
Immunoglobulin light chain
Encyclopedia
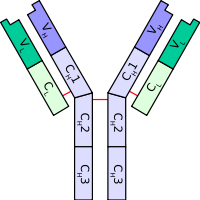
The immunoglobulin light chain is the small polypeptide
Peptide
Peptides are short polymers of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds. They are distinguished from proteins on the basis of size, typically containing less than 50 monomer units. The shortest peptides are dipeptides, consisting of two amino acids joined by a single peptide bond...
subunit of an antibody
Antibody
An antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, termed an antigen...
(immunoglobulin).
A typical antibody is composed of two immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy chains and two Ig light chains.
In humans
There are two types of light chain in humans (as in other mammals),- kappa (κ) chain, encoded by the immunoglobulin kappa locus (IGK@) on chromosome 2
- lambda (λ) chain, encoded by the immunoglobulin lambda locus (IGL@) on chromosome 22
Antibodies are produced by B lymphocytes, each expressing only one class of light chain. Once set, light chain class remains fixed for the life of the B lymphocyte. In a healthy individual, the total kappa to lambda ratio is roughly 2:1 in serum (measuring intact whole antibodies) or 1:1.5 if measuring free light chains, with a highly divergent ratio indicative of neoplasm.
The exact normal ratio of kappa to lambda ranges from 0.26 to 1.65. Both the kappa and the lambda chains can increase proportionately, maintaining a normal ratio. This is usually indicative of something other than a blood cell dyscrasia, such as kidney disease.
In other animals
The immunoglobulin light chain genes in tetrapodTetrapod
Tetrapods are vertebrate animals having four limbs. Amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals are all tetrapods; even snakes and other limbless reptiles and amphibians are tetrapods by descent. The earliest tetrapods evolved from the lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian...
s can be classified into three distinct groups: kappa (κ), lambda (λ), and sigma (σ). The divergence of the κ, λ, and σ isotypes preceded the radiation of tetrapods. The σ isotype was lost after the evolution of the amphibian lineage and before the emergence of the reptilian lineage.
Other types of light chains can be found in lower vertebrate
Vertebrate
Vertebrates are animals that are members of the subphylum Vertebrata . Vertebrates are the largest group of chordates, with currently about 58,000 species described. Vertebrates include the jawless fishes, bony fishes, sharks and rays, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds...
s, such as the Ig-Light-Iota chain of Chondrichthyes
Chondrichthyes
Chondrichthyes or cartilaginous fishes are jawed fish with paired fins, paired nares, scales, two-chambered hearts, and skeletons made of cartilage rather than bone...
and Teleostei
Teleostei
Teleostei is one of three infraclasses in class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes. This diverse group, which arose in the Triassic period, includes 20,000 extant species in about 40 orders; most living fishes are members of this group...
.
Camelid
Camelid
Camelids are members of the biological family Camelidae, the only living family in the suborder Tylopoda. Dromedaries, Bactrian Camels, llamas, alpacas, vicuñas, and guanacos are in this group....
s are unique among mammals as they have fully functional antibodies which have two heavy chains, but lack the light chains usually paired with each heavy chain. The functional role of this separate repertoire is unknown as yet.
Structure
Only one type of light chain is present in a typical antibody, thus the two light chains of an individual antibody are identical.Each light chain is composed of two tandem immunoglobulin domain
Immunoglobulin domain
The immunoglobulin domain is a type of protein domain that consists of a 2-layer sandwich of between 7 and 9 antiparallel β-strands arranged in two β-sheets with a Greek key topology....
s:
- one constant (CL) domain
- one variable domain (VL) that is important for binding antigenAntigenAn antigen is a foreign molecule that, when introduced into the body, triggers the production of an antibody by the immune system. The immune system will then kill or neutralize the antigen that is recognized as a foreign and potentially harmful invader. These invaders can be molecules such as...
The approximate length of a light chain protein is from 211 to 217 amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s.
In pathology
Ig light chains produced in neoplastic plasma cells, e.g. in multiple myelomaMultiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma , also known as plasma cell myeloma or Kahler's disease , is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell normally responsible for the production of antibodies...
, are called Bence Jones protein
Bence Jones protein
A Bence Jones protein is a monoclonal globulin protein found in the blood or urine, with a molecular weight of 22-24 kDa.Finding this protein is often suggestive of multiple myeloma or Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia....
s.

