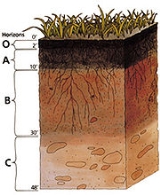
Humus
Overview
Soil science
Soil science is the study of soil as a natural resource on the surface of the earth including soil formation, classification and mapping; physical, chemical, biological, and fertility properties of soils; and these properties in relation to the use and management of soils.Sometimes terms which...
, humus (coined 1790–1800; < Latin: earth, ground) refers to any organic matter
Soil organic matter
Organic matter is matter that has come from a once-living organism; is capable of decay, or the product of decay; or is composed of organic compounds...
that has reached a point of stability, where it will break down no further and might, if conditions do not change, remain as it is for centuries, if not millennia.
In agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
, humus is sometimes also used to describe mature compost
Compost
Compost is organic matter that has been decomposed and recycled as a fertilizer and soil amendment. Compost is a key ingredient in organic farming. At its most essential, the process of composting requires simply piling up waste outdoors and waiting for the materials to break down from anywhere...
, or natural compost extracted from a forest or other spontaneous source for use to amend soil
Soil conditioner
A soil conditioner, also called a soil amendment, is a material added to soil to improve plant growth and health. A conditioner or a combination of conditioners corrects the soil's deficiencies in structure and-or nutrients.-Purpose:...
.

