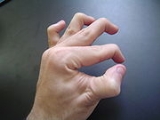
Hypermobility
Encyclopedia
Hypermobility describes joint
s that stretch farther than is normal. For example, some hypermobile people can bend their thumbs backwards to their wrists, bend their knee joints backwards, put their leg behind the head or other contortionist performances. It can affect a single joint
or multiple joints throughout the body.
These abnormalities cause abnormal distribution of wear and tear on joints, meaning that the joints wear out and can lead to osteoarthritis.
The condition tends to run in families, suggesting that there may be a genetic basis for at least some forms of hypermobility. The term double jointed is often used to describe hypermobility; however, the name is a misnomer
and should not to be taken literally, as an individual with hypermobility in a joint does not actually have two separate joints where others would have just one.
The picture of Hypermobile knee can be viewed by clicking on this link : https://fbcdn-sphotos-a.akamaihd.net/hphotos-ak-ash4/223251_2073393431673_1150026333_32606870_6850469_n.jpg
Some people have hypermobility with no other symptoms or medical conditions. However, people with hypermobility syndrome may experience many difficulties. For example, their joints may be easily injured, be more prone to complete dislocation due to the weakly stabilized joint and they may develop problems from muscle fatigue (as muscles must work harder to compensate for the excessive weakness in the ligaments that support the joints). Hypermobility syndrome can also lead to chronic pain.
Hypermobility may also be symptomatic of a serious medical condition, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
, Marfan syndrome
, rheumatoid arthritis
, osteogenesis imperfecta
, lupus
, polio
, Down syndrome
, morquio syndrome
, cleidocranial dysostosis
or myotonia congenita
.
In addition, hypermobility has been associated with chronic fatigue syndrome
and fibromyalgia
. During pregnancy certain hormones alter the physiology of ligaments making them able to stretch to accommodate the birthing process. For some women with hypermobility pregnancy-related pelvic girdle
pain can be debilitating due to these two converging factors, and prohibits her from standing up or walking. Use of a bedpan and wheelchair may be necessary, or even permanent in some cases due to hip stretching.
Symptoms of hypermobility include a dull but intense pain around the knee and ankle joints and the soles of the feet. The condition affecting these parts can be alleviated by using insoles in the footwear that have been specially made for the individual after assessment by an orthopaedic surgeon and orthotist.
and arthralgia
. It is relatively common among children and affects more females than males.
These four factors affect different people to varying degrees.
Generalized hypermobility is a common feature in all these hereditary connective tissue disorders and many features overlap, but often distinguishing features are present that enable differentiating these disorders.
The Beighton score is measured by adding 1 point for each of the following:
or hydrotherapy
can reduce symptoms of hypermobility, because strong muscles help to stabilise joints. These treatments can also help by stretching tight, overused muscles and ensuring the person uses joints within the ideal ranges of motion, avoiding hyperextension or hyperflexion. Low-impact exercise such as Pilates
or T'ai chi is usually recommended for hypermobile people as it is less likely to cause injury than high-impact exercise or contact sports.
Moist hot packs can relieve the pain of aching joints and muscles. For some patients, ice packs also help to relieve pain.
drugs (though these have been linked with an increase in pain and joint instability for some sufferers), and tricyclic antidepressants. Some people with hypermobility may benefit from other medications such as steroid
injections or gabapentin
, a drug originally used for treating epilepsy
. Europe is far ahead of the United States in terms of HMS recognition and its knowledge of how to treat it. Tramadol
, a non-narcotic yet opioid
pain reliever that is nearly as effective as narcotics, has been used in England to treat HMS joint pain, and it is available either by prescription from a doctor in the United States or from Mexico
. Benzodiazapines are also used in HMS sufferers who experience painful muscles spasms around loose joints.
Joint
A joint is the location at which two or more bones make contact. They are constructed to allow movement and provide mechanical support, and are classified structurally and functionally.-Classification:...
s that stretch farther than is normal. For example, some hypermobile people can bend their thumbs backwards to their wrists, bend their knee joints backwards, put their leg behind the head or other contortionist performances. It can affect a single joint
Joint
A joint is the location at which two or more bones make contact. They are constructed to allow movement and provide mechanical support, and are classified structurally and functionally.-Classification:...
or multiple joints throughout the body.
