
Input-output model
Encyclopedia
In economics
, an input-output model is a quantitative economic technique that represents the interdependencies between different branches of national economy or between branches of different, even competing economies. Wassily Leontief
(1905-1999) developed this type of analysis and took the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his development of this model. Earlier Francois Quesnay
developed a cruder version of this technique called Tableau économique
. And, in essence, Léon Walras
's work Elements of Pure Economics on general equilibrium theory is both a forerunner and generalization of Leontief's seminal concept. Leontief's main contribution was that he was able to simplify Walras's piece so that it could be implemented empirically.
The International Input-Output Association is dedicated to advancing knowledge in the field of input-output study, which includes "improvements in basic data, theoretical insights and modelling, and applications, both traditional and novel, of input-output techniques."
, but was developed in full generality by Léon Walras
in 1874. Leontif's contribution was to state the model in such a way as to make computation feasible. He used a matrix
representation of a nation's (or a region's) economy. His model depicts inter-industry relations of an economy. It shows how the output of one industry is an input to each other industry. Leontief put forward the display of this information in the form of a matrix. A given input is typically enumerated in the column of an industry and its outputs are enumerated in its corresponding row. This format, therefore, shows how dependent each industry is on all others in the economy both as customer of their outputs and as supplier of their inputs. Each column of the input-output matrix
reports the monetary value of an industry's inputs and each row represents the value of an industry's outputs.
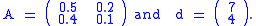
Intuitively, this corresponds to finding the amount of output each sector should produce given that we want 7 units of good A and 4 units of good B. Then solving the system of linear equations derived above gives us
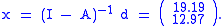
For practical purposes it is generally a poor idea to actually compute the inverse matrix, given that some input-output tables are in excess of hundreds of sectors.
Walter Isard
and his student, Leon Moses, were quick to see the spatial economy and transportation implications of input-output, and began work in this area in the 1950s developing a concept of interregional input-output. Take a one region versus the world case. We wish to know something about interregional commodity flows, so introduce a column into the table headed “exports” and we introduce an “import” row.
A more satisfactory way to proceed would be to tie regions together at the industry level. That is, we could identify both intra-region inter-industry transactions and inter-region inter-industry transactions. The problem here is that the table grows quickly.
Input-output is conceptually simple. Its extension to a model of equilibrium in the national economy is also relatively simple and attractive but requires great skill and high-quality data. One who wishes to do work with input-output systems must deal skillfully with industry classification, data estimation, and inverting very large, ill-conditioned matrices. Moreover, changes in relative prices are not readily handled by this modeling approach alone. Of course, input-output accounts are part and parcel to a more flexible form of modeling, Computable general equilibrium
models.
Two additional difficulties are of interest in transportation work. There is the question of substituting one input for another, and there is the question about the stability of coefficients as production increases or decreases. These are intertwined questions. They have to do with the nature of regional production functions.
through its System of National Accounts (SNA) : the replacement for the current 1993 SNA standard is pending.when? Because the data collection and preparation process for the input-output accounts is necessarily labor and computer intensive, input-output tables are often published long after the year in which the data were collected--typically as much as 5-7 years after. Moreover, the economic "snapshot" that the benchmark version of the tables provides of the economy's cross-section is typically taken only once every few years, at best.
However, many developed countries estimate input-output accounts annually and with much greater recency. This is because while most uses of the input-output analysis focus on the matrix set of interindustry exchanges, the actual focus of the analysis from the perspective of most national statistical agencies is the benchmarking
of gross domestic product
. Input-output tables therefore are an instrumental part of national accounts
. As suggested above, the core input-output table reports only intermediate goods and services that are exchanged among industries. But an array of row vectors, typically aligned below this matrix, record non-industrial inputs by industry like payments for labor; indirect business taxes; dividends, interest, and rents; capital consumption allowances (depreciation); other property-type income (like profits); and purchases from foreign suppliers (imports). At a national level, although excluding the imports, when summed this is called "gross product originating" or "gross domestic product by industry." Another array of column vectors is called "final demand" or "gross product product consumed." This displays columns of spending by households, governments, changes in industry stocks, and industries on investment, as well as net exports. (See also Gross domestic product
.) In any case, by employing the results of an economic census which asks for the sales, payrolls, and material/equipment/service input of each establishment, statistical agencies back into estimates of industry-level profits and investments using the input-output matrix as a sort of double-accounting framework.
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, an input-output model is a quantitative economic technique that represents the interdependencies between different branches of national economy or between branches of different, even competing economies. Wassily Leontief
Wassily Leontief
Wassily Wassilyovich Leontief , was a Russian-American economist notable for his research on how changes in one economic sector may have an effect on other sectors. Leontief won the Nobel Committee's Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1973, and three of his doctoral students have also...
(1905-1999) developed this type of analysis and took the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his development of this model. Earlier Francois Quesnay
François Quesnay
François Quesnay was a French economist of the Physiocratic school. He is known for publishing the "Tableau économique" in 1758, which provided the foundations of the ideas of the Physiocrats...
developed a cruder version of this technique called Tableau économique
Tableau économique
The Tableau économique or Economic Table is an economic model first described in François Quesnay in 1759, which lay the foundation of the Physiocrats’ economic theories....
