
Internal Market in Electricity Directive
Encyclopedia
Internal Market in Electricity Directive is the Directive 2003/54/EC of the European Parliament
and the Council
of 26 June 2003 concerning common rules for the internal market in electricity and repealing Directive 96/92/EC is based in the Treaty establishing the European Community, and in particular Article 47(2), Article 55 and Article 95 thereof. Note: The Directive 2003/54/EC has been replaced by the Directive 2009/72/EC.
Directive 96/92/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 December 1996 concerning common
rules for the internal market in electricity, has made significant contributions towards the creation of an
internal market for electricity. Experience in implementing this Directive shows the benefits that may result from the internal market in electricity, in terms of efficiency gains, price reductions, higher standards of service and increased competitiveness
.
However, important shortcomings and possibilities for improving the functioning of the market remained with the 96/92/EC directive, notably concrete provisions were needed to ensure a level playing field
in generation
and to reduce the risks of market dominance and predatory behaviour, ensuring non-discriminatory transmission and distribution
tariffs, through access to the network based on third-party access
rights and on the basis of tariffs published prior to their entry into force, and ensuring that the rights of small and vulnerable customers are protected and that information on energy sources for electricity generation is disclosed, as well as reference to sources, where available, giving information on their environmental impact
.
The freedoms which the Treaty guarantees European citizens – free movement of goods, freedom to provide services and freedom of establishment – are only possible in a fully open market
, which enables all consumers freely to choose their suppliers and all suppliers freely to deliver to their customers.
To ensure efficient and non-discriminatory network access, it is appropriate that distribution and transmission systems are operated through legally separate entities where vertically integrated undertaking
s exist. Independent management structures must be in place between the distribution system operators, the transmission system operators, and any generation/supply companies.
It is important however to distinguish between such legal separation and ownership
unbundling. Legal separation does not imply a change of ownership of assets and nothing prevents similar or identical employment conditions applying throughout the whole of the vertically integrated undertakings. However, a non-discriminatory decision-making process should be ensured through organisational measures regarding the independence of the decision-makers responsible.
To facilitate the conclusion of contracts electricity undertaking established in a Member State the supply of electricity to eligible customers in Member State
, Member States and, where appropriate, national regulatory authorities should work towards more homogeneous conditions and the same degree eligibility
for the whole of the internal market.
The existence of effective regulation, carried out by one or more national regulatory authorities, is an important
factor in guaranteeing non-discriminatory access to the network.
All Community industry and commerce, including small and medium-sized enterprises, and all Community citizens that enjoy the economic benefits of the internal market should also be able to enjoy high levels of consumer protection
, and in particular households and, where Member States deem it appropriate, small enterprises should also be able to enjoy public service
guarantees, in particular with regard to security of supply and reasonable tariffs, for reasons of fairness
, competitiveness and indirectly to create employment.
Electricity customers should be able to choose their supplier freely and ensure they have a real and effective right to choose their supplier.
Progressive market opening towards full competition should as soon as possible remove differences between
Member States. Transparency
and certainty
in the implementation of the Directive should be ensured.
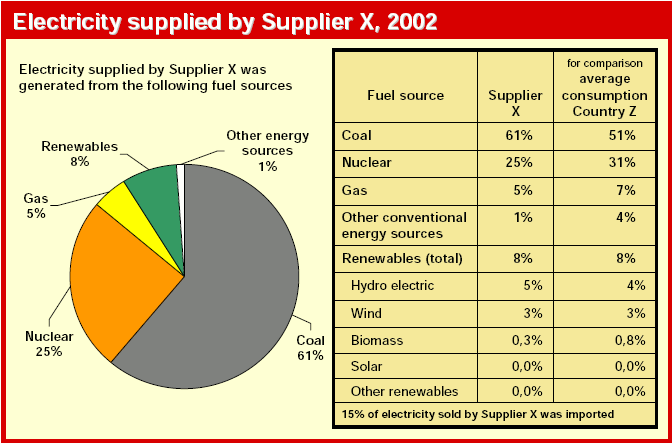 Nearly all Member States have chosen to ensure competition in the electricity generation market through a transparent authorisation procedure. However, Member States should ensure the possibility to contribute to security of supply through the launching of a tendering procedure or an equivalent procedure in the event that sufficient electricity generation capacity is not built on the basis of the authorisation procedure. Member States should have the possibility, in the interests of environmental protection
Nearly all Member States have chosen to ensure competition in the electricity generation market through a transparent authorisation procedure. However, Member States should ensure the possibility to contribute to security of supply through the launching of a tendering procedure or an equivalent procedure in the event that sufficient electricity generation capacity is not built on the basis of the authorisation procedure. Member States should have the possibility, in the interests of environmental protection
and the promotion of infant new technologies, of tendering for new capacity on the basis of published criteria. New capacity includes inter alia renewables
and combined heat and power
(CHP).