Causes
Hypermobility generally results from one or more of the following:- Misaligned joints
- Abnormally shaped ends of one or more boneBoneBones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
s at a jointJointA joint is the location at which two or more bones make contact. They are constructed to allow movement and provide mechanical support, and are classified structurally and functionally.-Classification:... - A Type 1 collagenCollagenCollagen is a group of naturally occurring proteins found in animals, especially in the flesh and connective tissues of mammals. It is the main component of connective tissue, and is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up about 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content...
or other connective tissueConnective tissue"Connective tissue" is a fibrous tissue. It is one of the four traditional classes of tissues . Connective Tissue is found throughout the body.In fact the whole framework of the skeleton and the different specialized connective tissues from the crown of the head to the toes determine the form of...
defect (found in Ehlers-Danlos syndromeEhlers-Danlos syndromeEhlers–Danlos syndrome is a group of inherited connective tissue disorders, caused by a defect in the synthesis of collagen . The collagen in connective tissue helps tissues to resist deformation...
, Marfan syndromeMarfan syndromeMarfan syndrome is a genetic disorder of the connective tissue. People with Marfan's tend to be unusually tall, with long limbs and long, thin fingers....
) resulting in weakened ligaments/ligamentous laxity, muscleMuscleMuscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
s and tendons. This same defect also results in weakened bones, which may result in osteoporosisOsteoporosisOsteoporosis is a disease of bones that leads to an increased risk of fracture. In osteoporosis the bone mineral density is reduced, bone microarchitecture is deteriorating, and the amount and variety of proteins in bone is altered...
and fractures - Abnormal jointJointA joint is the location at which two or more bones make contact. They are constructed to allow movement and provide mechanical support, and are classified structurally and functionally.-Classification:...
proprioceptionProprioceptionProprioception , from Latin proprius, meaning "one's own" and perception, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement...
(an impaired ability to determine where in space parts of the body are, and how stretched a jointJointA joint is the location at which two or more bones make contact. They are constructed to allow movement and provide mechanical support, and are classified structurally and functionally.-Classification:...
is)
These abnormalities cause abnormal distribution of wear and tear on joints, meaning that the joints wear out and can lead to osteoarthritis.
The condition tends to run in families, suggesting that there may be a genetic basis for at least some forms of hypermobility. The term double jointed is often used to describe hypermobility; however, the name is a misnomer
Misnomer
A misnomer is a term which suggests an interpretation that is known to be untrue. Such incorrect terms sometimes derive their names because of the form, action, or origin of the subject becoming named popularly or widely referenced—long before their true natures were known.- Sources of misnomers...
and should not to be taken literally, as an individual with hypermobility in a joint does not actually have two separate joints where others would have just one.
The picture of Hypermobile knee can be viewed by clicking on this link : https://fbcdn-sphotos-a.akamaihd.net/hphotos-ak-ash4/223251_2073393431673_1150026333_32606870_6850469_n.jpg
Some people have hypermobility with no other symptoms or medical conditions. However, people with hypermobility syndrome may experience many difficulties. For example, their joints may be easily injured, be more prone to complete dislocation due to the weakly stabilized joint and they may develop problems from muscle fatigue (as muscles must work harder to compensate for the excessive weakness in the ligaments that support the joints). Hypermobility syndrome can also lead to chronic pain.
Hypermobility may also be symptomatic of a serious medical condition, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndrome is a group of inherited connective tissue disorders, caused by a defect in the synthesis of collagen . The collagen in connective tissue helps tissues to resist deformation...
, Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome is a genetic disorder of the connective tissue. People with Marfan's tend to be unusually tall, with long limbs and long, thin fingers....
, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks synovial joints. The process produces an inflammatory response of the synovium secondary to hyperplasia of synovial cells, excess synovial fluid, and the development...
, osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta is a genetic bone disorder. People with OI are born with defective connective tissue, or without the ability to make it, usually because of a deficiency of Type-I collagen...
, lupus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus , often abbreviated to SLE or lupus, is a systemic autoimmune disease that can affect any part of the body. As occurs in other autoimmune diseases, the immune system attacks the body's cells and tissue, resulting in inflammation and tissue damage...
, polio
Poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis, often called polio or infantile paralysis, is an acute viral infectious disease spread from person to person, primarily via the fecal-oral route...
, Down syndrome
Down syndrome
Down syndrome, or Down's syndrome, trisomy 21, is a chromosomal condition caused by the presence of all or part of an extra 21st chromosome. It is named after John Langdon Down, the British physician who described the syndrome in 1866. The condition was clinically described earlier in the 19th...