. And, in essence, Léon Walras
Léon Walras
Marie-Esprit-Léon Walras was a French mathematical economist associated with the creation of the general equilibrium theory.-Life and career:...
's work Elements of Pure Economics on general equilibrium theory is both a forerunner and generalization of Leontief's seminal concept. Leontief's main contribution was that he was able to simplify Walras's piece so that it could be implemented empirically.
The International Input-Output Association is dedicated to advancing knowledge in the field of input-output study, which includes "improvements in basic data, theoretical insights and modelling, and applications, both traditional and novel, of input-output techniques."
Understanding the input-output model
An understanding of the economy as consisting of linked sectors goes back to the French economist François QuesnayFrançois Quesnay
François Quesnay was a French economist of the Physiocratic school. He is known for publishing the "Tableau économique" in 1758, which provided the foundations of the ideas of the Physiocrats...
, but was developed in full generality by Léon Walras
Léon Walras
Marie-Esprit-Léon Walras was a French mathematical economist associated with the creation of the general equilibrium theory.-Life and career:...
in 1874. Leontif's contribution was to state the model in such a way as to make computation feasible. He used a matrix
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions. The individual items in a matrix are called its elements or entries. An example of a matrix with six elements isMatrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element...
representation of a nation's (or a region's) economy. His model depicts inter-industry relations of an economy. It shows how the output of one industry is an input to each other industry. Leontief put forward the display of this information in the form of a matrix. A given input is typically enumerated in the column of an industry and its outputs are enumerated in its corresponding row. This format, therefore, shows how dependent each industry is on all others in the economy both as customer of their outputs and as supplier of their inputs. Each column of the input-output matrix
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions. The individual items in a matrix are called its elements or entries. An example of a matrix with six elements isMatrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element...
reports the monetary value of an industry's inputs and each row represents the value of an industry's outputs.
Example
Consider an economy with two goods, A and B. The matrix of coefficients and the final demand is given by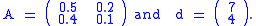
Intuitively, this corresponds to finding the amount of output each sector should produce given that we want 7 units of good A and 4 units of good B. Then solving the system of linear equations derived above gives us
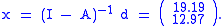
For practical purposes it is generally a poor idea to actually compute the inverse matrix, given that some input-output tables are in excess of hundreds of sectors.
Further research
There are many interesting aspects of the Leontief system, and there is an extensive literature. There is the Hawkins-Simon Condition on producibility. There has been interest in disaggregation to clustered inter-industry flows, and the study of constellations of industries. A great deal of empirical work has been done to identify coefficients, and data have been published for the national economy as well as for regions. This has been a healthy, exciting area for work by economists because the Leontief system can be extended to a model of general equilibrium; it offers a method of decomposing work done at a macro level.Introducing transportation
Transportation is implicit in the notion of inter-industry flows. It is explicitly recognized when transportation is identified as an industry – how much is purchased from transportation in order to produce. But this is not very satisfactory because transportation requirements differ, depending on industry locations and capacity constraints on regional production. Also, the receiver of goods generally pays freight cost, and often transportation data are lost because transportation costs are treated as part of the cost of the goods.Walter Isard
Walter Isard
Walter Isard was a prominent American economist, the principal founder of the discipline of Regional Science, as well as one of the main founders of the discipline of Peace Science....
and his student, Leon Moses, were quick to see the spatial economy and transportation implications of input-output, and began work in this area in the 1950s developing a concept of interregional input-output. Take a one region versus the world case. We wish to know something about interregional commodity flows, so introduce a column into the table headed “exports” and we introduce an “import” row.
| Economic Activities | 1 | 2 | … | … | Z | Exports | Final Demand | Total Outputs |
| 1 | |||||||
| 2 | |||||||
| … | |||||||
| … | |||||||
| Z | |||||||
| Imports |
A more satisfactory way to proceed would be to tie regions together at the industry level. That is, we could identify both intra-region inter-industry transactions and inter-region inter-industry transactions. The problem here is that the table grows quickly.
Input-output is conceptually simple. Its extension to a model of equilibrium in the national economy is also relatively simple and attractive but requires great skill and high-quality data. One who wishes to do work with input-output systems must deal skillfully with industry classification, data estimation, and inverting very large, ill-conditioned matrices. Moreover, changes in relative prices are not readily handled by this modeling approach alone. Of course, input-output accounts are part and parcel to a more flexible form of modeling, Computable general equilibrium
Computable general equilibrium
Computable general equilibrium models are a class of economic models that use actual economic data to estimate how an economy might react to changes in policy, technology or other external factors...
models.
Two additional difficulties are of interest in transportation work. There is the question of substituting one input for another, and there is the question about the stability of coefficients as production increases or decreases. These are intertwined questions. They have to do with the nature of regional production functions.
