
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
Encyclopedia
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (also known as "Anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia," and "Christ-Siemens-Touraine syndrome") is one of about 150 types of ectodermal dysplasia
in humans. Before birth, these disorders result in the abnormal development of structures including the skin
, hair
, nails, teeth, and sweat gland
s.
Affected individuals tend to have sparse scalp and body hair (hypotrichosis
). The hair is often light-coloured, brittle, and slow-growing. This condition is also characterized by absent teeth (hypodontia
) or teeth that are malformed. The teeth that are present are frequently small and pointed.
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia is associated with distinctive facial features including a prominent forehead, thick lips, and a flattened bridge of the nose. Additional features of this condition include thin, wrinkled, and dark-colored skin around the eyes; chronic skin problems such as eczema
; and a bad-smelling discharge from the nose (ozena).
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia is the most common form of ectodermal dysplasia in humans. It is estimated to affect at least 1 in 17,000 people worldwide.
 Mutations in the EDA
Mutations in the EDA
, EDAR
, and EDARADD
genes cause hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. The EDA, EDAR, and EDARADD genes provide instructions for making proteins that work together during embryonic development. These proteins form part of a signaling pathway that is critical for the interaction between two cell layers, the ectoderm and the mesoderm. In the early embryo, these cell layers form the basis for many of the body's organs and tissues. Ectoderm-mesoderm interactions are essential for the formation of several structures that arise from the ectoderm, including the skin, hair, nails, teeth, and sweat glands.
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia has several different inheritance patterns.
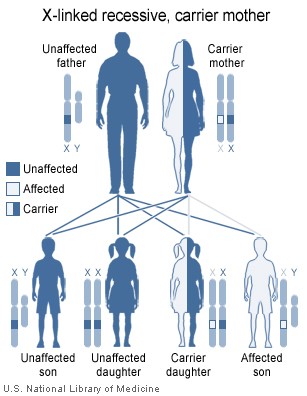
pattern. A condition is considered X-linked if the mutated gene that causes the disorder is located on the X chromosome, one of the two sex chromosomes. In males (who have only one X chromosome), one altered copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition. In females (who have two X chromosomes), a mutation must be present in both copies of the gene to cause the disorder. Males are affected by X-linked recessive disorders much more frequently than females. A striking characteristic of X-linked inheritance is that fathers cannot pass X-linked traits to their sons.
In X-linked recessive inheritance, a female with one altered copy of the gene in each cell is called a carrier. Since females operate on only one of their two X chromosomes (X inactivation) a female carrier may or may not manifest symptoms of the disease. If a female carrier is operating on her normal X she will not show symptoms. If a female is operating on her carrier X she will show symptoms.In about 70 percent of cases, carriers of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia experience some features of the condition. These signs and symptoms are usually mild and include a few missing or abnormal teeth, sparse hair, and some problems with sweat gland function. Some carriers, however, have more severe features of this disorder.
Ectodermal dysplasia
Ectodermal dysplasia is not a single disorder, but a group of syndromes all deriving from abnormalities of the ectodermal structures. More than 150 different syndromes have been identified. Despite some of the syndromes having different genetic causes the symptoms are sometimes very similar...
in humans. Before birth, these disorders result in the abnormal development of structures including the skin
Skin
-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
, hair
Hair
Hair is a filamentous biomaterial, that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Found exclusively in mammals, hair is one of the defining characteristics of the mammalian class....
, nails, teeth, and sweat gland
Sweat gland
Sweat glands, or sudoriferous glands, are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. There are two kinds of sweat glands:...
s.
Presentation
Most people with hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia have a reduced ability to sweat (hypohidrosis) because they have fewer sweat glands than normal or their sweat glands do not function properly. Sweating is a major way that the body controls its temperature; as sweat evaporates from the skin, it cools the body. An inability to sweat can lead to a dangerously high body temperature hyperthermia, particularly in hot weather. In some cases, hyperthermia can cause life-threatening medical problems.Affected individuals tend to have sparse scalp and body hair (hypotrichosis
Hypotrichosis
Hypotrichosis is a condition of abnormal hair patterns - predominantly loss or reduction. It occurs, most frequently, by the growth of vellus hair in areas of the body that normally produce terminal hair. Typically, the individual's hair growth is normal after birth, but shortly thereafter the hair...
