Imposition
Encyclopedia
Imposition is one of the fundamental steps in the prepress
printing process. It consists in the arrangement of the printed product’s pages on the printer’s sheet, in order to obtain faster printing, simplified binding
and less waste of paper
.
Correct imposition minimizes printing time by maximizing the number of pages per impression, reducing cost of press time and materials. To achieve this, the printed sheet must be filled as fully as possible.
Imposition is affected by five different parameters:
To understand how the pages are related to each other, an imposition dummy may be used. This is made by folding several sheets of paper in the way the press will print and fold the product. A little copy is then created, and this can help paginate the product.
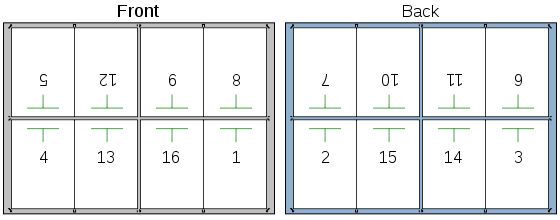
In the example above, a 16-page book is prepared for printing. There are eight pages on the front of the sheet, and the corresponding eight pages on the back. After printing, the paper is folded in half vertically (page two falls against page three). Then it is folded again horizontally (page four meets page five). A third fold completes this process (page nine meets page eight). The example below shows the final result prior to binding and trimming.

, pages were assembled in a metal frame called a chase, and locked into place using wedges called quoins.
By the late twentieth century, most typesetting was onto photographic film. These sheets were combined manually on a light table
, in a process called stripping. Skilled workers would spend many hours stripping pieces of film together in the correct sequence and orientation. The term stripping was also used for other changes to a prepared page, such as a spelling correction, or a stop press
story in a newspaper. Digital techniques rendered stripping less necessary, but what has forced increasing numbers to abandon it completely is the introduction of "platesetters", which put pages directly onto printing plates; these plates cannot be adjusted with a sharp knife. In addition, an extremely high precision would be needed for stripping of colour work, as each ink colour is on a separate piece of film.
Where an imposition layout is viewed on screen, it may be referred to as a printer's spread. This is used to contrast with reader's spread, which shows a finished printed piece on screen as it will appear to the reader, rather than the printer; specifically, in a reader's spread for a typical book, pairs of facing pages are shown side-by-side (that is, pages 2 and 3 together).
This test is performed to verify, through the formation of a prototype, that the imposition was successful. Typical checks are that the pages are on the correct spot and the crossover bleeds work. It cannot be used as a check proof for images or colors or layout because it is printed on a large, low-resolution inkjet printer.
Since the inkjet printer can print on only one side of the paper, the full proof (the front and rear sides) is printed on two separate sheets. They are first cut along the crossover bleeds, checking to see if they are in the correct position. The two sheets are then attached together to form a single sheet printed on both sides, and then this sheet is folded to form a prototype of the signature.
This proof is still called blue copy, digital blue copy to prototype, or blues plotter.
Prepress
Prepress is the term used in the printing and publishing industries for the processes and procedures that occur between the creation of a print layout and the final printing...
printing process. It consists in the arrangement of the printed product’s pages on the printer’s sheet, in order to obtain faster printing, simplified binding
Bookbinding
Bookbinding is the process of physically assembling a book from a number of folded or unfolded sheets of paper or other material. It usually involves attaching covers to the resulting text-block.-Origins of the book:...
and less waste of paper
Paper
Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets....
.
Correct imposition minimizes printing time by maximizing the number of pages per impression, reducing cost of press time and materials. To achieve this, the printed sheet must be filled as fully as possible.
Imposition is affected by five different parameters:
- FormatFormatFormat may refer to:* File format, layout for electronic files* Text formatting, typesetting of text elements* Format , a command-line utility in many computer operating systems* Format , a computer command to prepare hard disks...
of the product: The size of the finished page determines how many pages can be printed on a single sheet. - Number of pages of the printed product: The compositor must determine how many sheets are to be printed to create a finished book.
- Stitching/binding method: The compositor must understand how the sheets are placed to form the signatures that compose the finished book.
- Paper fiber direction: Many papers have a "grain," reflecting the alignment of the paper fibers. That these fibers must run lengthwise along the fold influences the alignment, hence the position, of the pages on the printed sheet.
- Finishing and bindingBookbindingBookbinding is the process of physically assembling a book from a number of folded or unfolded sheets of paper or other material. It usually involves attaching covers to the resulting text-block.-Origins of the book:...
To understand how the pages are related to each other, an imposition dummy may be used. This is made by folding several sheets of paper in the way the press will print and fold the product. A little copy is then created, and this can help paginate the product.

In the example above, a 16-page book is prepared for printing. There are eight pages on the front of the sheet, and the corresponding eight pages on the back. After printing, the paper is folded in half vertically (page two falls against page three). Then it is folded again horizontally (page four meets page five). A third fold completes this process (page nine meets page eight). The example below shows the final result prior to binding and trimming.

