
Hurricane Gilbert
Encyclopedia
Hurricane Gilbert was an extremely powerful Cape Verde-type hurricane
that formed during the 1988 Atlantic hurricane season
and created widespread destruction in the Caribbean Sea
and the Gulf of Mexico
. It is the second most intense hurricane
ever observed in the Atlantic basin
behind only Hurricane Wilma
of the very active 2005 Atlantic hurricane season
. Gilbert was also one of the largest tropical cyclones ever observed in the Atlantic basin. At one point, its tropical storm-force winds measured 588 mi (946.3 km) in diameter. In addition, Gilbert was the most intense tropical cyclone to strike Mexico
, slightly ahead of Hurricane Dean
in 2007
.
The seventh named storm and third hurricane of the 1988 Atlantic hurricane season
, Gilbert developed from a tropical wave
on September 8 while 400 mi (640 km) east of Barbados
. After it intensified into a tropical storm on September 9, Gilbert steadily strengthened as it tracked west-northwestward into the Caribbean Sea, and became a hurricane on the following day. Gilbert quickly intensified
into a Category 3 hurricane on September 11, and made landfall on the island of Jamaica on September 12. Rapid intensification occurred after Gilbert crossed Jamaica, and the storm became a Category 5 hurricane late on September 13. Gilbert weakened slightly, and made landfall on the Yucatan Peninsula
later that day while still at Category 5 hurricane. Gilbert significantly weakened over the Yucatan Peninsula, and was only a Category 2 hurricane when it emerged into the Gulf of Mexico on September 15. Re-intensification occurred gradually as Gilbert tracked across the Gulf of Mexico, and the storm was a Category 4 hurricane when it made landfall in mainland Mexico on September 16. Gilbert weakened after landfall, and eventually dissipated on September 19 over the Midwest
Gilbert wreaked havoc in the Caribbean and the Gulf of Mexico for nearly nine days. In total, it killed 433 people and caused about $7.1 billion (1988 USD, $ USD) in damages over the course of its path. As a result of the effects, the World Meteorological Organization
retired the name Gilbert in the spring of 1989, and was replaced with Gordon.
.
With no inhibiting factors to strengthening, Gilbert quickly became a hurricane late on September 10 and then a major hurricane on September 11. It moved consistently west-northwest influenced by a strong high pressure system to its north. This movement led to the hurricane's first landfall in Jamaica. The eye passed completely over Jamaica on September 12 with 125 mph (205 km/h) winds and a central pressure of 960 mbar (28.35 inHg), making it a Category 3 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale
.
 Gilbert strengthened rapidly after emerging from the coast of Jamaica. As the hurricane brushed the Cayman Islands
Gilbert strengthened rapidly after emerging from the coast of Jamaica. As the hurricane brushed the Cayman Islands
a reporting station on Grand Cayman
recorded a wind gust of 156 mph (252 km/h) while the storm passed just to the southeast on September 13. Extreme intensification continued until Gilbert reached a minimum pressure of 888 mbar (26.22 inHg) with sustained flight-level winds of 185 mph (295 km/h), having intensified by 72 mbar in a space of 24 hours. This pressure was the lowest ever observed in the Western hemisphere
and made Gilbert the most intense Atlantic hurricane on record, until it was surpassed by Hurricane Wilma in the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season.
Gilbert made landfall for a second time on the island of Cozumel
and then Mexico's Yucatán Peninsula on September 14 as a Category 5 hurricane, making it the first Category 5 to make landfall in the Atlantic basin since Hurricane David
hit Hispanola in 1979
; the minimum pressure at landfall in Cozumel was estimated to be 900 mbar (26.6 inHg). The storm weakened quickly while crossing land before emerging into the Gulf of Mexico
as a Category 2 hurricane. Gilbert restrengthened rapidly, however, and made landfall for a final time as a Category 3 hurricane near La Pesca, Tamaulipas
, on September 16.
On September 17 Gilbert brushed the inland city of Monterrey
, Nuevo León
before taking a sharp turn to the north. The storm spawned 29 tornadoes in Texas
on September 18 before moving across Oklahoma and being absorbed by a low-pressure system over Missouri
on September 19.
Gilbert claimed 433 lives, mostly in Mexico. Exact monetary damage figures are not available, but the total for all areas affected by Gilbert is estimated to be near $7.1 billion (1988 USD
). A preliminary report assessed Gilbert as the costliest Atlantic hurricane of all time with an initial damage total of over $10 billion (USD), though it was not later confirmed.
since Hurricane Charlie
in 1951. The storm left $4 billion (1988 USD) in damage. Gilbert also destroyed crops, buildings, houses and roads and even turned small aircraft into shambles.

