
Insertion loss
Encyclopedia
In telecommunications, insertion loss is the loss of signal power
resulting from the insertion of a device in a transmission line
or optical fiber
and is usually expressed in decibel
s (dB).
If the power transmitted to the load before insertion is PT and the power received by the load after insertion is PR, then the insertion loss in dB is given by,
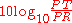
for an electronic filter
and this data is generally specified with a filter. Insertion loss is defined as a ratio of the signal level in a test configuration without the filter installed (|V1|) to the signal level with the filter installed (|V2|). This ratio is described in dB
by the following equation:
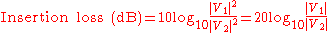
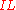 ) is defined as:
) is defined as:

and not, as often mistakenly thought, by:
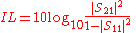 dB.
dB.
It is the extra loss produced by the introduction of the DUT between the 2 reference planes of the measurement. Notice that the extra loss can be introduced by intrinsic loss in the DUT and/or mismatch. In case of extra loss the insertion loss is defined to be positive.
For more detail, see the main article on Scattering Parameters.
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
resulting from the insertion of a device in a transmission line
Transmission line
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...
or optical fiber
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
and is usually expressed in decibel
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
s (dB).
If the power transmitted to the load before insertion is PT and the power received by the load after insertion is PR, then the insertion loss in dB is given by,
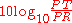
Electronic filters
Insertion loss is a figure of meritFigure of merit
A figure of merit is a quantity used to characterize the performance of a device, system or method, relative to its alternatives. In engineering, figures of merit are often defined for particular materials or devices in order to determine their relative utility for an application...
for an electronic filter
Electronic filter
Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both...
and this data is generally specified with a filter. Insertion loss is defined as a ratio of the signal level in a test configuration without the filter installed (|V1|) to the signal level with the filter installed (|V2|). This ratio is described in dB
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
by the following equation:
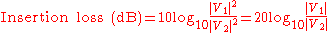
Link with Scattering parameters
In case the two measurement ports use the same reference impedance, the insertion loss ( ) is defined as:
) is defined as:
and not, as often mistakenly thought, by:
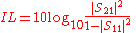 dB.
dB.It is the extra loss produced by the introduction of the DUT between the 2 reference planes of the measurement. Notice that the extra loss can be introduced by intrinsic loss in the DUT and/or mismatch. In case of extra loss the insertion loss is defined to be positive.
For more detail, see the main article on Scattering Parameters.

