lined with ciliated epithelia, leading from the ovaries of female mammals into the uterus, via the utero-tubal junction...
s. At certain intervals, typically approximately every 28 days, the ovaries release an ovum
Ovum
An ovum is a haploid female reproductive cell or gamete. Both animals and embryophytes have ova. The term ovule is used for the young ovum of an animal, as well as the plant structure that carries the female gametophyte and egg cell and develops into a seed after fertilization...
, which passes through the fallopian tube into the uterus. The lining of the uterus, called the endometrium
Endometrium
-Function:The endometrium is the innermost glandular layer and functions as a lining for the uterus, preventing adhesions between the opposed walls of the myometrium, thereby maintaining the patency of the uterine cavity. During the menstrual cycle or estrous cycle, the endometrium grows to a...
, and unfertilized ova are shed each cycle through a process known as menstruation
Menstruation
Menstruation is the shedding of the uterine lining . It occurs on a regular basis in sexually reproductive-age females of certain mammal species. This article focuses on human menstruation.-Overview:...
.

