
Implant (medicine)
Encyclopedia
Medical device
A medical device is a product which is used for medical purposes in patients, in diagnosis, therapy or surgery . Whereas medicinal products achieve their principal action by pharmacological, metabolic or immunological means. Medical devices act by other means like physical, mechanical, thermal,...
manufactured to replace a missing biological structure, support a damaged biological structure, or enhance an existing biological structure. Medical implants are man-made devices, in contrast to a transplant
Organ transplant
Organ transplantation is the moving of an organ from one body to another or from a donor site on the patient's own body, for the purpose of replacing the recipient's damaged or absent organ. The emerging field of regenerative medicine is allowing scientists and engineers to create organs to be...
, which is a transplanted biomedical tissue
Biomedical tissue
Biomedical tissue is biological tissue used for organ transplantation and medical research, particularly cancer research.Such tissues and organs may be referred to as: implant tissue, allograft, xenograft, skin graft tissue, human transplant tissue, implant bone. Tissue is stored in tissue...
. The surface of implants that contact the body might be made of a biomedical material
Biomaterial
A biomaterial is any matter, surface, or construct that interacts with biological systems. The development of biomaterials, as a science, is about fifty years old. The study of biomaterials is called biomaterials science. It has experienced steady and strong growth over its history, with many...
such as titanium
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It has a low density and is a strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color....
, silicone
Silicone
Silicones are inert, synthetic compounds with a variety of forms and uses. Typically heat-resistant and rubber-like, they are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medical applications , cookware, and insulation....
or apatite
Apatite
Apatite is a group of phosphate minerals, usually referring to hydroxylapatite, fluorapatite, chlorapatite and bromapatite, named for high concentrations of OH−, F−, Cl− or Br− ions, respectively, in the crystal...
depending on what is the most functional. In some cases implants contain electronics e.g. artificial pacemaker
Artificial pacemaker
A pacemaker is a medical device that uses electrical impulses, delivered by electrodes contacting the heart muscles, to regulate the beating of the heart...
and cochlear implant
Cochlear implant
A cochlear implant is a surgically implanted electronic device that provides a sense of sound to a person who is profoundly deaf or severely hard of hearing...
s. Some implants are bioactive, such as subcutaneous drug delivery devices in the form of implantable pills or drug-eluting stent
Drug-eluting stent
A drug-eluting stent ' is a peripheral or coronary stent placed into narrowed, diseased peripheral or coronary arteries that slowly releases a drug to block cell proliferation. This prevents fibrosis that, together with clots , could otherwise block the stented artery, a process called restenosis...
s.
Applications
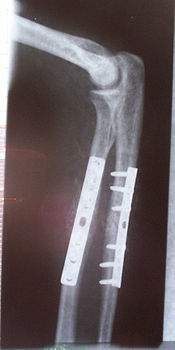
Among the most common types of medical implants are the pins, rods, screws and platesInternal fixator
Internal fixation is an operation in orthopedics that involves the surgical implementation of implants for the purpose of repairing a bone, a concept that dates to the mid-19th century...
used to anchor fractured bones while they heal.
Complications
The process of implantation of medical devices is subject to the same complications as any other invasive medical procedure, including infectionInfection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
, inflammation
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
, and pain
Pain
Pain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."...
. Implants also run the risk of rejection if they ellicit a reaction from the host immune system
Immune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
.
Failures
There have been many examples of implant failures, including rupture of silicone breast implants, hip replacementHip replacement
Hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the hip joint is replaced by a prosthetic implant. Hip replacement surgery can be performed as a total replacement or a hemi replacement. Such joint replacement orthopaedic surgery generally is conducted to relieve arthritis pain or fix severe...
joints and artificial heart valves, such as the Bjork–Shiley valve, all of which have caused FDA intervention. The consequences of implant failure depend on the critical nature of the implant, and its position in the body. Thus heart valve failure is likely to threaten the life of the individual, while breast implant or hip joint failure is less likely to be life-threatening.
See also
- Medical deviceMedical deviceA medical device is a product which is used for medical purposes in patients, in diagnosis, therapy or surgery . Whereas medicinal products achieve their principal action by pharmacological, metabolic or immunological means. Medical devices act by other means like physical, mechanical, thermal,...
- Orthosis
- Prosthetics in fictionProsthetics in fictionProsthetics, the artificial replacement of organic limbs or organs, often play a role in fiction, particularly science fiction, as either plot points or to give a character a beyond normal appearance...
- Medical grade siliconeMedical grade siliconeMedical grade silicones are silicones tested for biocompatibility and are appropriate to be used for medical applications. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration regulates materials implanted into the body. Medical grade silicones are generally grouped into three categories: non...
Further reading
- D.F. Williams, Williams Dictionary of Biomaterials. Liverpool University Press, 1999 ISBN 978-0-85323-734-1; ISBN 0-85323-734-4