 35,000 people were left homeless and 83 ships sank when Gilbert struck the Yucatán Peninsula
35,000 people were left homeless and 83 ships sank when Gilbert struck the Yucatán Peninsula
. 60,000 homes were destroyed, and damage was estimated at between $1 and 2 billion (1989 USD
). In the Cancún region, a further loss of $87 million (1989 USD
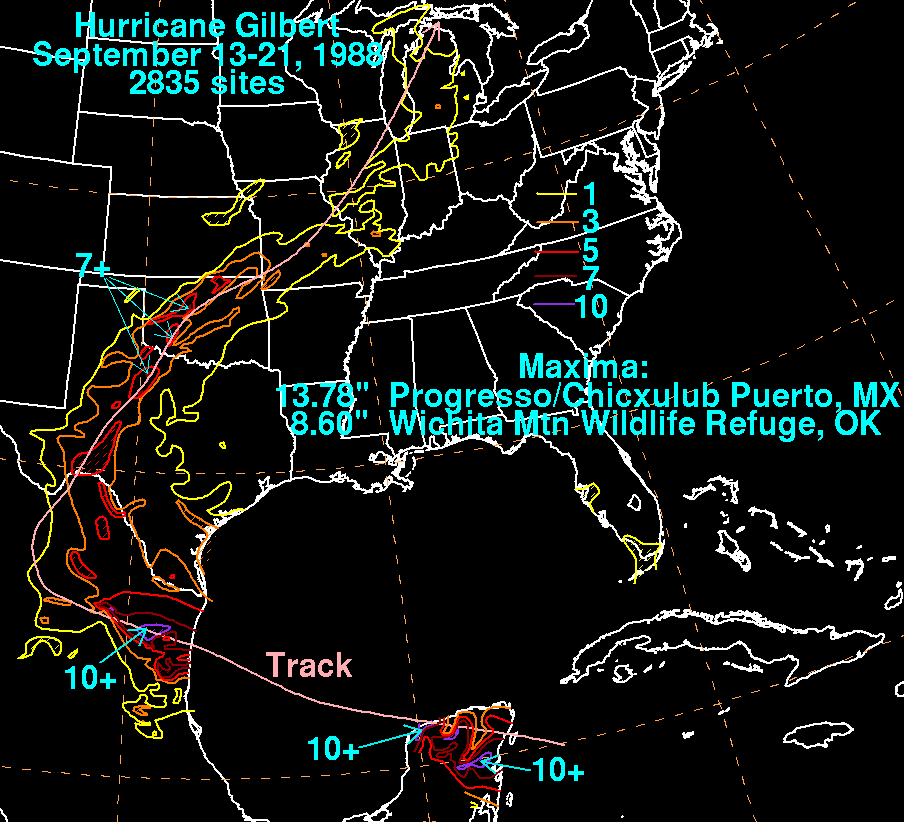
) due to a decline in tourism was estimated for the months October, November and December in 1988. Rainfall in the Yucatán Peninsula
peaked at 13.78 inches in Progreso, Yucatán
.
In northeastern Mexico, heavy rains in and around Monterrey
caused tremendous flooding. More than 100 people died when five buses carrying evacuees were overturned in the raging floodwaters. Rainfall in northeastern Mexico peaked at over 10 inches (254 mm) in localized areas of inland Tamaulipas
.
Oklahoma
recorded the highest measurement of rainfall in the United States, 8.6 inches, in Wichita Mountain Wildlife Refuge
. Isolated locations in Texas and Oklahoma reported over 7 inches (177.8 mm), while moderate rainfall of up to 3 inches (76.2 mm) fell in central Michigan
.
In Quintana Roo
, the Gilbert caused defoliation in the jungle. The debris eventually fueled a fire that started in 1989, which ultimately burned 460 sq mi (1,191.4 km²).
in the 1994 Atlantic hurricane season
.
