
IRT Second Avenue Line
Encyclopedia
The IRT Second Avenue Line, also known as the Second Avenue El, was an elevated railway
in Manhattan
, New York City
, United States
, operated by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company
until city takeover in 1940. It ended service on June 13, 1942, although the portion north of the 57th Street
closed on June 11, 1940, with the city takeover.
 In 1875 the Rapid Transit Commission granted the Gilbert Elevated Railway Company the right to construct the railway from Battery Park
In 1875 the Rapid Transit Commission granted the Gilbert Elevated Railway Company the right to construct the railway from Battery Park
to the Harlem River
along Second Avenue
. The commission also granted the Gilbert Elevated Railway Company the right to operate the Sixth Avenue Elevated
and soon afterward the Gilbert Elevated Railway change its name to the Metropolitan Elevated Railway.
As part of the Dual Contracts, this line was triple-tracked, allowing true express service.
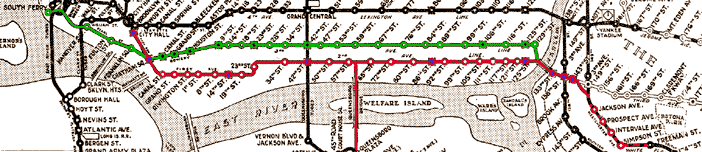
The Second Avenue El did not run entirely on Second Avenue. Its southern terminus was City Hall, and it continued to Chatham Square, where it split off from the Third Avenue El
and ran along Division Street and then Allen Street. At Houston Street it ran north on First Avenue
, where it turned left on 23rd Street ran north on Second Avenue to 129th Street. At that point it joined with the Third Avenue El and crossed the Harlem River into the Bronx.
The M15 bus, which runs along much of the IRT Second Avenue Elevated Line's route, carries more passengers than any other route in New York City. However, it does not carry as many passengers as a rapid transit line, and does not allow for interchange within rapid transit stations. A replacement rapid transit route, the Second Avenue Subway
has been under consideration since before the demolition of the IRT Second Avenue Line, and is under construction as of 2007. The first phase is scheduled to open in 2016.
Elevated railway
An elevated railway is a form of rapid transit railway with the tracks built above street level on some form of viaduct or other steel or concrete structure. The railway concerned may be constructed according to the standard gauge, narrow gauge, light rail, monorail or suspension railway system...
in Manhattan
Manhattan
Manhattan is the oldest and the most densely populated of the five boroughs of New York City. Located primarily on the island of Manhattan at the mouth of the Hudson River, the boundaries of the borough are identical to those of New York County, an original county of the state of New York...
, New York City
New York City
New York is the most populous city in the United States and the center of the New York Metropolitan Area, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. New York exerts a significant impact upon global commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and...
, United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, operated by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company
Interborough Rapid Transit Company
The Interborough Rapid Transit Company was the private operator of the original underground New York City Subway line that opened in 1904, as well as earlier elevated railways and additional rapid transit lines in New York City. The IRT was purchased by the City in June 1940...
until city takeover in 1940. It ended service on June 13, 1942, although the portion north of the 57th Street
57th Street (IRT Second Avenue Line)
57th Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had two levels. The lower level had three tracks and two island platforms and served trains coming from the Bronx. The upper level had two tracks and one island platform and served trains coming from Queens, from the IRT...
closed on June 11, 1940, with the city takeover.

Battery Park
Battery Park is a 25-acre public park located at the Battery, the southern tip of Manhattan Island in New York City, facing New York Harbor. The Battery is named for artillery batteries that were positioned there in the city's early years in order to protect the settlement behind them...
to the Harlem River
Harlem River
The Harlem River is a navigable tidal strait in New York City, USA that flows 8 miles between the Hudson River and the East River, separating the boroughs of Manhattan and the Bronx...
along Second Avenue
Second Avenue (Manhattan)
Second Avenue is an avenue on the East Side of the New York City borough of Manhattan extending from Houston Street at its south end to the Harlem River Drive at 128th Street at its north end. A one-way street, vehicular traffic runs only downtown. A bicycle lane in the left hand portion from 55th...
. The commission also granted the Gilbert Elevated Railway Company the right to operate the Sixth Avenue Elevated
IRT Sixth Avenue Line
The IRT Sixth Avenue Line, often called the Sixth Avenue Elevated or Sixth Avenue El, was the second elevated railway in Manhattan in New York City, following the Ninth Avenue Elevated. In addition to its transportation role, it also captured the imagination of artists and poets.The line ran south...
and soon afterward the Gilbert Elevated Railway change its name to the Metropolitan Elevated Railway.
As part of the Dual Contracts, this line was triple-tracked, allowing true express service.