The construction and maintenance of the necessary network infrastructure, including interconnection
capacity between areas and decentralised electricity generation, should contribute to ensuring a stable electricity supply.
The Commission has indicated its intention to take initiatives especially as regards the scope of the labelling provision
and notably on the manner in which the information on the environmental impact in terms of at least emissions of CO2 and the radioactive waste resulting from electricity production from different energy sources, could be made available in a
transparent, easily accessible and comparable manner throughout the European Union and on the manner in which the measures taken in the Member States to control the accuracy of the information provided by suppliers could be streamlined (see no-carbon renewable energy economy – NCREE
).
The respect of the public service
requirements is a fundamental requirement of this Directive, and it is
important that common minimum standards, respected by all Member States, are specified in this Directive.
European Parliament
The European Parliament is the directly elected parliamentary institution of the European Union . Together with the Council of the European Union and the Commission, it exercises the legislative function of the EU and it has been described as one of the most powerful legislatures in the world...
and the Council
Council of the European Union
The Council of the European Union is the institution in the legislature of the European Union representing the executives of member states, the other legislative body being the European Parliament. The Council is composed of twenty-seven national ministers...
of 26 June 2003 concerning common rules for the internal market in electricity and repealing Directive 96/92/EC is based in the Treaty establishing the European Community, and in particular Article 47(2), Article 55 and Article 95 thereof. Note: The Directive 2003/54/EC has been replaced by the Directive 2009/72/EC.
Directive 96/92/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 December 1996 concerning common
rules for the internal market in electricity, has made significant contributions towards the creation of an
internal market for electricity. Experience in implementing this Directive shows the benefits that may result from the internal market in electricity, in terms of efficiency gains, price reductions, higher standards of service and increased competitiveness
Competitiveness
Competitiveness is a comparative concept of the ability and performance of a firm, sub-sector or country to sell and supply goods and/or services in a given market...
.
However, important shortcomings and possibilities for improving the functioning of the market remained with the 96/92/EC directive, notably concrete provisions were needed to ensure a level playing field
Level playing field
A level playing field is a concept about fairness, not that each player has an equal chance to succeed, but that they all play by the same set of rules. A metaphorical playing field is said to be level if no external interference affects the ability of the players to compete fairly...
in generation
Generation
Generation , also known as procreation in biological sciences, is the act of producing offspring....
and to reduce the risks of market dominance and predatory behaviour, ensuring non-discriminatory transmission and distribution
Electricity distribution
File:Electricity grid simple- North America.svg|thumb|380px|right|Simplified diagram of AC electricity distribution from generation stations to consumers...
tariffs, through access to the network based on third-party access
Third-party access
Third party access policies require owners of natural monopoly infrastructure facilities to grant access to those facilities to parties other than their own customers, usually competitors in the provision of the relevant services, on commercial terms comparable to those that would apply in a...
rights and on the basis of tariffs published prior to their entry into force, and ensuring that the rights of small and vulnerable customers are protected and that information on energy sources for electricity generation is disclosed, as well as reference to sources, where available, giving information on their environmental impact
Environmental impact assessment
An environmental impact assessment is an assessment of the possible positive or negative impact that a proposed project may have on the environment, together consisting of the natural, social and economic aspects....
.
The freedoms which the Treaty guarantees European citizens – free movement of goods, freedom to provide services and freedom of establishment – are only possible in a fully open market
Open market
The term open market is used generally to refer to a situation close to free trade and in a more specific technical sense to interbank trade in securities.-Use of the term in economic theory:...
, which enables all consumers freely to choose their suppliers and all suppliers freely to deliver to their customers.
To ensure efficient and non-discriminatory network access, it is appropriate that distribution and transmission systems are operated through legally separate entities where vertically integrated undertaking
Undertaking
Undertaking may refer to:* The task performed by a funeral director* In business, in particular in "EU English", the term is used interchangeably with Company, i.e. a business entity...
s exist. Independent management structures must be in place between the distribution system operators, the transmission system operators, and any generation/supply companies.