, morquio syndrome
Morquio syndrome
Morquio's syndrome is an autosomal recessive mucopolysaccharide storage disease , usually inherited. It is a rare type of birth defect with serious consequences...
, cleidocranial dysostosis
Cleidocranial dysostosis
Cleidocranial dysostosis, also called Cleidocranial dysplasia, is a hereditary congenital disorder due to haploinsufficiency caused by mutations in the CBFA1 gene also called Runx2, located on the short arm of chromosome 6....
or myotonia congenita
Myotonia congenita
Congenital myotonia is a genetic, neuromuscular channelopathy that affects skeletal muscles . It is congenital, meaning that it is present from birth. Amongst other problems, it causes delayed relaxation of the muscles and rigidity...
.
In addition, hypermobility has been associated with chronic fatigue syndrome
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Chronic fatigue syndrome is the most common name used to designate a significantly debilitating medical disorder or group of disorders generally defined by persistent fatigue accompanied by other specific symptoms for a minimum of six months, not due to ongoing exertion, not substantially...
and fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a medical disorder characterized by chronic widespread pain and allodynia, a heightened and painful response to pressure. It is an example of a diagnosis of exclusion...
. During pregnancy certain hormones alter the physiology of ligaments making them able to stretch to accommodate the birthing process. For some women with hypermobility pregnancy-related pelvic girdle
Pelvic girdle pain
Pregnancy related Pelvic Girdle Pain causes pain, instability and limitation of mobility and functioning in any of the three pelvic joints...
pain can be debilitating due to these two converging factors, and prohibits her from standing up or walking. Use of a bedpan and wheelchair may be necessary, or even permanent in some cases due to hip stretching.
Symptoms of hypermobility include a dull but intense pain around the knee and ankle joints and the soles of the feet. The condition affecting these parts can be alleviated by using insoles in the footwear that have been specially made for the individual after assessment by an orthopaedic surgeon and orthotist.
Anxiety and joint hypermobility
In 1998, a study was done concerning the link between panic disorder with joint hypermobility. The prevalence of panic disorder among patients with joint hypermobility syndrome was 67.7% compared to the control psychiatric group (10.1%). Women and subjects who were younger were found to be over 20 times more likely to have the hypermobile joints than their counterparts in the control group. In the study, there was also a higher prevalence for mitral valve prolapse (8%). The study does not determine whether hypermobility is associated in any way with psychiatric dysfunction or dysautonomia; many factors could explain the relation, and hypermobility's unwelcome gift of chronic pain may very well cause many people anxiety or depression.Hypermobility syndrome
Hypermobility syndrome is generally considered to comprise hypermobility together with other symptoms, such as myalgiaMyalgia
Myalgia means "muscle pain" and is a symptom of many diseases and disorders. The most common causes are the overuse or over-stretching of a muscle or group of muscles. Myalgia without a traumatic history is often due to viral infections...
and arthralgia
Arthralgia
Arthralgia literally means joint pain; it is a symptom of injury, infection, illnesses or an allergic reaction to medication....
. It is relatively common among children and affects more females than males.
Causes
Current thinking suggests that there are four factors:These four factors affect different people to varying degrees.
- The shape of the ends of the bones: Some joints normally have a large range of movement, like the shoulder and hip. Both these joints are ball in sockets. If a shallow rather than a deep socket is inherited, a relatively large range of movement will be possible at the affected joints. If the hip socket is particularly shallow, then the hip may dislocate easily.
- Weak or stretched ligaments caused by protein or hormone problems: ligaments are made up of several types of protein fibre. These proteins include elastin, which gives elasticity, which may be altered in some people. Also, the female sex hormones alter the collagen proteins. Women are generally more supple just before a period, and even more so in the latter stages of pregnancy, because of the effect of a hormone called relaxin. This hormone allows the pelvis to expand so the head of the baby can pass through. Different races have differences in their joint mobility, which may reflect differences in the structure of the collagen proteins. People from the Indian sub-continent, for example, often have much more supple hands than Europeans.
- The tone of the muscles: The tone (or stiffness) of the muscles is controlled by your nervous system, and influences the range of movement in the joints. Some people use special techniques to change their muscle tone and increase their flexibility. Yoga, for example, can help to relax the muscles and make the joints more supple. Gymnasts and athletes can sometimes acquire hypermobility in at least some of their joints through the exercises they do in training.