The Second Avenue El did not run entirely on Second Avenue. Its southern terminus was City Hall, and it continued to Chatham Square, where it split off from the Third Avenue El
IRT Third Avenue Line
The IRT Third Avenue Line, commonly known as the Third Avenue El, was an elevated railway in Manhattan and the Bronx, New York City. Originally operated by an independent railway company, it was acquired by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company and eventually became part of the New York subway...
and ran along Division Street and then Allen Street. At Houston Street it ran north on First Avenue
First Avenue (Manhattan)
First Avenue is a north-south thoroughfare on the East Side of the New York City borough of Manhattan, running from Houston Street northbound for over 125 blocks before terminating at the Willis Avenue Bridge into The Bronx at the Harlem River near East 127th Street. South of Houston Street, the...
, where it turned left on 23rd Street ran north on Second Avenue to 129th Street. At that point it joined with the Third Avenue El and crossed the Harlem River into the Bronx.
The M15 bus, which runs along much of the IRT Second Avenue Elevated Line's route, carries more passengers than any other route in New York City. However, it does not carry as many passengers as a rapid transit line, and does not allow for interchange within rapid transit stations. A replacement rapid transit route, the Second Avenue Subway
Second Avenue Subway
The Second Avenue Subway is a planned rapid transit subway line, part of the New York City Subway system. Phase I, consisting of two miles of tunnel and three stations, is currently under construction underneath Second Avenue in the borough of Manhattan.A plan for more than 75 years, the Second...
has been under consideration since before the demolition of the IRT Second Avenue Line, and is under construction as of 2007. The first phase is scheduled to open in 2016.
Station listing
| Station | Tracks | Opened | Closed | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Merges with IRT Third Avenue Line IRT Third Avenue Line The IRT Third Avenue Line, commonly known as the Third Avenue El, was an elevated railway in Manhattan and the Bronx, New York City. Originally operated by an independent railway company, it was acquired by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company and eventually became part of the New York subway... |
||||
| 125th Street 125th Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 125th Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had three tracks and two island platforms. The next stop to the north was 129th Street for terminating trains and 133rd Street for through trains. The next stop to the south was 121st Street for local trains and 86th Street for... |
all | After the line opened | ||
| 121st Street 121st Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 121st Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had three tracks and two side platforms. The next stop to the north was 125th Street. The next stop to the south was 117th Street. The station closed on June 11, 1940.... |
local | |||
| 117th Street 117th Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 117th Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had three tracks and two side platforms. The next stop to the north was 121st Street. The next stop to the south was 111th Street. The station closed on June 11, 1940.... |
local | |||
| 111th Street 111th Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 111th Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had three tracks and two side platforms. The next stop to the north was 117th Street. The next stop to the south was 105th Street. The station closed on June 11, 1940.... |
local | |||
| 105th Street 105th Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 105th Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had three tracks and two side platforms. The next stop to the north was 111th Street. The next stop to the south was 99th Street. The station closed on June 11, 1940.... |
local | After the line opened | ||
| 99th Street 99th Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 99th Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had three tracks and two side platforms. The next stop to the north was 105th Street. The next stop to the south was 92nd Street. The station closed on June 13, 1942.... |
local | |||
| 92nd Street 92nd Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 92nd Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had three tracks and two side platforms. The next stop to the north was 99th Street. The next stop to the south was 86th Street. The station closed on June 11, 1940.... |
local | |||
| 86th Street 86th Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 86th Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had two levels. The lower level had two tracks and two side platforms, and was served by local trains. The upper level was built as a part of the Dual Contracts and had one track and two side platforms for express trains. The... |
all | |||
| 80th Street 80th Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 80th Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had three tracks and two side platforms. The next stop to the north was 86th Street. The next stop to the south was 72nd Street. The station closed on June 11, 1940.... |
local | |||
| 72nd Street 72nd Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 72nd Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had three tracks and two side platforms. The next stop to the north was 80th Street. The next stop to the south was 65th Street. The station closed on June 11, 1940.... |
local | |||
| 65th Street 65th Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 65th Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had three tracks and two side platforms. The next stop to the north was 72nd Street. The next stop to the south was 57th Street. The station closed on June 11, 1940.... |
local | March 1, 1880 | ||
| Branch over Queensboro Bridge Queensboro Bridge The Ed Koch Queensboro Bridge, also known as the 59th Street Bridge – because its Manhattan end is located between 59th and 60th Streets – or simply the Queensboro Bridge, is a cantilever bridge over the East River in New York City that was completed in 1909... to Queensboro Plaza leaves at 59th Street |
||||
| 57th Street 57th Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 57th Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had two levels. The lower level had three tracks and two island platforms and served trains coming from the Bronx. The upper level had two tracks and one island platform and served trains coming from Queens, from the IRT... |
all | |||
| 50th Street 50th Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 50th Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line in New York City. It had three tracks and two side platforms. The next stop to the north was 57th Street. The next stop to the south was 42nd Street. The station closed on June 13, 1942.... |
