
International medical graduate
Encyclopedia
An International Medical Graduate or "IMGs", earlier known as a Foreign Medical Graduate or "FMGs", is a term used to describe a physician
who has graduated from a medical school outside of the country in which he or she intends to practice. Generally, the medical school of graduation is one listed in the International Medical Education Directory
(or IMED) as accredited by the Foundation for Advancement of International Medical Education and Research
or the World Health Organization
.
Medical schools around the world vary in educational standards, curriculum, and evaluation methods. The purpose of ECFMG Certification is to assess the readiness of international medical graduates to enter clinical specialty training programs as resident physicians and fellowship programs in the United States.
must obtain certification from the Australian Medical Council (AMC). To do so, an IMG must obtain an AMC certificate and sit for a series of exams.
Those IMGs who have successfully passed the necessary exams and obtained AMC certification can then apply to an Australian specialty training positions.http://www.amc.org.au/prelim1.asp
Australia is in the process of establishing a national registration process for all the doctors under Medical Board of Australia.
There is still lot of inconsistency and unpredictability in the process of accreditation and registration process of International Medical Graduates in Australia.
An urgent enquiry with a report was requested by the minister of health and ageing on the matter regarding the registration process and support for international medical graduates currently employed in Australia.http://www.amplelife.org
In addition to undergoing the regular licencing process as required of all Canadian medical school graduates, IMG's must also achieve a pass mark on the LMCC Evaluating Examination. IMGs in Canada also have a harder time getting into residency programs compared to Canadian graduates - only ten percent of IMG applicants get a position.
Graduates of United States M.D. programs are not considered IMGs and are thus exempt from the Evaluating Examination, but graduates of U.S. osteopathic medical schools are considered IMGs.
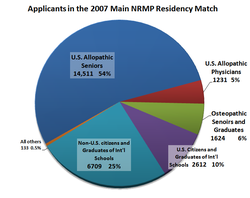
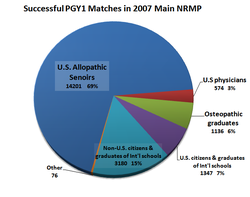 Graduates of Canadian M.D. programs are not considered IMGs in the United States.
Graduates of Canadian M.D. programs are not considered IMGs in the United States.
is to complete a U.S. residency
hospital program. The general method to apply for residency programs is through the National Resident Matching Program
(abbreviated NRMP, but also called "the Match"). To participate in the NRMP, an IMG is required to have an ECFMG certification by the "rank order list certification deadline" time (usually in February of the year of the match). To acquire an ECFMG certification, the main requirements are:
In comparison, regular graduates from medical schools in the United States need to complete USMLE Steps 1 and 2 as well, but can participate in the NRMP while still doing their final year of medical school before acquiring their medical diplomas. In effect, taking regular administrative delays into account, and with residency programs starting around July, there is a gap of at least half a year for IMGs between graduation from medical school and beginning of a residency program.
Those IMGs who have successfully passed the necessary USMLE exams and obtained the ECFMG certification can then apply to U.S. residency positions via the NRMP and ERAS.
One study came to the result that almost half of IMGs were unsuccessful in their first attempts in the pursuit of a U.S. residency position, and three-quarters having begun a residency after five years. It also indicated that IMGs were considerably older when they first applied for a residency position than are most U.S. medical graduates, with mean age of IMGs when the ECFMG certificate was issued being 31.3 years, with a standard deviation of 5.6 years.
Source: 2007 AMA Masterfile
Physician
A physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
who has graduated from a medical school outside of the country in which he or she intends to practice. Generally, the medical school of graduation is one listed in the International Medical Education Directory
International Medical Education Directory
The International Medical Education Directory is a public database of worldwide medical schools. The IMED is published as a joint collaboration of the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates and the Foundation for Advancement of International Medical Education and Research...
(or IMED) as accredited by the Foundation for Advancement of International Medical Education and Research
Foundation for Advancement of International Medical Education and Research
The is a nonprofit organization whose mission is to "support the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates as it promotes international health professions education through programmatic and research activities." These activities include:*Creating Educational Opportunities for Health...
or the World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
.
Medical schools around the world vary in educational standards, curriculum, and evaluation methods. The purpose of ECFMG Certification is to assess the readiness of international medical graduates to enter clinical specialty training programs as resident physicians and fellowship programs in the United States.
License requirements by country
The requirements to obtain a license to practice varies by country and often by state or province.Australia
IMGs who wish to be licensed in AustraliaAustralia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
must obtain certification from the Australian Medical Council (AMC). To do so, an IMG must obtain an AMC certificate and sit for a series of exams.
Those IMGs who have successfully passed the necessary exams and obtained AMC certification can then apply to an Australian specialty training positions.http://www.amc.org.au/prelim1.asp
Australia is in the process of establishing a national registration process for all the doctors under Medical Board of Australia.
There is still lot of inconsistency and unpredictability in the process of accreditation and registration process of International Medical Graduates in Australia.