It is important however to distinguish between such legal separation and ownership
Ownership
Ownership is the state or fact of exclusive rights and control over property, which may be an object, land/real estate or intellectual property. Ownership involves multiple rights, collectively referred to as title, which may be separated and held by different parties. The concept of ownership has...
unbundling. Legal separation does not imply a change of ownership of assets and nothing prevents similar or identical employment conditions applying throughout the whole of the vertically integrated undertakings. However, a non-discriminatory decision-making process should be ensured through organisational measures regarding the independence of the decision-makers responsible.
To facilitate the conclusion of contracts electricity undertaking established in a Member State the supply of electricity to eligible customers in Member State
Member state
A member state is a state that is a member of an international organisation.The World Trade Organization has members that are sovereign states and members that are not, thus WTO members are not called member states.- Worldwide :...
, Member States and, where appropriate, national regulatory authorities should work towards more homogeneous conditions and the same degree eligibility
Eligibility
Eligibility may refer to:* The right to run for office , sometimes called passive suffrage or voting eligibility* Desirability as a marriage partner, as in the term eligible bachelor...
for the whole of the internal market.
The existence of effective regulation, carried out by one or more national regulatory authorities, is an important
factor in guaranteeing non-discriminatory access to the network.
All Community industry and commerce, including small and medium-sized enterprises, and all Community citizens that enjoy the economic benefits of the internal market should also be able to enjoy high levels of consumer protection
Consumer protection
Consumer protection laws designed to ensure fair trade competition and the free flow of truthful information in the marketplace. The laws are designed to prevent businesses that engage in fraud or specified unfair practices from gaining an advantage over competitors and may provide additional...
, and in particular households and, where Member States deem it appropriate, small enterprises should also be able to enjoy public service
Public services
Public services is a term usually used to mean services provided by government to its citizens, either directly or by financing private provision of services. The term is associated with a social consensus that certain services should be available to all, regardless of income...
guarantees, in particular with regard to security of supply and reasonable tariffs, for reasons of fairness
Distributive justice
Distributive justice concerns what some consider to be socially just allocation of goods in a society. A society in which incidental inequalities in outcome do not arise would be considered a society guided by the principles of distributive justice...
, competitiveness and indirectly to create employment.
Electricity customers should be able to choose their supplier freely and ensure they have a real and effective right to choose their supplier.
Progressive market opening towards full competition should as soon as possible remove differences between
Member States. Transparency
Transparency (humanities)
Transparency, as used in science, engineering, business, the humanities and in a social context more generally, implies openness, communication, and accountability. Transparency is operating in such a way that it is easy for others to see what actions are performed...
and certainty
Certainty
Certainty can be defined as either:# perfect knowledge that has total security from error, or# the mental state of being without doubtObjectively defined, certainty is total continuity and validity of all foundational inquiry, to the highest degree of precision. Something is certain only if no...
in the implementation of the Directive should be ensured.

Environmental protection
Environmental protection is a practice of protecting the environment, on individual, organizational or governmental level, for the benefit of the natural environment and humans. Due to the pressures of population and our technology the biophysical environment is being degraded, sometimes permanently...
and the promotion of infant new technologies, of tendering for new capacity on the basis of published criteria. New capacity includes inter alia renewables
Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
and combined heat and power
Combined Heat and Power
Combined Heat and Power may refer to:* Cogeneration* Combined Heat and Power Solar...
(CHP).
The construction and maintenance of the necessary network infrastructure, including interconnection
Interconnection
In telecommunications, interconnection is the physical linking of a carrier's network with equipment or facilities not belonging to that network...
capacity between areas and decentralised electricity generation, should contribute to ensuring a stable electricity supply.
The Commission has indicated its intention to take initiatives especially as regards the scope of the labelling provision
Fuel mix disclosure
]According to the European Union's Internal Market in Electricity Directive from July 1, 2004, electric power consumers must be informed about the sources from which the electricity they have purchased was generated...
and notably on the manner in which the information on the environmental impact in terms of at least emissions of CO2 and the radioactive waste resulting from electricity production from different energy sources, could be made available in a
transparent, easily accessible and comparable manner throughout the European Union and on the manner in which the measures taken in the Member States to control the accuracy of the information provided by suppliers could be streamlined (see no-carbon renewable energy economy – NCREE
Low-carbon economy
A Low-Carbon Economy or Low-Fossil-Fuel Economy is an economy that has a minimal output of greenhouse gas emissions into the environment biosphere, but specifically refers to the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide...
).
The respect of the public service
Public services
Public services is a term usually used to mean services provided by government to its citizens, either directly or by financing private provision of services. The term is associated with a social consensus that certain services should be available to all, regardless of income...
requirements is a fundamental requirement of this Directive, and it is
important that common minimum standards, respected by all Member States, are specified in this Directive.