local | |||
| 42nd Street 42nd Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 42nd Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had three tracks and two island platforms. The next stop to the north was 50th Street for local trains and 57th Street for express trains. The next stop to the south was 34th Street for locaal trains and 14th Street for express... |
all | March 1, 1880 | ||
| 34th Street 34th Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 34th Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had two levels. The upper level had three tracks and two side platforms and was used for the Second Avenue line trains. The lower level had two tracks and one island platform and was used by 34th Street shuttle trains. The next... |
local | Transfer to branch to 34th Street Ferry 34th Street Ferry (IRT elevated station) 34th Street Ferry was a station on the 34th Street Shuttle that branched off of the IRT Third Avenue Line. The elevated spur operated from July 1, 1880 to July 14, 1930. Located on the east side of First Avenue, the station had two tracks and one island platform... |
||
| 23rd Street 23rd Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 23rd Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had two levels. The lower level had two tracks and two side platforms and served local trains. The upper level had one track for express trains. The next stop to the north was 34th Street. The next stop to the south was 19th... |
local | March 1, 1880 | ||
| 19th Street 19th Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 19th Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had two levels. The lower level had two tracks and two side platforms and served local trains. The upper level had one track for express trains. The next stop to the north was 23rd Street. The next stop to the south was 14th... |
local | |||
| 14th Street 14th Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) 14th Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line, located at the intersection of 14th Street and First Avenue. It had two levels. The lower level had three tracks and two side platforms and was served by local trains. The upper level had two tracks and two side platforms and was... |
all | March 1, 1880 | ||
| Eighth Street | local | March 1, 1880 | ||
| First Street First Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) First Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line, located at the intersection of First Street and First Avenue. It had two levels. The lower level had two tracks and two side platforms and the upper level had one track that served express trains,. The next stop to the north was... |
local | March 1, 1880 | ||
| Rivington Street Rivington Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) Rivington Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line on the New York City Subway. It had two levels. The lower level had two tracks and two side platforms and the upper level had one track that served the express trains. The next stop to the north was First Street. The next stop... |
local | March 1, 1880 | ||
| Grand Street Grand Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) Grand Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had two levels. The lower level had two tracks and two side platforms and the upper level had one track that served the express trains. The next stop to the north was Rivington Street. The next stop to the south was Canal... |
local | March 1, 1880 | ||
| Canal Street Canal Street (IRT Second Avenue Line) Canal Street was a station on the demolished IRT Second Avenue Line. It had two levels. The lower level had two tracks and two side platforms and the upper level had one track that served the express trains. The next stop to the north was Grand Street. The next stop to the south was Chatham Square.... |
local | March 1, 1880 | ||
| Chatham Square Chatham Square (IRT Third Avenue Line) Chatham Square was a station on the demolished IRT Third Avenue Line. It had two levels. The lower level had two tracks and one island platform that served trains of both the IRT Second Avenue Line and IRT Third Avenue Line. The upper level had three tracks and two island platforms that served... |
all | March 1, 1880 | Transfer to Third Avenue Line IRT Third Avenue Line The IRT Third Avenue Line, commonly known as the Third Avenue El, was an elevated railway in Manhattan and the Bronx, New York City. Originally operated by an independent railway company, it was acquired by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company and eventually became part of the New York subway... and branch to City Hall City Hall (IRT Second Avenue Line) City Hall was a station on the IRT Second Avenue Line, which also served trains of the IRT Third Avenue Line. It had 2 levels. The lower level served Third Avenue trains and had two tracks with two side platforms for exiting passengers, and a center island platform for entering passengers... |
|
| Merges with IRT Third Avenue Line IRT Third Avenue Line The IRT Third Avenue Line, commonly known as the Third Avenue El, was an elevated railway in Manhattan and the Bronx, New York City. Originally operated by an independent railway company, it was acquired by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company and eventually became part of the New York subway... |
||||
| Franklin Square Franklin Square (IRT Third Avenue Line) Franklin Square was a station on the demolished IRT Third Avenue Line in New York City. It had two tracks and one island platform, and was the northernmost station on the line that shared both Second Avenue and Third Avenue trains. The next stop to the north was Chatham Square. The next stop to the... |
all | August 26, 1878 | ||
| Fulton Street Fulton Street (IRT Third Avenue Line) Fulton Street was a station on the demolished IRT Third Avenue Line. It had two tracks and one island platform. The next stop to the north was Franklin Square. The next stop to the south was Hanover Square. The station closed on December 22, 1950.... |
all | August 26, 1878 | ||
| Hanover Square Hanover Square (IRT Third Avenue Line) Hanover Square was a station on the demolished IRT Third Avenue Line. It had two tracks and one island platform. The station was originally built in 1878 by the New York Elevated Railroad. The next stop to the north was Fulton Street. The next stop to the south was South Ferry... |
all | August 26, 1878 | ||
| Merges with IRT Ninth Avenue Line IRT Ninth Avenue Line The IRT Ninth Avenue Line, often called the Ninth Avenue El, was the first elevated railway in New York City. It opened in 1868 as the West Side and Yonkers Patent Railway, a cable-hauled line. It ceased operation in 1940.... |
||||
| South Ferry | all | August 26, 1878 | ||
Further reading
- "Second Avenue El in Manhattan". By NJI Publishing with text provided by Joe Cunningham. 1995. ISBN 0-934088-33-0

