.gif)
I Ching (monk)
Encyclopedia
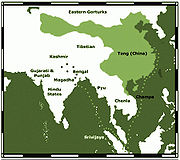
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
Chinese Buddhist monk, originally named Zhang Wenming (Ch. 張文明). The written records of his travels contributed to the world knowledge of the ancient kingdom of Srivijaya
Srivijaya
Srivijaya was a powerful ancient thalassocratic Malay empire based on the island of Sumatra, modern day Indonesia, which influenced much of Southeast Asia. The earliest solid proof of its existence dates from the 7th century; a Chinese monk, I-Tsing, wrote that he visited Srivijaya in 671 for 6...
, as well as providing information about the other kingdoms lying on the route between China and the Nālandā
Nalanda
Nālandā is the name of an ancient center of higher learning in Bihar, India.The site of Nalanda is located in the Indian state of Bihar, about 55 miles south east of Patna, and was a Buddhist center of learning from the fifth or sixth century CE to 1197 CE. It has been called "one of the...
Buddhist university in India. He was also responsible for the translation of a large number of Buddhist scriptures from Sanskrit into Chinese. Yijing's full Buddhist title was "Tripiṭaka
Tripiṭaka
' is a traditional term used by various Buddhist sects to describe their various canons of scriptures. As the name suggests, a traditionally contains three "baskets" of teachings: a , a and an .-The three categories:Tripitaka is the three main categories of texts that make up the...
Dharma Master Yijing" (Ch. 三藏法師義淨).
In some 19th century publications, Yijing's name may appear as I Tsing, following an antiquated method of Chinese romanization
Romanization
In linguistics, romanization or latinization is the representation of a written word or spoken speech with the Roman script, or a system for doing so, where the original word or language uses a different writing system . Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written...
.
Journey to Srivijaya and Nālandā
Zhang Wen Ming became a monk at age 14 and was an admirer of Fa Xian and XuanzangXuanzang
Xuanzang was a famous Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator who described the interaction between China and India in the early Tang period...
, both famous monks of his childhood. Provided funding by an otherwise unknown benefactor named Fong, he decided to visit the famous Buddhist university of Nālandā, in Bihar, India, to further study Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
. Traveling by a Persian boat out of Guangzhou
Guangzhou
Guangzhou , known historically as Canton or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of the Guangdong province in the People's Republic of China. Located in southern China on the Pearl River, about north-northwest of Hong Kong, Guangzhou is a key national transportation hub and trading port...
, he arrived in Srivijaya
Srivijaya
Srivijaya was a powerful ancient thalassocratic Malay empire based on the island of Sumatra, modern day Indonesia, which influenced much of Southeast Asia. The earliest solid proof of its existence dates from the 7th century; a Chinese monk, I-Tsing, wrote that he visited Srivijaya in 671 for 6...
(today's Palembang
Palembang
Palembang is the capital city of the South Sumatra province in Indonesia. Palembang is one of the oldest cities in Indonesia, and has a history of being a capital of a maritime empire. Located on the Musi River banks on the east coast of southern Sumatra island, it has an area of 400.61 square...
of Sumatra) after 22 days, where he spent the next 6 months learning Sanskrit
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
grammar and Malay language. He went on to record visits to the nations of Malayu
Melayu Kingdom
Melayu Kingdom was a classical Southeast Asian kingdom that existed between the 7th and the 13th century of the common era. It was established around present-day Dharmasraya on Sumatera, Indonesia, approximately 300 km north of Palembang...
and Kiteh (Kedah
Kedah
Kedah is a state of Malaysia, located in the northwestern part of Peninsular Malaysia. The state covers a total area of over 9,000 km², and it consists of the mainland and Langkawi. The mainland has a relatively flat terrain, which is used to grow rice...
), and in 673 after ten days additional travel reached the 'naked kingdom' (south west of Shu
Shu
Shu may refer to:*Shū ** , Japanese Kanji.*Shu * 蜀 , an abbreviation of Sichuan province of the People's Republic of China, as well as the following historical regimes that have existed in this region:...
). Yijing recorded his impression of the 'Kunlun peoples', using an ancient Chinese word for Malay peoples. "Kunlun people have curly hair, dark bodies, bare feet and wear sarongs." He then arrived at the East coast of India, where he met a senior monk and stayed a year to study Sanskrit. Both later followed a group of merchants and visited 30 other principalities. Halfway to Nālandā, Yijing fell sick and was unable to walk; gradually he was left behind by the group. He was looted by bandits and stripped naked. He heard the natives would catch white skins to offer sacrifice to the gods, so he jumped into mud and used leaves to cover his lower body; he walked slowly to Nālandā where he stayed for 11 years. Yijing praises the high level of Buddhist scholarship in Srivijaya, he advised Chinese monks to study there prior to making the journey to Nālandā India.