- The sense of joint movement (proprioception): if it is difficult to detect the exact position of the joints with closed eyes, then it is possible to develop hypermobile joints because of over-stretching.
Symptoms
People with hypermobility syndrome may develop other conditions caused by their unstable joints. These conditions include:- Joint instability causing frequent sprains, tendinitis, or bursitisBursitisBursitis is the inflammation of one or more bursae of synovial fluid in the body. The bursae rest at the points where internal functionaries, such as muscles and tendons, slide across bone. Healthy bursae create a smooth, almost frictionless functional gliding surface making normal movement painless...
when doing activities that would not affect the normal individual - Early-onset osteoarthritisOsteoarthritisOsteoarthritis also known as degenerative arthritis or degenerative joint disease, is a group of mechanical abnormalities involving degradation of joints, including articular cartilage and subchondral bone. Symptoms may include joint pain, tenderness, stiffness, locking, and sometimes an effusion...
- SubluxationSubluxationA subluxation may have different meanings, depending on the medical specialty involved. It implies the presence of an incomplete or partial dislocation of a joint or organ. The World Health Organization defines both the medical subluxation and the chiropractic subluxation...
s or dislocations, especially in the shoulderShoulderThe human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle , the scapula , and the humerus as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder make up the shoulder joints. The major joint of the shoulder is the glenohumeral joint, which... - KneeKneeThe knee joint joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two articulations: one between the fibula and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body and is very complicated. The knee is a mobile trocho-ginglymus , which permits flexion and extension as...
painPainPain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."... - Back painBack painBack pain is pain felt in the back that usually originates from the muscles, nerves, bones, joints or other structures in the spine.The pain can often be divided into neck pain, upper back pain, lower back pain or tailbone pain...
, prolapsed discs or spondylolisthesisSpondylolisthesisSpondylolisthesis describes the anterior or posterior displacement of a vertebra or the vertebral column in relation to the vertebrae below. It was first described in 1782 by Belgian obstetrician, Dr. Herbinaux. He reported a bony prominence anterior to the sacrum that obstructed the vagina of a... - JointJointA joint is the location at which two or more bones make contact. They are constructed to allow movement and provide mechanical support, and are classified structurally and functionally.-Classification:...
s that make clicking noisesCrepitusCrepitus is a medical term to describe the grating, crackling or popping sounds and sensations experienced under the skin and joints.-Causes:... - Susceptibility to whiplashWhiplash (medicine)Whiplash is a non-medical term describing a range of injuries to the neck caused by or related to a sudden distortion of the neck associated with extension. The term "whiplash" is a colloquialism...
- Temporomandibular Joint SyndromeTemporomandibular jointThe temporomandibular joint is the joint of the jaw and is frequently referred to as TMJ. There are two TMJs, one on either side, working in unison. The name is derived from the two bones which form the joint: the upper temporal bone which is part of the cranium , and the lower jaw bone called the...
also known as TMJ - Increased nerve compression disorders (e.g. carpal tunnel syndromeCarpal tunnel syndromeCarpal Tunnel Syndrome is an entrapment idiopathic median neuropathy, causing paresthesia, pain, and other symptoms in the distribution of the median nerve due to its compression at the wrist in the carpal tunnel. The pathophysiology is not completely understood but can be considered compression...
) - The ability of Finger Locking
- Do not respond well to normal doses of anaesthetic or pain medication
- "Growing pains" as described in children in late afternoon or night
Diagnosis
Joint hypermobility syndrome needs to be distinguished from other disorders that share many common features, such as Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, and osteogenesis imperfecta. In the last couple of years collaborations of experts in connective tissue disorders formally agreed that there was little distinction between Hypermobility Syndrome and Ehlers Danlos Syndrome and that they are in fact the same disorder. Information on this can be found in an article titled "The lack of clinical distinction between the hypermobility type of Ehlers–Danlos syndrome and the joint hypermobility syndrome (a.k.a. hypermobility syndrome)"Generalized hypermobility is a common feature in all these hereditary connective tissue disorders and many features overlap, but often distinguishing features are present that enable differentiating these disorders.