Measuring input-output tables
The mathematics of input-output economics is straightforward, but the data requirements are enormous because the expenditures and revenues of each branch of economic activity have to be represented. As a result, not all countries collect the required data and data quality varies, even though a set of standards for the data's collection has been set out by the United NationsUnited Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
through its System of National Accounts (SNA) : the replacement for the current 1993 SNA standard is pending.when? Because the data collection and preparation process for the input-output accounts is necessarily labor and computer intensive, input-output tables are often published long after the year in which the data were collected--typically as much as 5-7 years after. Moreover, the economic "snapshot" that the benchmark version of the tables provides of the economy's cross-section is typically taken only once every few years, at best.
However, many developed countries estimate input-output accounts annually and with much greater recency. This is because while most uses of the input-output analysis focus on the matrix set of interindustry exchanges, the actual focus of the analysis from the perspective of most national statistical agencies is the benchmarking
Benchmarking
Benchmarking is the process of comparing one's business processes and performance metrics to industry bests and/or best practices from other industries. Dimensions typically measured are quality, time and cost...
of gross domestic product
Gross domestic product
Gross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living....
. Input-output tables therefore are an instrumental part of national accounts
National accounts
National accounts or national account systems are the implementation of complete and consistent accounting techniques for measuring the economic activity of a nation. These include detailed underlying measures that rely on double-entry accounting...
. As suggested above, the core input-output table reports only intermediate goods and services that are exchanged among industries. But an array of row vectors, typically aligned below this matrix, record non-industrial inputs by industry like payments for labor; indirect business taxes; dividends, interest, and rents; capital consumption allowances (depreciation); other property-type income (like profits); and purchases from foreign suppliers (imports). At a national level, although excluding the imports, when summed this is called "gross product originating" or "gross domestic product by industry." Another array of column vectors is called "final demand" or "gross product product consumed." This displays columns of spending by households, governments, changes in industry stocks, and industries on investment, as well as net exports. (See also Gross domestic product
Gross domestic product
Gross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living....
.) In any case, by employing the results of an economic census which asks for the sales, payrolls, and material/equipment/service input of each establishment, statistical agencies back into estimates of industry-level profits and investments using the input-output matrix as a sort of double-accounting framework.
Input-output Analysis Versus Consistency Analysis
Despite the clear ability of the input-output model to depict and analyze the dependence of one industry or sector on another, Leontief and others never managed to introduce the full spectrum of dependency relations in a market economy. In 2003, Mohammad Ganihttp://sb.iub.edu.bd/Dr_Mohammad_Osman_Gani.html, a pupil of Leontief, introduced Consistency Analysis in his book 'Foundations of Economic Science' (ISBN 984320655X), which formally looks exactly like the input-output table but explores the dependency relations in terms of payments and intermediation relations. Consistency analysis explores the consistency of plans of buyers and sellers by decomposing the input-output table into four matrices, each for a different kind of means of payment. It integrates micro and macroeconomics in one model and deals with money in an ideology-free manner. It deals with the flow of funds via the movement of goods.See also
- Computable general equilibriumComputable general equilibriumComputable general equilibrium models are a class of economic models that use actual economic data to estimate how an economy might react to changes in policy, technology or other external factors...
- Economic base analysisEconomic base analysisEconomic base analysis was developed by Robert Murray Haig in his work on the Regional Plan of New York in 1928. Briefly, activities in an area divide into two categories – basic and non-basic. Basic industries are those exporting from the region and bringing wealth from outside; non-basic ...
- EIOLCAEIOLCAEconomic input-output life cycle assessment, or EIO-LCA involves use of aggregate sector-level data quantifying how much environmental impact can be directly attributed to each sector of the economy and how much each sector purchases from other sectors in producing its output...
- Gross OutputGross OutputGross output is an economic concept used in national accounts such as the United Nations System of National Accounts and the US National Income and Product Accounts...
- Industrial organizationIndustrial organizationIndustrial organization is the field of economics that builds on the theory of the firm in examining the structure of, and boundaries between, firms and markets....
- IPO ModelIPO ModelThe Input-Process-Output Model also known as the IPO+S Model is a functional model and conceptual schema of a general system. An IPO chart identifies a program’s inputs, its outputs, and the processing steps required to transform the inputs into the outputs.- Overview :The IPO model has many...
- Net outputNet outputNet output is an accounting concept used in national accounts such as the United Nations System of National Accounts and the NIPAs, and sometimes in corporate or government accounts. The concept was originally invented to measure the total net addition to a country's stock of wealth created by...
- Shift-share analysisShift-share analysisShift/share analysis is a widely used analytical technique sometimes used for retrospectively decomposing changes, usually in employment, in a set of urban areas or regions...
External links
- International Input-Output Association
- Input-Output Analysis and Related Methods, San José State University
- Doing Business project input/output tables for reforms
- Energy Economics. Input-Output Analysis: Lecture - 6 and Lecture 7 - two introductory videos on Input-Output methodology with a focus on energy economics from IIT KharagpurIndian Institute of Technology KharagpurThe Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur is an autonomous engineering, technology and management oriented institute of higher education established by the government of India in 1951...
.