Return home
In the year 687, Yijing stopped in the kingdom of SrivijayaSrivijaya
Srivijaya was a powerful ancient thalassocratic Malay empire based on the island of Sumatra, modern day Indonesia, which influenced much of Southeast Asia. The earliest solid proof of its existence dates from the 7th century; a Chinese monk, I-Tsing, wrote that he visited Srivijaya in 671 for 6...
on his way back to (Tang
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
) China. At that time Palembang
Palembang
Palembang is the capital city of the South Sumatra province in Indonesia. Palembang is one of the oldest cities in Indonesia, and has a history of being a capital of a maritime empire. Located on the Musi River banks on the east coast of southern Sumatra island, it has an area of 400.61 square...
was a centre of Buddhism where foreign scholars gathered, and Yijing stayed there for two years to translate original Sanskrit Buddhist scriptures to Chinese. In the year 689 he returned to Guangzhou to obtain ink and papers (note: Srivijaya then had no paper and ink) and returned again to Srivijaya the same year. In year 695, he completed all translation works and finally returned to Tang China at Luoyang
Luoyang
Luoyang is a prefecture-level city in western Henan province of Central China. It borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang to the south, Sanmenxia to the west, Jiyuan to the north, and Jiaozuo to the northeast.Situated on the central plain of...
, and received a grand welcome back by Empress Wu
Empress Wu
Empress Wu may mean or refer to:* Empress Wu , the wife of Liu Bei, the first emperor of Shu Han* Empress Wu, a title name for Wu Zetian* Consort Wu , Wu Zetian's grandniece, who was posthumously honored as an empress...
. His total journey took 25 years. He brought back some 400 Buddhist translated texts. 南海寄歸內法傳 & 大唐西域求法高僧傳(Account of Buddhism sent from the South Seas & Buddhist Monks Pilgrimage of Tang Dynasty) are two of Yijing's best travel diaries, describing his adventurous journey to Srivijaya and India, the society of India, the lifestyles of various local peoples, and more. He translated more than 60 sutras into Chinese, including:
- Saravanabhava Vinaya (一切有部毗奈耶)
- AvadanaAvadanaAvadāna is the name given to a type of Buddhist literature correlating past lives' virtuous deeds to subsequent lives' events...
, i.e. stories of great deeds (譬喻經) in 710710Year 710 was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 710 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.- Asia :* The Asuka period, the second and last part...
. - Suvarnaprabhascottamaraja-sutra, i.e. Sutra of the Most Honored King (金光明最勝王經) in 703703Year 703 was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 703 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.- Asia :* Byzantine Empire: Abdallah ibn Abd al-Malik...
.
Buddhism in Srivijaya
Yijing praised the high level of Buddhist scholarship in SrivijayaSrivijaya
Srivijaya was a powerful ancient thalassocratic Malay empire based on the island of Sumatra, modern day Indonesia, which influenced much of Southeast Asia. The earliest solid proof of its existence dates from the 7th century; a Chinese monk, I-Tsing, wrote that he visited Srivijaya in 671 for 6...
and advised Chinese monks to study there prior to making the journey to Nālandā
Nalanda
Nālandā is the name of an ancient center of higher learning in Bihar, India.The site of Nalanda is located in the Indian state of Bihar, about 55 miles south east of Patna, and was a Buddhist center of learning from the fifth or sixth century CE to 1197 CE. It has been called "one of the...
, India.
Yijing's visits to Srivijaya gave him the opportunity to meet with others who had come from other neighboring islands. According to him, the Javanese kingdom of Ho-ling was due east of the city of Bhoga at a distance that could be spanned by a 4–5 days journey by sea. He also wrote that Buddhism was flourishing throughout the islands of Southeast Asia. "Many of the kings and chieftains in the islands of the Southern Sea admire and believe in Buddhism, and their hearts are set on accumulating good actions."
External links
- Translators in Sui Dynasty and Tang Dynasty
- http://www.buddhanet.net/bodh_gaya/bodh_gaya01.htm
- http://www.andaman.org/NICOBAR/book/history/prehistory+general/prehistory.htm
- http://www.iranchamber.com/culture/articles/iranian_cultural_impact_southeastasia.php