Brighton criteria
As of July 2000, hypermobility is diagnosed using the Brighton criteria. The Brighton criteria will not replace the Beighton score but instead will use the previous criteria in conjunction with other symptoms. HMS will be diagnosed in the presence of either two major criteria, one major and two minor criteria, or four minor criteria. The criteria are as follows:Major criteria
- A Beighton score of 4/9 or more (either current or historic)
- ArthralgiaArthralgiaArthralgia literally means joint pain; it is a symptom of injury, infection, illnesses or an allergic reaction to medication....
for more than three months in four or more joints
Minor criteria
- A Beighton score of 1, 2 or 3/9 (0, 1, 2 or 3 if aged 50+)
- Arthralgia (> 3 months) in one to three joints or back pain (> 3 months), spondylosis, spondylolysis/spondylolisthesis.
- Dislocation/subluxation in more than one joint, or in one joint on more than one occasion.
- Soft tissue rheumatismRheumatismRheumatism or rheumatic disorder is a non-specific term for medical problems affecting the joints and connective tissue. The study of, and therapeutic interventions in, such disorders is called rheumatology.-Terminology:...
. > 3 lesions (e.g. epicondylitis, tenosynovitisTenosynovitisTenosynovitis is the inflammation of the fluid-filled sheath that surrounds a tendon. Symptoms of tenosynovitis include pain, swelling and difficulty moving the particular joint where the inflammation occurs. When the condition causes the finger to "stick" in a flexed position, this is called...
, bursitis). - MarfanoidMarfanoidMarfanoid is a term used to describe a constellation of findings including long limbs, arachnodactyly and hyperlaxity.Associated conditions include:* Marfan syndrome...
habitus (tall, slim, span/height ratio >1.03, upper: lower segment ratio less than 0.89, arachnodactyly (positive Steinberg thumb / Walker wrist signs). - Abnormal skin: striae, hyperextensibility, thin skin, papyraceous scarring.
- Eye signs: drooping eyelids, myopiaMyopiaMyopia , "shortsightedness" ) is a refractive defect of the eye in which collimated light produces image focus in front of the retina under conditions of accommodation. In simpler terms, myopia is a condition of the eye where the light that comes in does not directly focus on the retina but in...
or antimongoloid slant (Palpebral slant) - Varicose veinsVaricose veinsVaricose veins are veins that have become enlarged and tortuous. The term commonly refers to the veins on the leg, although varicose veins can occur elsewhere. Veins have leaflet valves to prevent blood from flowing backwards . Leg muscles pump the veins to return blood to the heart, against the...
or herniaHerniaA hernia is the protrusion of an organ or the fascia of an organ through the wall of the cavity that normally contains it. A hiatal hernia occurs when the stomach protrudes into the mediastinum through the esophageal opening in the diaphragm....
or uterine/rectal prolapseRectal prolapseRectal prolapse normally describes a medical condition wherein the walls of the rectum protrude through the anus and hence become visible outside the body.-Types:There are three chief conditions which come under the title rectal prolapse:...
.
Beighton score
The Beighton score is an edited version of the Carter & Wilkinson scoring system which has been used for many years as an indicator of widespread hyper-mobility. However medical professionals varied in their interpretations of the results; some accepting as low as 1/9 and some 4/9 as a diagnosis of HMS. Therefore it was incorporated, with clearer guidelines, into the Brighton Criteria.The Beighton score is measured by adding 1 point for each of the following:
- Placing flat hands on the floor with straight legs
- Left knee bending backward
- Right knee bending backward
- Left elbow bending backward
- Right elbow bending backward
- Left thumb touching the forearm
- Right thumb touching the forearm
- Left little finger bending backward past 90 degrees
- Right little finger bending backward past 90 degrees
Physical therapy
It is important that the individual with hypermobility remain extremely fit - even more so than the average individual - to prevent recurrent injuries. Regular exercise and physical therapyPhysical therapy
Physical therapy , often abbreviated PT, is a health care profession. Physical therapy is concerned with identifying and maximizing quality of life and movement potential within the spheres of promotion, prevention, diagnosis, treatment/intervention,and rehabilitation...
or hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy, formerly called hydropathy, involves the use of water for pain-relief and treating illness. The term hydrotherapy itself is synonymous with the term water cure as it was originally marketed by practitioners and promoters in the 19th century...
can reduce symptoms of hypermobility, because strong muscles help to stabilise joints. These treatments can also help by stretching tight, overused muscles and ensuring the person uses joints within the ideal ranges of motion, avoiding hyperextension or hyperflexion. Low-impact exercise such as Pilates
Pilates
Pilates is a physical fitness system developed in the early 20th century by Joseph Pilates in Germany, the UK and the USA. As of 2005, there were 11 million people practicing the discipline regularly and 14,000 instructors in the United States....
or T'ai chi is usually recommended for hypermobile people as it is less likely to cause injury than high-impact exercise or contact sports.