Cape Verde-type hurricane
A Cape Verde-type hurricane is an Atlantic hurricane that develops near the Cape Verde islands, off the west coast of Africa. The average hurricane season has about two Cape Verde-type hurricanes, which are usually the largest and most intense storms of the season because they often have plenty of...
that formed during the 1988 Atlantic hurricane season
1988 Atlantic hurricane season
The 1988 Atlantic hurricane season was a moderately active season that proved costly and deadly, with 15 tropical cyclones directly affecting land. The season officially began on June 1, 1988, and lasted until November 30, 1988, although activity began on May 30 when a tropical...
and created widespread destruction in the Caribbean Sea
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean located in the tropics of the Western hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico and Central America to the west and southwest, to the north by the Greater Antilles, and to the east by the Lesser Antilles....
and the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
. It is the second most intense hurricane
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
ever observed in the Atlantic basin
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
behind only Hurricane Wilma
Hurricane Wilma
Hurricane Wilma was the most intense tropical cyclone ever recorded in the Atlantic basin. Wilma was the twenty-second storm , thirteenth hurricane, sixth major hurricane, and fourth Category 5 hurricane of the record-breaking 2005 season...
of the very active 2005 Atlantic hurricane season
2005 Atlantic hurricane season
The 2005 Atlantic hurricane season was the most active Atlantic hurricane season in recorded history, repeatedly shattering numerous records. The impact of the season was widespread and ruinous with an estimated 3,913 deaths and record damage of about $159.2 billion...
. Gilbert was also one of the largest tropical cyclones ever observed in the Atlantic basin. At one point, its tropical storm-force winds measured 588 mi (946.3 km) in diameter. In addition, Gilbert was the most intense tropical cyclone to strike Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
, slightly ahead of Hurricane Dean
Hurricane Dean
The name Dean was used for five tropical cyclones in the Northern Atlantic Ocean:*1983's Tropical Storm Dean, which struck the coast of Virginia, causing minor erosion and flooding...
in 2007
2007 Atlantic hurricane season
The 2007 Atlantic hurricane season was an active Atlantic hurricane season that produced 17 tropical cyclones, 15 tropical storms, six hurricanes, and two major hurricanes. It officially started on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates which conventionally delimit the...
.
The seventh named storm and third hurricane of the 1988 Atlantic hurricane season
Atlantic hurricane season
The Atlantic hurricane season is the period in a year when hurricanes usually form in the Atlantic Ocean. Tropical cyclones in the North Atlantic are called hurricanes, tropical storms, or tropical depressions. In addition, there have been several storms over the years that have not been fully...
, Gilbert developed from a tropical wave
Tropical wave
Tropical waves, easterly waves, or tropical easterly waves, also known as African easterly waves in the Atlantic region, are a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which move from east to west across the tropics causing areas of...
on September 8 while 400 mi (640 km) east of Barbados
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles. It is in length and as much as in width, amounting to . It is situated in the western area of the North Atlantic and 100 kilometres east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea; therein, it is about east of the islands of Saint...
. After it intensified into a tropical storm on September 9, Gilbert steadily strengthened as it tracked west-northwestward into the Caribbean Sea, and became a hurricane on the following day. Gilbert quickly intensified
Rapid deepening
Rapid deepening, also known as rapid intensification, is a meteorological condition that occurs when the minimum sea-level atmospheric pressure of a tropical cyclone decreases drastically in a short period of time. The National Weather Service describes rapid deepening as a decrease of...
into a Category 3 hurricane on September 11, and made landfall on the island of Jamaica on September 12. Rapid intensification occurred after Gilbert crossed Jamaica, and the storm became a Category 5 hurricane late on September 13. Gilbert weakened slightly, and made landfall on the Yucatan Peninsula
Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula, in southeastern Mexico, separates the Caribbean Sea from the Gulf of Mexico, with the northern coastline on the Yucatán Channel...
later that day while still at Category 5 hurricane. Gilbert significantly weakened over the Yucatan Peninsula, and was only a Category 2 hurricane when it emerged into the Gulf of Mexico on September 15. Re-intensification occurred gradually as Gilbert tracked across the Gulf of Mexico, and the storm was a Category 4 hurricane when it made landfall in mainland Mexico on September 16. Gilbert weakened after landfall, and eventually dissipated on September 19 over the Midwest
Gilbert wreaked havoc in the Caribbean and the Gulf of Mexico for nearly nine days. In total, it killed 433 people and caused about $7.1 billion (1988 USD, $ USD) in damages over the course of its path. As a result of the effects, the World Meteorological Organization
World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
retired the name Gilbert in the spring of 1989, and was replaced with Gordon.
