
Indicators of spatial association
Encyclopedia
Indicators of spatial association are statistics
that evaluate the existence of clusters in the spatial
arrangement of a given variable. For instance if we are studying cancer
rates among census tract
s in a given city local clusters in the rates mean that there are areas that have higher or lower rates than is to be expected by chance alone; that is, the values occurring are above or below those of a random distribution in space.
, defined by:
where
The matrix W is required because in order to address spatial autocorrelation and also model spatial interaction, we need to impose a structure to constrain the number of neighbors to be considered. This is related to Tobler’s first law of geography
, which states that Everything depends on everything else, but closer things more so - in other words, the law implies a spatial distance decay
function, such that even though all observations have an influence on all other observations, after some distance threshold that influence can be neglected.
But if there is no global autocorrelation or no clustering, we can still find clusters at a local level using local spatial autocorrelation. The fact that Moran's I is a summation of individual crossproducts is exploited by the "Local indicators of spatial association" (LISA) to evaluate the clustering in those individual units by calculating Local Moran's I for each spatial unit and evaluating the statistical significance for each Ii. From the previous equation we then obtain:
where:
then,
where N is the number of observations, I is the Moran's I measure of global autocorrelation, and Ii is local.
LISAs can for example be calculated in GeoDA
, which uses the Local Moran's I, proposed by Luc Anselin
in 1995.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
that evaluate the existence of clusters in the spatial
Space
Space is the boundless, three-dimensional extent in which objects and events occur and have relative position and direction. Physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum...
arrangement of a given variable. For instance if we are studying cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
rates among census tract
Census tract
A census tract, census area, or census district is a geographic region defined for the purpose of taking a census. Usually these coincide with the limits of cities, towns or other administrative areas and several tracts commonly exist within a county...
s in a given city local clusters in the rates mean that there are areas that have higher or lower rates than is to be expected by chance alone; that is, the values occurring are above or below those of a random distribution in space.
Global spatial autocorrelation
Global spatial autocorrelation is a measure of the overall clustering of the data. One of the statistics used to evaluate global spatial autocorrelation is Moran's IMoran's I
In statistics, Moran's I is a measure of spatial autocorrelation developed by Patrick A.P. Moran. Spatial autocorrelation is characterized by a correlation in a signal among nearby locations in space. Spatial autocorrelation is more complex than one-dimensional autocorrelation because spatial...
, defined by:

where
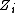 is the deviation of the variable of interest with respect to the mean;
is the deviation of the variable of interest with respect to the mean;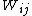 is the matrix of weights that in some cases is equivalent to a binary matrix with ones in position i,j whenever observation i is a neighbor of observation j, and zero otherwise;
is the matrix of weights that in some cases is equivalent to a binary matrix with ones in position i,j whenever observation i is a neighbor of observation j, and zero otherwise;- and
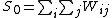 .
.
The matrix W is required because in order to address spatial autocorrelation and also model spatial interaction, we need to impose a structure to constrain the number of neighbors to be considered. This is related to Tobler’s first law of geography
First law of geography
The first law of geography according to Waldo Tobler is "Everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things."This observation is embedded in the gravity model of trip distribution...
, which states that Everything depends on everything else, but closer things more so - in other words, the law implies a spatial distance decay
Distance decay
Distance decay is a geographical term which describes the effect of distance on cultural or spatial interactions. The distance decay effect states that the interaction between two locales declines as the distance between them increases...
function, such that even though all observations have an influence on all other observations, after some distance threshold that influence can be neglected.
Global versus local
Global spatial analysis or global spatial autocorrelation analysis yields only one statistic to summarize the whole study area. In other words, global analysis assumes homogeneity. If that assumption does not hold, then having only one statistic does not make sense as the statistic should differ over space.But if there is no global autocorrelation or no clustering, we can still find clusters at a local level using local spatial autocorrelation. The fact that Moran's I is a summation of individual crossproducts is exploited by the "Local indicators of spatial association" (LISA) to evaluate the clustering in those individual units by calculating Local Moran's I for each spatial unit and evaluating the statistical significance for each Ii. From the previous equation we then obtain:

where:

then,

where N is the number of observations, I is the Moran's I measure of global autocorrelation, and Ii is local.
LISAs can for example be calculated in GeoDA
GeoDA
GeoDa is a free software package that conducts spatial data analysis, geovisualization, spatial autocorrelation and spatial modeling. OpenGeoDa is the cross-platform, open source version of Legacy GeoDa. While Legacy GeoDa only runs on Windows XP, OpenGeoDa runs on different versions of Windows ,...
, which uses the Local Moran's I, proposed by Luc Anselin
Luc Anselin
-Life and contributions:Luc Anselin is currently Walter Isard Chair and Director of the where he attracted some of the leading spatial econometrics scholars. He also founded and directs the at ASU to develop, implement, apply, and disseminate spatial analysis methods...
in 1995.