Non-digital techniques
Imposition has been a requirement since the earliest days of printing. When pages were set using movable typeMovable type
Movable type is the system of printing and typography that uses movable components to reproduce the elements of a document ....
, pages were assembled in a metal frame called a chase, and locked into place using wedges called quoins.
By the late twentieth century, most typesetting was onto photographic film. These sheets were combined manually on a light table
Light table
A light table is a viewing device that is used to review photographic film or artwork placed on top of it. It provides even illumination of the subject from below through a translucent cover and fluorescent lights that emit little heat. They can also be found mounted on the walls of hospitals and...
, in a process called stripping. Skilled workers would spend many hours stripping pieces of film together in the correct sequence and orientation. The term stripping was also used for other changes to a prepared page, such as a spelling correction, or a stop press
Stop press
"Stop Press" is a phrase stemming from the printed news media as an exclamation signifying the discovery of the need to change the content of an issue just before, or during its printing...
story in a newspaper. Digital techniques rendered stripping less necessary, but what has forced increasing numbers to abandon it completely is the introduction of "platesetters", which put pages directly onto printing plates; these plates cannot be adjusted with a sharp knife. In addition, an extremely high precision would be needed for stripping of colour work, as each ink colour is on a separate piece of film.
Digital techniques
Manual imposition processes tend to cause bottlenecks of the whole printing production. The advent of digital imposition has not only helped a lot in making sure layout and sheet arrangement are correct with higher register precision, but it improves a lot on reducing the usual imposition errors (e.g., slight movements of register due to parallax). An entire book may be imposed and many complex functions applied in an instant. Binding options may be changed on the fly and impositions produced to multiple output devices at once, often with no user intervention. In turn, digital techniques help to reduce material costs, time and resolves production bottlenecks. There are several different approaches to digital imposition.- Imposition in the design application. Software packages that can be used to design single pages can often be used to design entire printed sheets, sometimes by a process as simple as copy/paste onto a larger sheet. This is still in use, especially for low volumes of work, but a popular alternative is an imposition function built in, or added in, to the design tool. This typically takes a document prepared as single pages and creates a new document with full-sheet layouts. This larger layout is then printed to film or a plate.
- Post-design imposition. A post-design application might take a PostScriptPostScriptPostScript is a dynamically typed concatenative programming language created by John Warnock and Charles Geschke in 1982. It is best known for its use as a page description language in the electronic and desktop publishing areas. Adobe PostScript 3 is also the worldwide printing and imaging...
or PDFPortable Document FormatPortable Document Format is an open standard for document exchange. This file format, created by Adobe Systems in 1993, is used for representing documents in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems....
file in single pages and produce a new PostScript or PDF file with imposed sheet layouts for printing. A variation of this is to take a large number of single-page source files as input. This is especially suitable for a magazine or newspaper, where pages may be worked on by different groups simultaneously.
- Print driver imposition. Some printer drivers enable the source application's single-page printed output to be sent to the printer as full sheets. This is not often found in professional production, but is popular for such things as booklet printing on office laser printers. A variation of this offers the ability to print layouts as an option in the application.
- Output device imposition. This is sometimes called "in-RIPRaster image processorA raster image processor is a component used in a printing system which produces a raster image also known as a bitmap. The bitmap is then sent to a printing device for output. The input may be a page description in a high-level page description language such as PostScript, Portable Document...
imposition". This allows regular pages to be printed by any suitable means, and the output device handles imposition. While this offers the advantage of enabling specific tuning of the imposition for an output device, the cost is that there is no preview until the output is produced. This may mean a costly printing plate that takes some time to produce, or even (with a digital press) errors in finished copies: expensive mistakes are possible.
Where an imposition layout is viewed on screen, it may be referred to as a printer's spread. This is used to contrast with reader's spread, which shows a finished printed piece on screen as it will appear to the reader, rather than the printer; specifically, in a reader's spread for a typical book, pairs of facing pages are shown side-by-side (that is, pages 2 and 3 together).
Imposition proof
The imposition proof is the last test that is performed before beginning the print run.This test is performed to verify, through the formation of a prototype, that the imposition was successful. Typical checks are that the pages are on the correct spot and the crossover bleeds work. It cannot be used as a check proof for images or colors or layout because it is printed on a large, low-resolution inkjet printer.
Since the inkjet printer can print on only one side of the paper, the full proof (the front and rear sides) is printed on two separate sheets. They are first cut along the crossover bleeds, checking to see if they are in the correct position. The two sheets are then attached together to form a single sheet printed on both sides, and then this sheet is folded to form a prototype of the signature.
This proof is still called blue copy, digital blue copy to prototype, or blues plotter.