Meteorological history
On September 3, 1988, a tropical wave emerged off the African Coast. Over the next several days, a low-pressure area slowly developed from this wave, going on to develop an organized circulation center on September 8. Early on September 9, the storm was designated Tropical Depression Twelve while 400 mi (640 km) east of Barbados. It quickly strengthened into Tropical Storm Gilbert that afternoon, becoming the seventh named storm of the season while crossing the Lesser AntillesLesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles are a long, partly volcanic island arc in the Western Hemisphere. Most of its islands form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea with the Atlantic Ocean, with the remainder located in the southern Caribbean just north of South America...
.
With no inhibiting factors to strengthening, Gilbert quickly became a hurricane late on September 10 and then a major hurricane on September 11. It moved consistently west-northwest influenced by a strong high pressure system to its north. This movement led to the hurricane's first landfall in Jamaica. The eye passed completely over Jamaica on September 12 with 125 mph (205 km/h) winds and a central pressure of 960 mbar (28.35 inHg), making it a Category 3 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale
Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale
The Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale , or the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale , classifies hurricanes — Western Hemisphere tropical cyclones that exceed the intensities of tropical depressions and tropical storms — into five categories distinguished by the intensities of their sustained winds...
.

Cayman Islands
The Cayman Islands is a British Overseas Territory and overseas territory of the European Union located in the western Caribbean Sea. The territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac, and Little Cayman, located south of Cuba and northwest of Jamaica...
a reporting station on Grand Cayman
Grand Cayman
Grand Cayman is the largest of the three Cayman Islands and the location of the nation's capital, George Town. In relation to the other two Cayman Islands, it is approximately 75 miles southwest of Little Cayman and 90 miles southwest of Cayman Brac.-Geography:Grand Cayman encompasses 76% of...
recorded a wind gust of 156 mph (252 km/h) while the storm passed just to the southeast on September 13. Extreme intensification continued until Gilbert reached a minimum pressure of 888 mbar (26.22 inHg) with sustained flight-level winds of 185 mph (295 km/h), having intensified by 72 mbar in a space of 24 hours. This pressure was the lowest ever observed in the Western hemisphere
Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere or western hemisphere is mainly used as a geographical term for the half of the Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian and east of the Antimeridian , the other half being called the Eastern Hemisphere.In this sense, the western hemisphere consists of the western portions...
and made Gilbert the most intense Atlantic hurricane on record, until it was surpassed by Hurricane Wilma in the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season.
Gilbert made landfall for a second time on the island of Cozumel
Cozumel
Cozumel is an island in the Caribbean Sea off the eastern coast of Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula, opposite Playa del Carmen, and close to the Yucatan Channel. Cozumel is one of the ten municipalities of the state of Quintana Roo...
and then Mexico's Yucatán Peninsula on September 14 as a Category 5 hurricane, making it the first Category 5 to make landfall in the Atlantic basin since Hurricane David
Hurricane David
Hurricane David was the fourth named tropical cyclone, second hurricane, and first major hurricane of the 1979 Atlantic hurricane season. A Category 5 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale, David was among the deadliest hurricanes in the latter half of the 20th century, killing...
hit Hispanola in 1979
1979 Atlantic hurricane season
The 1979 Atlantic hurricane season was the first in which the Atlantic hurricane naming list included both male and female names. It officially began on June 1 and lasted until November 30, and there was tropical cyclone activity in every month. The dates conventionally delimit the period of each...
; the minimum pressure at landfall in Cozumel was estimated to be 900 mbar (26.6 inHg). The storm weakened quickly while crossing land before emerging into the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
as a Category 2 hurricane. Gilbert restrengthened rapidly, however, and made landfall for a final time as a Category 3 hurricane near La Pesca, Tamaulipas
Tamaulipas
Tamaulipas officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Tamaulipas is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 43 municipalities and its capital city is Ciudad Victoria. The capital city was named after Guadalupe Victoria, the...
, on September 16.
On September 17 Gilbert brushed the inland city of Monterrey
Monterrey
Monterrey , is the capital city of the northeastern state of Nuevo León in the country of Mexico. The city is anchor to the third-largest metropolitan area in Mexico and is ranked as the ninth-largest city in the nation. Monterrey serves as a commercial center in the north of the country and is the...
, Nuevo León
Nuevo León
Nuevo León It is located in Northeastern Mexico. It is bordered by the states of Tamaulipas to the north and east, San Luis Potosí to the south, and Coahuila to the west. To the north, Nuevo León has a 15 kilometer stretch of the U.S.-Mexico border adjacent to the U.S...
before taking a sharp turn to the north. The storm spawned 29 tornadoes in Texas
Texas
Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
on September 18 before moving across Oklahoma and being absorbed by a low-pressure system over Missouri
Missouri
Missouri is a US state located in the Midwestern United States, bordered by Iowa, Illinois, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Oklahoma, Kansas and Nebraska. With a 2010 population of 5,988,927, Missouri is the 18th most populous state in the nation and the fifth most populous in the Midwest. It...
on September 19.
