Hypernatremia
Encyclopedia
Hypernatremia or hypernatraemia (see American and British English spelling differences
) is an electrolyte disturbance
that is defined by an elevated sodium
level in the blood. Hypernatremia is generally not caused by an excess of sodium, but rather by a relative deficit of free water
in the body. For this reason, hypernatremia is often synonymous with the less precise term, dehydration
.
Water is lost from the body in a variety of ways, including perspiration, insensible losses from breathing, and in the feces
and urine
. If the amount of water ingested consistently falls below the amount of water lost, the serum sodium level will begin to rise, leading to hypernatremia. Rarely, hypernatremia can result from massive salt
ingestion, such as may occur from drinking seawater
.
Ordinarily, even a small rise in the serum sodium concentration above the normal range results in a strong sensation of thirst
, an increase in free water intake, and correction of the abnormality. Therefore, hypernatremia most often occurs in people such as infant
s, those with impaired mental status
, or the elderly, who may have an intact thirst mechanism but are unable to ask for or obtain water.
. With more severe elevations of the sodium level, seizure
s and coma
may occur.
Severe symptoms are usually due to acute elevation of the plasma sodium concentration to above 158 mEq/L (normal is typically about 135-145 mEq/L). Values above 180 mEq/L are associated with a high mortality rate, particularly in adults. However such high levels of sodium rarely occur without severe coexisting medical conditions.
 Common causes
Common causes
of hypernatremia include:
) adapts to the higher sodium concentration. Rapidly lowering the sodium concentration with free water, once this adaptation has occurred, causes water to flow into brain cells and causes them to swell. This can lead to cerebral edema
, potentially resulting in seizures, permanent brain damage
, or death. Therefore, significant hypernatremia should be treated carefully by a physician
or other medical professional with experience in treatment of electrolyte imbalances.
American and British English spelling differences
One of the ways in which American English and British English differ is in spelling.-Historical origins:In the early 18th century, English spelling was not standardized. Differences became noticeable after the publishing of influential dictionaries...
) is an electrolyte disturbance
Electrolyte disturbance
Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis within the body. They help to regulate myocardial and neurological function, fluid balance, oxygen delivery, acid-base balance and much more. Electrolyte imbalances can develop by the following mechanisms: excessive ingestion; diminished...
that is defined by an elevated sodium
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
level in the blood. Hypernatremia is generally not caused by an excess of sodium, but rather by a relative deficit of free water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
in the body. For this reason, hypernatremia is often synonymous with the less precise term, dehydration
Dehydration
In physiology and medicine, dehydration is defined as the excessive loss of body fluid. It is literally the removal of water from an object; however, in physiological terms, it entails a deficiency of fluid within an organism...
.
Water is lost from the body in a variety of ways, including perspiration, insensible losses from breathing, and in the feces
Feces
Feces, faeces, or fæces is a waste product from an animal's digestive tract expelled through the anus or cloaca during defecation.-Etymology:...
and urine
Urine
Urine is a typically sterile liquid by-product of the body that is secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination and excreted through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require elimination from the bloodstream...
. If the amount of water ingested consistently falls below the amount of water lost, the serum sodium level will begin to rise, leading to hypernatremia. Rarely, hypernatremia can result from massive salt
Salt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
ingestion, such as may occur from drinking seawater
Seawater
Seawater is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% . This means that every kilogram of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts . The average density of seawater at the ocean surface is 1.025 g/ml...
.
Ordinarily, even a small rise in the serum sodium concentration above the normal range results in a strong sensation of thirst
Thirst
Thirst is the craving for fluids, resulting in the basic instinct of animals to drink. It is an essential mechanism involved in fluid balance. It arises from a lack of fluids and/or an increase in the concentration of certain osmolites, such as salt...
, an increase in free water intake, and correction of the abnormality. Therefore, hypernatremia most often occurs in people such as infant
Infant
A newborn or baby is the very young offspring of a human or other mammal. A newborn is an infant who is within hours, days, or up to a few weeks from birth. In medical contexts, newborn or neonate refers to an infant in the first 28 days after birth...
s, those with impaired mental status
Cognition
In science, cognition refers to mental processes. These processes include attention, remembering, producing and understanding language, solving problems, and making decisions. Cognition is studied in various disciplines such as psychology, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science...
, or the elderly, who may have an intact thirst mechanism but are unable to ask for or obtain water.
Signs and symptoms
Clinical manifestations of hypernatremia can be subtle, consisting of lethargy, weakness, irritability, and edemaEdema
Edema or oedema ; both words from the Greek , oídēma "swelling"), formerly known as dropsy or hydropsy, is an abnormal accumulation of fluid beneath the skin or in one or more cavities of the body that produces swelling...
