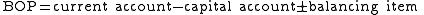Interest Equalization Tax
Encyclopedia
Interest Equalization Tax was a domestic tax measure implemented by U.S. President John F. Kennedy
in July 1963. It was meant to make it less profitable for U.S. investors to invest abroad by taxing the purchase of foreign securities. The design of the tax was to reduce the balance-of-payment
deficit. Although it was originally intended to be a temporary tax, it lasted until 1974.
The identity for the capital account is: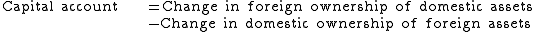
So when capital outflows are decreased, the capital account decreases. When the capital account decreases, the balance-of-payments increases.
Since many factors influence the balance-of-payments account, the effect of the tax is unclear. However, there was a positive trend in the years after it was enacted.
John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald "Jack" Kennedy , often referred to by his initials JFK, was the 35th President of the United States, serving from 1961 until his assassination in 1963....
in July 1963. It was meant to make it less profitable for U.S. investors to invest abroad by taxing the purchase of foreign securities. The design of the tax was to reduce the balance-of-payment
Balance of payments
Balance of payments accounts are an accounting record of all monetary transactions between a country and the rest of the world.These transactions include payments for the country's exports and imports of goods, services, financial capital, and financial transfers...
deficit. Although it was originally intended to be a temporary tax, it lasted until 1974.
Purpose
The purpose of the tax was to decrease the balance of payments deficit in the US. This was achieved conceptually by making investments in foreign securities less appealing. By increasing the price of the security, investors will buy fewer of them, all else equal. With fewer domestic investors purchasing foreign securities, capital outflows will be lower, thereby reducing the balance-of-payments deficit. The equation for the balance of payments is:The identity for the capital account is:
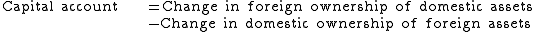
So when capital outflows are decreased, the capital account decreases. When the capital account decreases, the balance-of-payments increases.
Dates Effective
The tax was effective on purchases made after July 18, 1963. It was scheduled to expire on January 1, 1966, but was extended multiple times, and eventually abolished in 1974.Amount of the tax
- For foreign stockStockThe capital stock of a business entity represents the original capital paid into or invested in the business by its founders. It serves as a security for the creditors of a business since it cannot be withdrawn to the detriment of the creditors...
s, the tax is 15% of the price - For debt obligations there is a range between the following bounds:
- For debt obligations having 3 to 3.5 years remaining until maturityMaturity (finance)In finance, maturity or maturity date refers to the final payment date of a loan or other financial instrument, at which point the principal is due to be paid....
, the tax is 2.75% of purchase price - For debt obligations having 28.5 years remaining until maturity, the tax is 15% of purchase price
Exemptions
- Debt obligations with less than 3 years remaining until maturityMaturity (finance)In finance, maturity or maturity date refers to the final payment date of a loan or other financial instrument, at which point the principal is due to be paid....
- Investments in developing countries
- Investments that result in the U.S. citizen owning a 10% or more voting stock in the foreign corporation
- Debt obligations that were issued to a U.S. person in order for that foreign corporation to purchase U.S.-produced goods
- Foreign securities that would endanger international monetary stability. The President will determine if any foreign securities qualify for this exemption. Canadian-issued securities were the only initial exemption from the tax in 1963
- Debt obligations acquired by commercial banks to make loans (deposits, etc.)
- Insurance companies who invest in foreign securities with premiums collected from foreigners
- Labor unions that invest in foreign securities with the money from dues collected abroad from foreign members
- Investment banks that underwrite foreign securities are exempt from the tax when they acquire and resell such securities from the corporation
- U.S.-controlled foreign corporations (>50% owned by U.S. persons and registered on U.R. securities exchanges)
Effect on the Deficit
As the original intent of the Interest Equalization Tax was the reduce the balance-of-payments deficit, a majority consider the tax successful.- Between 1961 and 1964, the deficit averaged $2.5 billion
- In the years 1965 to 1966, the deficit averaged $1.1 billion
- In 1967, the deficit was $3.5 billion
- In 1968, there was a surplus of $93 million
Since many factors influence the balance-of-payments account, the effect of the tax is unclear. However, there was a positive trend in the years after it was enacted.