Impact
| Country | Deaths | Damage |
|---|---|---|
| Mexico | 240 | $2 billion |
| Jamaica Jamaica Jamaica is an island nation of the Greater Antilles, in length, up to in width and 10,990 square kilometres in area. It is situated in the Caribbean Sea, about south of Cuba, and west of Hispaniola, the island harbouring the nation-states Haiti and the Dominican Republic... |
49 | $4 billion |
| Haiti Haiti Haiti , officially the Republic of Haiti , is a Caribbean country. It occupies the western, smaller portion of the island of Hispaniola, in the Greater Antillean archipelago, which it shares with the Dominican Republic. Ayiti was the indigenous Taíno or Amerindian name for the island... |
54 | $91.2 million |
| St. Lucia | 45 | $1 billion |
| Guatemala Guatemala Guatemala is a country in Central America bordered by Mexico to the north and west, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, Belize to the northeast, the Caribbean to the east, and Honduras and El Salvador to the southeast... |
16 | Unknown |
| Honduras Honduras Honduras is a republic in Central America. It was previously known as Spanish Honduras to differentiate it from British Honduras, which became the modern-day state of Belize... |
12 | Unknown |
| Dominican Republic Dominican Republic The Dominican Republic is a nation on the island of La Hispaniola, part of the Greater Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean region. The western third of the island is occupied by the nation of Haiti, making Hispaniola one of two Caribbean islands that are shared by two countries... |
5 | Unknown |
| Venezuela Venezuela Venezuela , officially called the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela , is a tropical country on the northern coast of South America. It borders Colombia to the west, Guyana to the east, and Brazil to the south... |
5 | Unknown |
| United States | 3 | $80 million |
| Costa Rica Costa Rica Costa Rica , officially the Republic of Costa Rica is a multilingual, multiethnic and multicultural country in Central America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Caribbean Sea to the east.... |
2 | Unknown |
| Nicaragua Nicaragua Nicaragua is the largest country in the Central American American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south. The country is situated between 11 and 14 degrees north of the Equator in the Northern Hemisphere, which places it entirely within the tropics. The Pacific Ocean... |
2 | Unknown |
| Total | 433 | $7.1 billion |
Gilbert claimed 433 lives, mostly in Mexico. Exact monetary damage figures are not available, but the total for all areas affected by Gilbert is estimated to be near $7.1 billion (1988 USD
United States dollar
The United States dollar , also referred to as the American dollar, is the official currency of the United States of America. It is divided into 100 smaller units called cents or pennies....
). A preliminary report assessed Gilbert as the costliest Atlantic hurricane of all time with an initial damage total of over $10 billion (USD), though it was not later confirmed.
Venezuela
Outflow bands from Gilbert produced flash floods in northern Venezuela, which killed five people.Jamaica
Hurricane Gilbert produced a 19 ft (5.8 m) storm surge and brought over 700 mm (27 inches) of rain in the mountainous areas of Jamaica, causing inland flash flooding. About 45 people died. Gilbert was the most severe hurricane to hit JamaicaJamaica
Jamaica is an island nation of the Greater Antilles, in length, up to in width and 10,990 square kilometres in area. It is situated in the Caribbean Sea, about south of Cuba, and west of Hispaniola, the island harbouring the nation-states Haiti and the Dominican Republic...
since Hurricane Charlie
Hurricane Charlie (1951)
Hurricane Charlie was the deadliest tropical cyclone of the 1951 Atlantic hurricane season. The third named storm, second hurricane, and second major hurricane of the season, it developed from a tropical wave east of the Lesser Antilles. It moved briskly west-northwest, passing between the islands...
in 1951. The storm left $4 billion (1988 USD) in damage. Gilbert also destroyed crops, buildings, houses and roads and even turned small aircraft into shambles.
Cayman Islands
Gilbert passed 30 miles (48.3 km) to the south of the Cayman Islands, with a gust of 157 mi/h reported early on September 13. However, the islands largely escaped the hurricane's wrath due to Gilbert's rather quick forward motion, and the deepness of the water surrounding the islands limited the height of the storm surge to 5 ft (1.5 m) Nevertheless, there was very severe damage to crops, trees and pastures, and a number of private homes were ruined.Mexico


Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula, in southeastern Mexico, separates the Caribbean Sea from the Gulf of Mexico, with the northern coastline on the Yucatán Channel...
