
Hydroxyquinone
Encyclopedia
Hydroxyquinone often refers to a hydroxybenzoquinone, any organic compound
with formula which can be viewed as a derivative of a benzoquinone through replacement of one hydrogen
atom (H) by an hydroxyl
group (-OH). When unqualified, the terms usually mean specifically the compound 2-hydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone, derived from 1,4-benzoquinone
or para-benzoquinone (which often called just "quinone").
More generally, the term may refer to any derivative of any quinone
(such as 1,2-benzoquinone
, 1,4-naphthoquinone or 9,10-anthraquinone
), where any number n of hydrogens have been replaced by n hydroxyls. In this case the number n is indicated by a multiplier prefix
(mono-, di-, tri-, etc.), and the parent quinone's name is used instead of just "quinone" — as in tetrahydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone
.
The hydroxyquinones (in the particular or the general sense) include many biologically and industrially important compounds, and are a building block of many medicinal drugs.
Hydroxyquinones with hydroxyls adjacent to the ketone
groups often exhibit intramolecular hydrogen bonding, which affects their redox properties and their biochemical
properties.
The term "hydroxyquinone" should not be confused with hydroquinone
, the common name of benzene-1,4-diol.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with formula which can be viewed as a derivative of a benzoquinone through replacement of one hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atom (H) by an hydroxyl
Hydroxyl
A hydroxyl is a chemical group containing an oxygen atom covalently bonded with a hydrogen atom. In inorganic chemistry, the hydroxyl group is known as the hydroxide ion, and scientists and reference works generally use these different terms though they refer to the same chemical structure in...
group (-OH). When unqualified, the terms usually mean specifically the compound 2-hydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone, derived from 1,4-benzoquinone
1,4-Benzoquinone
1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as para-quinone, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H4O2. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odor, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic. Impure samples are often dark-colored due to the presence...
or para-benzoquinone (which often called just "quinone").
| 2-Hydroxy- 1,4-benzoquinone (Hydroxyquinone) |
More generally, the term may refer to any derivative of any quinone
Quinone
A quinone is a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds [such as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds," resulting in "a fully conjugated cyclic dione structure."...
(such as 1,2-benzoquinone
1,2-Benzoquinone
1,2-Benzoquinone, also called ortho-benzoquinone or cyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,2-dione, is a ketone, with formula C6H4O2. It is one of the two isomers of quinone, the other being 1,4-benzoquinone....
, 1,4-naphthoquinone or 9,10-anthraquinone
Anthraquinone
Anthraquinone, also called anthracenedione or dioxoanthracene is an aromatic organic compound with formula . Several isomers are possible, each of which can be viewed as a quinone derivative...
), where any number n of hydrogens have been replaced by n hydroxyls. In this case the number n is indicated by a multiplier prefix
Prefix
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the root of a word. Particularly in the study of languages,a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the words to which it is affixed.Examples of prefixes:...
(mono-, di-, tri-, etc.), and the parent quinone's name is used instead of just "quinone" — as in tetrahydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone
Tetrahydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone
Tetrahydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone, also called tetrahydroxy-p-benzoquinone, tetrahydoxybenzoquinone, or tetrahydroxyquinone , is an organic compound with formula C6O24...
.
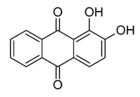 | ||
| Tetrahydroxy- 1,4-benzoquinone | 5-Hydroxy- 1,4-naphthoquinone (Juglone) | 1,2-Dihydroxy- 9,10-anthraquinone (Alizarin) |
The hydroxyquinones (in the particular or the general sense) include many biologically and industrially important compounds, and are a building block of many medicinal drugs.
Hydroxyquinones with hydroxyls adjacent to the ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
groups often exhibit intramolecular hydrogen bonding, which affects their redox properties and their biochemical
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
properties.
The term "hydroxyquinone" should not be confused with hydroquinone
Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone, also benzene-1,4-diol or quinol, is an aromatic organic compound that is a type of phenol, having the chemical formula C6H42. Its chemical structure, shown in the table at right, has two hydroxyl groups bonded to a benzene ring in a para position. It is a white granular solid...
, the common name of benzene-1,4-diol.

