
Intermembral index
Encyclopedia
The intermembral index is a ratio
used to compare limb proportions, expressed as a percentage
. It is equal to the length of forelimb
s (humerus
plus radius
) divided by the length of the hind limb
s (femur
plus tibia
) multiplied by 100, otherwise written mathematically as:
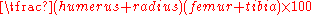
It is used frequently in primatology
since it helps predict primate
locomotor patterns. For scores lower than 100, the forelimbs are shorter than the hind limbs, which is common in leaping
primates and bipedal hominids. Quadrupedal primates tend to have scores around 100, while brachiating
primates have scores significantly higher than 100. This information can also be used to predict locomotor patterns for extinct primates in cases where forelimb and hind limb fossil
s have been found.
Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio is a relationship between two numbers of the same kind , usually expressed as "a to b" or a:b, sometimes expressed arithmetically as a dimensionless quotient of the two which explicitly indicates how many times the first number contains the second In mathematics, a ratio is...
used to compare limb proportions, expressed as a percentage
Percentage
In mathematics, a percentage is a way of expressing a number as a fraction of 100 . It is often denoted using the percent sign, “%”, or the abbreviation “pct”. For example, 45% is equal to 45/100, or 0.45.Percentages are used to express how large/small one quantity is, relative to another quantity...
. It is equal to the length of forelimb
Forelimb
A forelimb is an anterior limb on an animal's body. When referring to quadrupeds , the term foreleg is often instead used....
s (humerus
Humerus
The humerus is a long bone in the arm or forelimb that runs from the shoulder to the elbow....
plus radius
Radius (bone)
The radius is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna, which exceeds it in length and size. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally...
) divided by the length of the hind limb
Hind limb
A hind limb is a posterior limb on an animal. When referring to quadrupeds, the term hind leg is often instead used....
s (femur
Femur
The femur , or thigh bone, is the most proximal bone of the leg in tetrapod vertebrates capable of walking or jumping, such as most land mammals, birds, many reptiles such as lizards, and amphibians such as frogs. In vertebrates with four legs such as dogs and horses, the femur is found only in...
plus tibia
Tibia
The tibia , shinbone, or shankbone is the larger and stronger of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates , and connects the knee with the ankle bones....
) multiplied by 100, otherwise written mathematically as:
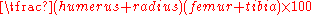
It is used frequently in primatology
Primatology
Primatology is the scientific study of primates. It is a diverse discipline and researchers can be found in academic departments of anatomy, anthropology, biology, medicine, psychology, veterinary sciences and zoology, as well as in animal sanctuaries, biomedical research facilities, museums and zoos...
since it helps predict primate
Primate
A primate is a mammal of the order Primates , which contains prosimians and simians. Primates arose from ancestors that lived in the trees of tropical forests; many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging three-dimensional environment...
locomotor patterns. For scores lower than 100, the forelimbs are shorter than the hind limbs, which is common in leaping
Jumping
Jumping or leaping is a form of locomotion or movement in which an organism or non-living mechanical system propels itself through the air along a ballistic trajectory...
primates and bipedal hominids. Quadrupedal primates tend to have scores around 100, while brachiating
Brachiation
Brachiation is a form of arboreal locomotion in which primates swing from tree limb to tree limb using only their arms.- Brachiators :...
primates have scores significantly higher than 100. This information can also be used to predict locomotor patterns for extinct primates in cases where forelimb and hind limb fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
s have been found.