). The hair is often light-coloured, brittle, and slow-growing. This condition is also characterized by absent teeth (hypodontia
Hypodontia
In dentistry, hypodontia is the condition at which the patient has missing teeth as a result of their failure to develop. Hypodontia describes a situation where the patient is missing up to 6 teeth, excluding the 3rd molars. Missing third molars occur in 9-30% of population...
) or teeth that are malformed. The teeth that are present are frequently small and pointed.
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia is associated with distinctive facial features including a prominent forehead, thick lips, and a flattened bridge of the nose. Additional features of this condition include thin, wrinkled, and dark-colored skin around the eyes; chronic skin problems such as eczema
Eczema
Eczema is a form of dermatitis, or inflammation of the epidermis . In England, an estimated 5.7 million or about one in every nine people have been diagnosed with the disease by a clinician at some point in their lives.The term eczema is broadly applied to a range of persistent skin conditions...
; and a bad-smelling discharge from the nose (ozena).
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia is the most common form of ectodermal dysplasia in humans. It is estimated to affect at least 1 in 17,000 people worldwide.
Genetics

EDA (gene)
Ectodysplasin-A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EDA gene.-Further reading:...
, EDAR
EDAR
Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member EDAR is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EDAR gene.It can be associated with Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia.- Further reading :...
, and EDARADD
EDARADD
Ectodysplasin-A receptor-associated adapter protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EDARADD gene.-Further reading:...
genes cause hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. The EDA, EDAR, and EDARADD genes provide instructions for making proteins that work together during embryonic development. These proteins form part of a signaling pathway that is critical for the interaction between two cell layers, the ectoderm and the mesoderm. In the early embryo, these cell layers form the basis for many of the body's organs and tissues. Ectoderm-mesoderm interactions are essential for the formation of several structures that arise from the ectoderm, including the skin, hair, nails, teeth, and sweat glands.
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia has several different inheritance patterns.
EDA (X-linked)
Most cases are caused by mutations in the EDA gene, which are inherited in an X-linked recessiveX-linked recessive
X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome causes the phenotype to be expressed in males and in females who are homozygous for the gene mutation X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on...
pattern. A condition is considered X-linked if the mutated gene that causes the disorder is located on the X chromosome, one of the two sex chromosomes. In males (who have only one X chromosome), one altered copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition. In females (who have two X chromosomes), a mutation must be present in both copies of the gene to cause the disorder. Males are affected by X-linked recessive disorders much more frequently than females. A striking characteristic of X-linked inheritance is that fathers cannot pass X-linked traits to their sons.
In X-linked recessive inheritance, a female with one altered copy of the gene in each cell is called a carrier. Since females operate on only one of their two X chromosomes (X inactivation) a female carrier may or may not manifest symptoms of the disease. If a female carrier is operating on her normal X she will not show symptoms. If a female is operating on her carrier X she will show symptoms.In about 70 percent of cases, carriers of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia experience some features of the condition. These signs and symptoms are usually mild and include a few missing or abnormal teeth, sparse hair, and some problems with sweat gland function. Some carriers, however, have more severe features of this disorder.
EDAR or EDARADD (autosomal)
Less commonly, hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia results from mutations in the EDAR or EDARADD gene. EDAR mutations can have an autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance, and EDARADD mutations have an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance. Autosomal dominant inheritance means one copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder. Autosomal recessive inheritance means two copies of the gene in each cell are altered. Most often, the parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder are carriers of one copy of the altered gene but do not show signs and symptoms of the disorder.External links
- GeneReview/NIH/UW entry on Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia
- Author Web Site for Bonnie J. Rough, whose award-winning memoir "Carrier: Untangling the Danger in My DNA" describes one family's experience with hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
- Bonnie J. Rough speaks about her family's history with HED on KRUI's The Lit Show

