Hyperprolinemia
Encyclopedia
Hyperprolinemia, also referred to as prolinemia or prolinuria, is a condition which occurs when the amino acid
proline
is not broken down properly by the enzymes proline oxidase
or pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogense, causing a build up of proline in the body.
.
People with hyperprolinemia type I have proline
levels in their blood between 3 and 10 times the normal level. Some individuals with type I exhibit seizure
s, mental retardation
or other neurological problems.
Hyperprolinemia can also occur with other conditions, such as malnutrition or liver disease. In particular, individuals with conditions that cause elevated levels of lactic acid in the blood, such as lactic acidemia, are likely to have elevated proline
levels, because lactic acid inhibits the breakdown of proline.
 Mutations in the ALDH4A1
Mutations in the ALDH4A1
and PRODH genes cause hyperprolinemia.
Hyperprolinemia type I is caused by a mutation in the PRODH gene, which codes for the enzyme proline oxidase
. This enzyme begins the process of degrading proline by starting the reaction that converts it to pyrroline-5-carboxylate.
Hyperprolinemia type II is caused by a mutation in the ALDH4A1 gene, for the enzyme 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase
. This enzyme helps to break down the pyrroline-5-carboxylate produced in the previous reaction, converting it to the amino acid glutamine
. The conversion between proline and glutamine, and the reverse reaction controlled by different enzymes, are important factors required to maintain proper metabolism and protein production.
A deficiency of either proline oxidase or pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase results in a buildup of proline in the body. A deficiency of the latter enzyme leads to higher levels of proline and a buildup of the intermediate breakdown product pyrroline-5-carboxylate, causing the signs and symptoms of hyperprolinemia type II.
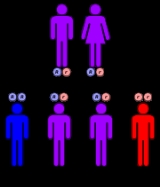
Hyperprolinemia is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means two copies of the gene in each cell are altered. Most often, the parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder are heterozygous carriers, having only one copy of the altered gene, without having signs and symptoms of the disorder.
In about one-third of cases of hyperprolinemia, individuals carrying one copy of an altered PRODH gene have moderately elevated levels of proline in their blood, but these levels do not cause any health problems. Individuals with one altered ALDH4A1 gene have normal levels of proline in their blood.
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
proline
Proline
Proline is an α-amino acid, one of the twenty DNA-encoded amino acids. Its codons are CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG. It is not an essential amino acid, which means that the human body can synthesize it. It is unique among the 20 protein-forming amino acids in that the α-amino group is secondary...
is not broken down properly by the enzymes proline oxidase
Proline oxidase
Proline dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRODH gene.The protein encoded by this gene is a mitochondrial proline dehydrogenase which catalyzes the first step in proline catabolism. Deletion of this gene has been associated with type I hyperprolinemia...
or pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogense, causing a build up of proline in the body.
Hyperprolinemia type I
It is difficult to determine the prevalence of hyperprolinemia type I, as many people with the condition are asymptomaticAsymptomatic
In medicine, a disease is considered asymptomatic if a patient is a carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. A condition might be asymptomatic if it fails to show the noticeable symptoms with which it is usually associated. Asymptomatic infections are also called subclinical...
.
People with hyperprolinemia type I have proline
Proline
Proline is an α-amino acid, one of the twenty DNA-encoded amino acids. Its codons are CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG. It is not an essential amino acid, which means that the human body can synthesize it. It is unique among the 20 protein-forming amino acids in that the α-amino group is secondary...
levels in their blood between 3 and 10 times the normal level. Some individuals with type I exhibit seizure
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
s, mental retardation
Mental retardation
Mental retardation is a generalized disorder appearing before adulthood, characterized by significantly impaired cognitive functioning and deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors...
or other neurological problems.
Hyperprolinemia type II
Hyperprolinemia type II results in proline levels in the blood between 10 and 15 times higher than normal, and high levels of a related compound called pyrroline-5-carboxylate. This rare form of the disorder may appear benign at times, but often involves seizures, convulsions, and mental retardation.Hyperprolinemia can also occur with other conditions, such as malnutrition or liver disease. In particular, individuals with conditions that cause elevated levels of lactic acid in the blood, such as lactic acidemia, are likely to have elevated proline
Proline
Proline is an α-amino acid, one of the twenty DNA-encoded amino acids. Its codons are CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG. It is not an essential amino acid, which means that the human body can synthesize it. It is unique among the 20 protein-forming amino acids in that the α-amino group is secondary...
levels, because lactic acid inhibits the breakdown of proline.
Genetics

ALDH4A1
Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH4A1 gene.-Further reading:...
and PRODH genes cause hyperprolinemia.
Hyperprolinemia type I is caused by a mutation in the PRODH gene, which codes for the enzyme proline oxidase
Proline oxidase
Proline dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRODH gene.The protein encoded by this gene is a mitochondrial proline dehydrogenase which catalyzes the first step in proline catabolism. Deletion of this gene has been associated with type I hyperprolinemia...
. This enzyme begins the process of degrading proline by starting the reaction that converts it to pyrroline-5-carboxylate.
Hyperprolinemia type II is caused by a mutation in the ALDH4A1 gene, for the enzyme 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase
1-Pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase
In enzymology, a 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThe three substrates of this enzyme are -1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate, NAD+, and H2O, whereas its three products are glutamate, NADH, and H+....
. This enzyme helps to break down the pyrroline-5-carboxylate produced in the previous reaction, converting it to the amino acid glutamine
Glutamine
Glutamine is one of the 20 amino acids encoded by the standard genetic code. It is not recognized as an essential amino acid but may become conditionally essential in certain situations, including intensive athletic training or certain gastrointestinal disorders...
. The conversion between proline and glutamine, and the reverse reaction controlled by different enzymes, are important factors required to maintain proper metabolism and protein production.
A deficiency of either proline oxidase or pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase results in a buildup of proline in the body. A deficiency of the latter enzyme leads to higher levels of proline and a buildup of the intermediate breakdown product pyrroline-5-carboxylate, causing the signs and symptoms of hyperprolinemia type II.
Hyperprolinemia is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means two copies of the gene in each cell are altered. Most often, the parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder are heterozygous carriers, having only one copy of the altered gene, without having signs and symptoms of the disorder.
In about one-third of cases of hyperprolinemia, individuals carrying one copy of an altered PRODH gene have moderately elevated levels of proline in their blood, but these levels do not cause any health problems. Individuals with one altered ALDH4A1 gene have normal levels of proline in their blood.

