
Imino acid
Encyclopedia
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
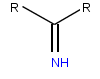
, an imino acid is any molecule that contains both imino
Imine
An imine is a functional group or chemical compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond, with the nitrogen attached to a hydrogen atom or an organic group. If this group is not a hydrogen atom, then the compound is known as a Schiff base...
(>C=NH) and carboxyl (-C(=O)-OH) functional group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
s.
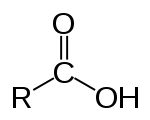
Imino acids are related to amino acids, which contain both amino (-NH2) and carboxyl (-COOH) functional group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
s. Amino acids containing a secondary amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
group (the only proteinogenic amino acid
Proteinogenic amino acid
Proteinogenic amino acids are those amino acids that can be found in proteins and require cellular machinery coded for in the genetic code of any organism for their isolated production. There are 22 standard amino acids, but only 21 are found in eukaryotes. Of the 22, 20 are directly encoded by...
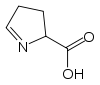
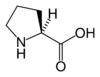
of this type is proline
Proline
Proline is an α-amino acid, one of the twenty DNA-encoded amino acids. Its codons are CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG. It is not an essential amino acid, which means that the human body can synthesize it. It is unique among the 20 protein-forming amino acids in that the α-amino group is secondary...
) are sometimes named imino acids, though this usage is disputed by some.
The term imino acid is also the obsolete term for imido acids, containing the -C(=NH)-OH group, and should not be used for them.
The amino acid oxidase enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s are able to convert amino acids into imino acids. Also the direct biosynthetical
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
precursor to the amino acid proline is the imino acid (S)-Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C).

