
Ingvaeonic
Encyclopedia
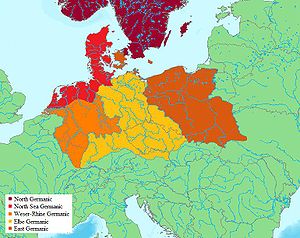
West Germanic languages
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three traditional branches of the Germanic family of languages and include languages such as German, English, Dutch, Afrikaans, the Frisian languages, and Yiddish...
that comprises Old Frisian
Old Frisian
Old Frisian is a West Germanic language spoken between the 8th and 16th centuries in the area between the Rhine and Weser on the European North Sea coast. The Frisian settlers on the coast of South Jutland also spoke Old Frisian but no medieval texts of this area are known...
, Old English
Old English language
Old English or Anglo-Saxon is an early form of the English language that was spoken and written by the Anglo-Saxons and their descendants in parts of what are now England and southeastern Scotland between at least the mid-5th century and the mid-12th century...
and Old Saxon
Old Saxon
Old Saxon, also known as Old Low German, is the earliest recorded form of Low German, documented from the 8th century until the 12th century, when it evolved into Middle Low German. It was spoken on the north-west coast of Germany and in the Netherlands by Saxon peoples...
.
Ingvaeonic is named after the Ingaevones
Ingaevones
The Ingaevones or, as Pliny has it, apparently more accurately, Ingvaeones , as described in Tacitus's Germania, written c. 98 AD, were a West Germanic cultural group living along the North Sea coast in the areas of Jutland, Holstein, Frisia and the Danish islands, where they had by the 1st...
, a West Germanic cultural group or proto-tribe along the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
coast. It is not thought of as a monolithic proto-language
Proto-language
A proto-language in the tree model of historical linguistics is the common ancestor of the languages that form a language family. Occasionally, the German term Ursprache is used instead.Often the proto-language is not known directly...
, but rather as a group of closely related dialects that underwent several areal changes in relative unison.
The grouping was first proposed in Nordgermanen und Alemanen (1942) by German linguist and philologist Friedrich Maurer (1898-1984), as an alternative to the strict tree diagram
Tree diagram
The term tree diagram refers to a specific type of diagram that has a unique network topology. It can be seen as a specific type of network diagram, which in turn can be seen as a special kind of cluster diagram.-Applications:...
s which had become popular following the work of 19th century linguist August Schleicher
August Schleicher
August Schleicher was a German linguist. His great work was A Compendium of the Comparative Grammar of the Indo-European Languages, in which he attempted to reconstruct the Proto-Indo-European language...
and which assumed the existence of a special Anglo-Frisian
Anglo-Frisian languages
The Anglo-Frisian languages form a group of West Germanic languages consisting of Old English, Old Frisian, and their descendants...
group. The other groupings are Istvaeonic, from the Istvaeones
Istvaeones
The Istvaeones, also called Istaevones, Istriaones, Istriones, Sthraones, Thracones, Rhine Germans and Weser-Rhine Germans , were a West Germanic cultural group or proto-tribe...
, including Netherlandic, Afrikaans
Afrikaans
Afrikaans is a West Germanic language, spoken natively in South Africa and Namibia. It is a daughter language of Dutch, originating in its 17th century dialects, collectively referred to as Cape Dutch .Afrikaans is a daughter language of Dutch; see , , , , , .Afrikaans was historically called Cape...
, and related languages; and Irminonic
High German languages
The High German languages or the High German dialects are any of the varieties of standard German, Luxembourgish and Yiddish, as well as the local German dialects spoken in central and southern Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, Switzerland, Luxembourg and in neighboring portions of Belgium and the...
, from the Irminones
Irminones
The Irminones, also referred to as Herminones or Hermiones, were a group of early Germanic tribes settling in the Elbe watershed and by the 1st century AD expanding into Bavaria, Swabia and Bohemia...
, including the High German languages
High German languages
The High German languages or the High German dialects are any of the varieties of standard German, Luxembourgish and Yiddish, as well as the local German dialects spoken in central and southern Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, Switzerland, Luxembourg and in neighboring portions of Belgium and the...
.
Characteristics
Linguistic evidence for Ingvaeonic are common innovations observed in Old Frisian, Old English and Old Saxon such as the following:- The so-called Ingvaeonic nasal spirant lawIngvaeonic nasal spirant lawIn historical linguistics, the Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law is a description of a phonological development in some dialects of West Germanic, which is attested in Old English, Old Frisian, and Old Saxon...
, which (e.g.) converted *munþ "mouth" (cf. Old High GermanOld High GermanThe term Old High German refers to the earliest stage of the German language and it conventionally covers the period from around 500 to 1050. Coherent written texts do not appear until the second half of the 8th century, and some treat the period before 750 as 'prehistoric' and date the start of...
mund) into *mūþ (cf. Old English mūþ). - The loss of the Germanic reflexive pronounReflexive pronounA reflexive pronoun is a pronoun that is preceded by the noun, adjective, adverb or pronoun to which it refers within the same clause. In generative grammar, a reflexive pronoun is an anaphor that must be bound by its antecedent...
- The reduction of the three Germanic verbVerbA verb, from the Latin verbum meaning word, is a word that in syntax conveys an action , or a state of being . In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle to, is the infinitive...
al pluralPluralIn linguistics, plurality or [a] plural is a concept of quantity representing a value of more-than-one. Typically applied to nouns, a plural word or marker is used to distinguish a value other than the default quantity of a noun, which is typically one...
forms into one form ending in -þ - The development of Class III weak verbs into a relic class consisting of four verbs (*sagjan "to say", *hugjan "to think", *habjan "to have", *libjan "to live")
- The split of the Class II weak verb ending *-ō- into *-ō-/-ōja-
- Development of a plural ending *-ōs in a-stem nouns (note, GothicGothic languageGothic is an extinct Germanic language that was spoken by the Goths. It is known primarily from the Codex Argenteus, a 6th-century copy of a 4th-century Bible translation, and is the only East Germanic language with a sizable Text corpus...
also has -ōs, but this is an independent development, caused by terminal devoicing of *-ōz) - Possibly, the monophthongMonophthongA monophthong is a pure vowel sound, one whose articulation at both beginning and end is relatively fixed, and which does not glide up or down towards a new position of articulation....
ization of Germanic *ai to ē/ā (this may represent independent changes in Old Saxon and Anglo-Frisian)
Further reading
- Bremmer, Rolf H. (2009). An Introduction to Old Frisian. Amsterdam: John Benjamins B.V. ISBN: 978-90-272-3255-7. Sonderegger, Stefan (1979). Grundzüge deutscher Sprachgeschichte. Diachronie des Sprachsystems. Band I: Einführung – Genealogie – Konstanten. Berlin/New York: Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 3-11-003570-7.
- Volyes, Joseph B. (1992). Early Germanic Grammar: Pre-, Proto-, and Post-Germanic. San Diego: Academic Press. ISBN: 0-12-728270-X.
- Maurer, Friedrich (1942) Nordgermanen und Alemannen. Studien zur germanischen und frühdeutschen Sprachgeschichte, Stammes- und Volkskunde, Bern: Francke Verlag.