. With more severe elevations of the sodium level, seizure
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
s and coma
Coma
In medicine, a coma is a state of unconsciousness, lasting more than 6 hours in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light or sound, lacks a normal sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. A person in a state of coma is described as...
may occur.
Severe symptoms are usually due to acute elevation of the plasma sodium concentration to above 158 mEq/L (normal is typically about 135-145 mEq/L). Values above 180 mEq/L are associated with a high mortality rate, particularly in adults. However such high levels of sodium rarely occur without severe coexisting medical conditions.
Cause

Etiology
Etiology is the study of causation, or origination. The word is derived from the Greek , aitiologia, "giving a reason for" ....
of hypernatremia include:
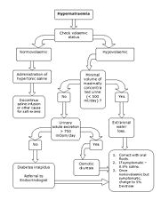
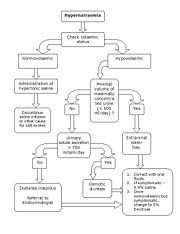
- Hypovolemic
- Inadequate intake of water, typically in elderly or otherwise disabled patients who are unable to take in water as their thirst dictates. This is the most common cause of hypernatremia.
- Excessive losses of water from the urinary tract, which may be caused by glycosuriaGlycosuriaGlycosuria or glucosuria is the excretion of glucose into the urine. Ordinarily, urine contains no glucose because the kidneys are able to reclaim all of the filtered glucose back into the bloodstream. Glycosuria is nearly always caused by elevated blood glucose levels, most commonly due to...
, or other osmotic diuretics. - Water losses associated with extreme sweating.
- Severe watery diarrhea
- Euvolemic
- Excessive excretion of water from the kidneys caused by diabetes insipidusDiabetes insipidusDiabetes insipidus is a condition characterized by excessive thirst and excretion of large amounts of severely diluted urine, with reduction of fluid intake having no effect on the concentration of the urine. There are several different types of DI, each with a different cause...
, which involves either inadequate production of the hormone, vasopressinVasopressinArginine vasopressin , also known as vasopressin, argipressin or antidiuretic hormone , is a neurohypophysial hormone found in most mammals, including humans. Vasopressin is a peptide hormone that controls the reabsorption of molecules in the tubules of the kidneys by affecting the tissue's...
, from the pituitary gland or impaired responsiveness of the kidneys to vasopressin.
- Excessive excretion of water from the kidneys caused by diabetes insipidus
- Hypervolemic
- Intake of a hypertonic fluid (a fluid with a higher concentration of solutes than the remainder of the body). This is relatively uncommon, though it can occur after a vigorous resuscitation where a patient receives a large volume of a concentrated sodium bicarbonateSodium bicarbonateSodium bicarbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate is the chemical compound with the formula Na HCO3. Sodium bicarbonate is a white solid that is crystalline but often appears as a fine powder. It has a slightly salty, alkaline taste resembling that of washing soda . The natural mineral form is...
solution. Ingesting seawaterSeawaterSeawater is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% . This means that every kilogram of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts . The average density of seawater at the ocean surface is 1.025 g/ml...
also causes hypernatremia because seawater is hypertonic. - Mineralcorticoid excess due to a disease state such as Conn's syndromeConn's syndromePrimary aldosteronism, also known as primary hyperaldosteronism, is characterized by the overproduction of the mineralocorticoid hormone aldosterone by the adrenal glands., when not a result of excessive renin secretion. Aldosterone causes increase in sodium and water retention and potassium...
or Cushing's diseaseCushing's diseaseCushing's disease is a cause of Cushing's Syndrome characterised by increased secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone from the anterior pituitary. This is most often as a result of a pituitary adenoma...
- Intake of a hypertonic fluid (a fluid with a higher concentration of solutes than the remainder of the body). This is relatively uncommon, though it can occur after a vigorous resuscitation where a patient receives a large volume of a concentrated sodium bicarbonate
Treatment
The cornerstone of treatment is administration of free water to correct the relative water deficit. Water can be replaced orally or intravenously. Water alone cannot be administered as intravenously (because of osmolarity issue) rather can be given with addition to dextrose or saline infusion solutions. However, overly rapid correction of hypernatremia is potentially very dangerous. The body (in particular the brainBrain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
) adapts to the higher sodium concentration. Rapidly lowering the sodium concentration with free water, once this adaptation has occurred, causes water to flow into brain cells and causes them to swell. This can lead to cerebral edema
Cerebral edema
Cerebral edema or cerebral œdema is an excess accumulation of water in the intracellular or extracellular spaces of the brain.-Vasogenic:Due to a breakdown of tight endothelial junctions which make up the blood-brain barrier...
, potentially resulting in seizures, permanent brain damage
Brain damage
"Brain damage" or "brain injury" is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors...
, or death. Therefore, significant hypernatremia should be treated carefully by a physician
Physician
A physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
or other medical professional with experience in treatment of electrolyte imbalances.

