
Integral energy
Encyclopedia
Integral energy is the amount of energy required to remove water from an initial water content
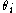 to water content of
to water content of 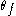 (where
(where 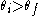 ). It is calculated by integrating the water retention curve
). It is calculated by integrating the water retention curve
, soil water potential
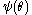 with respect to
with respect to 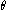 :
:
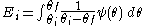
It is proposed by Minasny and McBratney (2003) as alternative to available water capacity
. (AWC)
The AWC concept assumes equal availability of water between two potentials and does not consider the path along the water retention curve. Integral energy takes into the account the path or energy (characterised by water retention curve) required to dry a soil
at particular soil moisture content
Water content
Water content or moisture content is the quantity of water contained in a material, such as soil , rock, ceramics, fruit, or wood. Water content is used in a wide range of scientific and technical areas, and is expressed as a ratio, which can range from 0 to the value of the materials' porosity at...
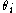 to water content of
to water content of 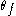 (where
(where 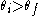 ). It is calculated by integrating the water retention curve
). It is calculated by integrating the water retention curveWater retention curve
Water retention curve is the relationship between the water content, θ, and the soil water potential, ψ. This curve is characteristic for different types of soil, and is also called the soil moisture characteristic....
, soil water potential
Water potential
Water potential is the potential energy of water per unit volume relative to pure water in reference conditions. Water potential quantifies the tendency of water to move from one area to another due to osmosis, gravity, mechanical pressure, or matrix effects such as surface tension...
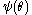 with respect to
with respect to 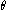 :
: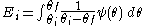
It is proposed by Minasny and McBratney (2003) as alternative to available water capacity
Available water capacity
Available water capacity or available water content is the range of available water that can be stored in soil and be available for growing crops....
. (AWC)
The AWC concept assumes equal availability of water between two potentials and does not consider the path along the water retention curve. Integral energy takes into the account the path or energy (characterised by water retention curve) required to dry a soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
at particular soil moisture content

