
ITU Terrain Model
Encyclopedia
The ITU
Terrain Loss Model is a radio propagation model
that provides a method to predict the median
path loss
for a telecommunication
link. Developed on the basis of diffraction
theory, this model predicts the path loss as a function of the height of path blockage and the First Fresnel zone
for the transmission link.
This model accounts for obstructions in the middle of the telecommunication link, and therefore, is suitable to be used inside cities as well as in open fields.
Where,
To use the model, one computes the additional loss to each path obstruction (A). These losses are summed and then added to the predicted line of sight path loss which is calculated using Friis transmission equation
or a similar theoretical or empirical model.
This model's output is only as good as the data on which it is based and the LOS model it is used to correct.
Itu
Itu is an old and historic municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population in 2009 was 157,384 and the area is 641.68 km². The elevation is 583 m. This place name comes from the Tupi language, meaning big waterfall. Itu is linked with the highway numbered the SP-75 and are flowed...
Terrain Loss Model is a radio propagation model
Radio propagation model
A radio propagation model, also known as the Radio Wave Propagation Model or the Radio Frequency Propagation Model, is an empirical mathematical formulation for the characterization of radio wave propagation as a function of frequency, distance and other conditions...
that provides a method to predict the median
Median
In probability theory and statistics, a median is described as the numerical value separating the higher half of a sample, a population, or a probability distribution, from the lower half. The median of a finite list of numbers can be found by arranging all the observations from lowest value to...
path loss
Path loss
Path loss is the reduction in power density of an electromagnetic wave as it propagates through space. Path loss is a major component in the analysis and design of the link budget of a telecommunication system....
for a telecommunication
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
link. Developed on the basis of diffraction
Diffraction
Diffraction refers to various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word "diffraction" and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1665...
theory, this model predicts the path loss as a function of the height of path blockage and the First Fresnel zone
Fresnel zone
In optics and radio communications , a Fresnel zone , named for physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel, is one of a number of concentric ellipsoids which define volumes in the radiation pattern of a circular aperture...
for the transmission link.
Applicable to / under conditions
This model is applicable on any terrain.This model accounts for obstructions in the middle of the telecommunication link, and therefore, is suitable to be used inside cities as well as in open fields.
Mathematical formulation
The model is mathematically formulated as:Where,
-
 = Additional loss (in excess of free-space loss) due to diffraction (dB)
= Additional loss (in excess of free-space loss) due to diffraction (dB)
-
 = Normalized terrain clearance
= Normalized terrain clearance
-
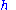 = The height difference (negative in the case that the LOS path is completely obscured) (m)
= The height difference (negative in the case that the LOS path is completely obscured) (m)
-
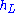 = Height of the line-of-sightLine-of-sight propagationLine-of-sight propagation refers to electro-magnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation. Electromagnetic transmission includes light emissions traveling in a straight line...
= Height of the line-of-sightLine-of-sight propagationLine-of-sight propagation refers to electro-magnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation. Electromagnetic transmission includes light emissions traveling in a straight line...
link (m)
-
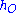 = Height of the obstruction (km)
= Height of the obstruction (km)
-
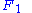 = Radius of the First Fresnel Zone (km)
= Radius of the First Fresnel Zone (km)
-
 = Distance of obstruction from one terminal (km)
= Distance of obstruction from one terminal (km)
-
 = Distance of obstruction from the other terminal (km)
= Distance of obstruction from the other terminal (km)
-
 = Frequency of transmission (GHz)
= Frequency of transmission (GHz)
-
 = Distance from transmitter to receiver (km)
= Distance from transmitter to receiver (km)
To use the model, one computes the additional loss to each path obstruction (A). These losses are summed and then added to the predicted line of sight path loss which is calculated using Friis transmission equation
Friis transmission equation
The Friis transmission equation is used in telecommunications engineering, and gives the power received by one antenna under idealized conditions given another antenna some distance away transmitting a known amount of power. The formula was derived in 1945 by Danish-American radio engineer Harald T...
or a similar theoretical or empirical model.
Limitations
This model is considered valid for losses over 15 dB and may be valid for losses as low as 6 dB. In the event that the loss is less than 6 dB or is negative (i.e., gain), this A-value should be discarded.This model's output is only as good as the data on which it is based and the LOS model it is used to correct.