Moist hot packs can relieve the pain of aching joints and muscles. For some patients, ice packs also help to relieve pain.
Medication
Medications frequently used to reduce pain and inflammation caused by hypermobility include analgesics, anti-inflammatoryAnti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory refers to the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation. Anti-inflammatory drugs make up about half of analgesics, remedying pain by reducing inflammation as opposed to opioids, which affect the central nervous system....
drugs (though these have been linked with an increase in pain and joint instability for some sufferers), and tricyclic antidepressants. Some people with hypermobility may benefit from other medications such as steroid
Steroid
A steroid is a type of organic compound that contains a characteristic arrangement of four cycloalkane rings that are joined to each other. Examples of steroids include the dietary fat cholesterol, the sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, and the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone.The core...
injections or gabapentin
Gabapentin
Gabapentin is a pharmaceutical drug, specifically a GABA analogue. It was originally developed for the treatment of epilepsy, and currently is also used to relieve neuropathic pain...
, a drug originally used for treating epilepsy
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
. Europe is far ahead of the United States in terms of HMS recognition and its knowledge of how to treat it. Tramadol
Tramadol
Tramadol hydrochloride is a centrally acting synthetic opioid analgesic used in treating moderate pain. The drug has a wide range of applications, including treatment for restless legs syndrome and fibromyalgia...
, a non-narcotic yet opioid
Opioid
An opioid is a psychoactive chemical that works by binding to opioid receptors, which are found principally in the central and peripheral nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract...
pain reliever that is nearly as effective as narcotics, has been used in England to treat HMS joint pain, and it is available either by prescription from a doctor in the United States or from Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
. Benzodiazapines are also used in HMS sufferers who experience painful muscles spasms around loose joints.
Lifestyle modification
For some people with hypermobility, lifestyle changes decrease the severity of symptoms. For example:- If writing is painful, people may be able to reduce the pain by typingTypingTyping is the process of inputting text into a device, such as a typewriter, cell phone, computer, or a calculator, by pressing keys on a keyboard. It can be distinguished from other means of input, such as the use of pointing devices like the computer mouse, and text input via speech...
. - If typing is painful, they may try voice control software for their computerComputerA computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
or a more ergonomic keyboard. - If standing is painful, keep a bend in the knees or use a wheelchair.
- Avoid activities that can bring on symptoms. These include standing, stretching the joints (such as in some forms of yoga), and lifting heavy objects or weights.
- A decrease in heavy exercise, such as lifting heavy weights or running with wrist weights, which can be jarring to many joints, can be replaced with a more gentle run on an elliptical machine. Swimming fans could try using a kickboard to exercise in a pool (careful not to hyperextend knees while kicking the water and keep a bend in your elbows if you swim; if you have weak shoulders then avoid "arms-only" "pull" exercises in the water and try to focus on kicking without hyperextension while keeping a relaxed pace with your arms.)
- Posture should be closely monitored. Weakened ligaments and muscles contribute to poor posture, which may result in numerous other medical conditions. Isometric exercises and attention to where joints are (avoid crossing legs for example if you have hip problems) are helpful to keep posture from leading to more pain.
- Remember to ask for help when needed, as to not risk excessive strain when extra assistance can be acquired.
Other treatments
- Bracing to support weak joints may be helpful when joints are injured or painful, but caution must be used not to weaken the joints further.
- ProlotherapyProlotherapyProlotherapy is also known as "proliferation therapy" or "regenerative injection therapy." involves injecting an otherwise non-pharmacological and non-active irritant solution into the body, generally in the region of tendons or ligaments for the purpose of strengthening weakened connective tissue...
injections work for some, according to testimonies. Though not a typical route to take, it may be preferable to steroid injections for some. Prolotherapy supposedly works by strengthening weak ligaments by injecting saline. It takes the strain off the overworked muscles, which tweak due to over-compensation. Injured areas, coupled with HMS, take more injections sessions to improve.