. 60,000 homes were destroyed, and damage was estimated at between $1 and 2 billion (1989 USD
United States dollar
The United States dollar , also referred to as the American dollar, is the official currency of the United States of America. It is divided into 100 smaller units called cents or pennies....
). In the Cancún region, a further loss of $87 million (1989 USD
United States dollar
The United States dollar , also referred to as the American dollar, is the official currency of the United States of America. It is divided into 100 smaller units called cents or pennies....
) due to a decline in tourism was estimated for the months October, November and December in 1988. Rainfall in the Yucatán Peninsula
Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula, in southeastern Mexico, separates the Caribbean Sea from the Gulf of Mexico, with the northern coastline on the Yucatán Channel...
peaked at 13.78 inches in Progreso, Yucatán
Progreso, Yucatán
Progreso is a port city in the Mexican state of Yucatán, located on the Gulf of Mexico in the north-west of the state some 30 minutes north of state capital Mérida by highway. As of the Mexican census of 2005, Progreso had an official population of 35,519 inhabitants, the fifth-largest community...
.
In northeastern Mexico, heavy rains in and around Monterrey
Monterrey
Monterrey , is the capital city of the northeastern state of Nuevo León in the country of Mexico. The city is anchor to the third-largest metropolitan area in Mexico and is ranked as the ninth-largest city in the nation. Monterrey serves as a commercial center in the north of the country and is the...
caused tremendous flooding. More than 100 people died when five buses carrying evacuees were overturned in the raging floodwaters. Rainfall in northeastern Mexico peaked at over 10 inches (254 mm) in localized areas of inland Tamaulipas
Tamaulipas
Tamaulipas officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Tamaulipas is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 43 municipalities and its capital city is Ciudad Victoria. The capital city was named after Guadalupe Victoria, the...
.
United States
Despite concerns that Texas might suffer a direct hit, there was only minor damage reported in southern Texas from Gilbert's landfall, 60 miles (96.6 km) to the south. Winds gusted to hurricane force in a few places, but the main impact felt in the state was beach erosion from a 3-5-foot storm surge, and tornadoes, which mainly affected the San Antonio area.Oklahoma
Oklahoma
Oklahoma is a state located in the South Central region of the United States of America. With an estimated 3,751,351 residents as of the 2010 census and a land area of 68,667 square miles , Oklahoma is the 28th most populous and 20th-largest state...
recorded the highest measurement of rainfall in the United States, 8.6 inches, in Wichita Mountain Wildlife Refuge
Wichita Mountain Wildlife Refuge
Wichita Mountains Wildlife Refuge, located in southwestern Oklahoma near Lawton, has protected unique wildlife habitats since 1901 and is the oldest managed wildlife facility in the United States Fish and Wildlife Service system. Measuring about , the Refuge hosts a great diversity of species: 806...
. Isolated locations in Texas and Oklahoma reported over 7 inches (177.8 mm), while moderate rainfall of up to 3 inches (76.2 mm) fell in central Michigan
Michigan
Michigan is a U.S. state located in the Great Lakes Region of the United States of America. The name Michigan is the French form of the Ojibwa word mishigamaa, meaning "large water" or "large lake"....
.
Aftermath
Hurricane Gilbert was the most destructive storm in the history of Jamaica.In Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Quintana Roo is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 10 municipalities and its capital city is Chetumal....
, the Gilbert caused defoliation in the jungle. The debris eventually fueled a fire that started in 1989, which ultimately burned 460 sq mi (1,191.4 km²).
Retirement
Due to its extreme intensity, extensive death toll and path of destruction, the name Gilbert was retired in the spring of 1989, and will never again be used for an Atlantic hurricane. It was replaced by GordonHurricane Gordon (1994)
Hurricane Gordon was a long-lived and erratic late-season hurricane of the 1994 Atlantic hurricane season. The twelfth and final tropical cyclone of the season, Gordon formed in the southwestern Caribbean on November 8 after two tropical waves enhanced convection around in area of disturbed...
in the 1994 Atlantic hurricane season
1994 Atlantic hurricane season
The 1994 Atlantic hurricane seasonofficially began June 1, 1994, and officially ended November 30, 1994. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin....
.
See also
- List of Atlantic hurricanes
- List of Category 5 Atlantic hurricanes