An urgent enquiry with a report was requested by the minister of health and ageing on the matter regarding the registration process and support for international medical graduates currently employed in Australia.http://www.amplelife.org
Canada
Several organizations have put pressure on the government such as the Association For Access to Health Care Services and Association of International Physicians and Surgeons of Ontario. 20 months ago, the McGuinty Ontario government passed Bill 97, Increasing Access to Qualified Health Professionals for Ontarians Act 2008 that requires the College of Physicians and Surgeons to provide adequate numbers of doctors by issuing transitional licenses. However, the College has refused to obey the law.In addition to undergoing the regular licencing process as required of all Canadian medical school graduates, IMG's must also achieve a pass mark on the LMCC Evaluating Examination. IMGs in Canada also have a harder time getting into residency programs compared to Canadian graduates - only ten percent of IMG applicants get a position.
Graduates of United States M.D. programs are not considered IMGs and are thus exempt from the Evaluating Examination, but graduates of U.S. osteopathic medical schools are considered IMGs.
United States


Progress
The main pathway for IMGs who wish to be licensed as a physician in the United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
is to complete a U.S. residency
Residency (medicine)
Residency is a stage of graduate medical training. A resident physician or resident is a person who has received a medical degree , Podiatric degree , Dental Degree and who practices...
hospital program. The general method to apply for residency programs is through the National Resident Matching Program
National Resident Matching Program
The National Resident Matching Program is a United States-based non-profit non-governmental organization created in 1952 to help match medical school students with residency programs...
(abbreviated NRMP, but also called "the Match"). To participate in the NRMP, an IMG is required to have an ECFMG certification by the "rank order list certification deadline" time (usually in February of the year of the match). To acquire an ECFMG certification, the main requirements are:
- Completion of USMLE Step 1USMLE Step 1The USMLE Step 1 is the first part of the United States Medical Licensing Examination. It assesses whether medical school students or graduates can apply important concepts of the sciences fundamental to the practice of medicine. US medical students typically take Step 1 at the end of the second...
, USMLE Step 2 Clinical Knowledge and USMLE Step 2 Clinical Skills - A medical diploma of medical educationMedical educationMedical education is education related to the practice of being a medical practitioner, either the initial training to become a doctor or additional training thereafter ....
taken at a institution registered in the International Medical Education DirectoryInternational Medical Education DirectoryThe International Medical Education Directory is a public database of worldwide medical schools. The IMED is published as a joint collaboration of the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates and the Foundation for Advancement of International Medical Education and Research...
(IMED)
In comparison, regular graduates from medical schools in the United States need to complete USMLE Steps 1 and 2 as well, but can participate in the NRMP while still doing their final year of medical school before acquiring their medical diplomas. In effect, taking regular administrative delays into account, and with residency programs starting around July, there is a gap of at least half a year for IMGs between graduation from medical school and beginning of a residency program.
Those IMGs who have successfully passed the necessary USMLE exams and obtained the ECFMG certification can then apply to U.S. residency positions via the NRMP and ERAS.
One study came to the result that almost half of IMGs were unsuccessful in their first attempts in the pursuit of a U.S. residency position, and three-quarters having begun a residency after five years. It also indicated that IMGs were considerably older when they first applied for a residency position than are most U.S. medical graduates, with mean age of IMGs when the ECFMG certificate was issued being 31.3 years, with a standard deviation of 5.6 years.
Origin by Country
| Country of medical school | Percentage of IMG's | Total number (2007) |
| India | 19.9% | 47,581 |
| Philippines | 8.7% | 20,861 |
| Mexico | 5.8% | 13,929 |
| Pakistan | 4.8% | 11,330 |
| Dominican Republic | 3.3% | 7,892 |
| Former USSR | 2.5% | 6,039 |
| Grenada | 2.4% | 5,708 |
| Egypt | 2.2% | 5,202 |
| Korea | 2.1% | 4,982 |
| Italy | 2.1% | 4,978 |
| China | 2.0% | 4,834 |
| Iran | 2.0% | 4,741 |
| Spain | 1.9% | 4,570 |
| Dominica | 1.9% | 4,501 |
| Germany | 1.9% | 4,457 |
| Iran | 1.9% | 4,741 |
| Syria | 1.5% | 3,676 |
| Colombia | 1.4% | 3,335 |
| Israel | 1.4% | 3,260 |
| United Kingdom | 1.4% | 3,245 |
| Montserrat | 1.3% | 3,111 |
Source: 2007 AMA Masterfile
Quality of care
An analysis among patients with congestive heart failure or acute heart attack in Pennsylvania, United States, found that patients of international medical graduates entering medical school as non-U.S. citizens had the lowest death rates. There was not statistically significant difference in mortality between patients of all international medical graduates and U.S. medical graduates. There was a statistically significant lowering of mortality by U.S. medical graduates when compared to U.S.-citizen international medical graduates alone, but the odds ratio failed to show the difference was not due to factors outside of the study parameters. When US citizen international medical graduates were compared to non-US citizen international medical graduates, the difference was "striking", which was consistent with previous research which found US citizens who graduated from foreign medical schools , particularly from Caribbean medical schools, were associated with lower scores in other types of evaluations (e.g., specialty board scores), than other graduates.External links
www.groups.yahoo.com/group/associationforaccesstohealthcareservices- http://www.ecfmg.org
- http://www.usmle.org
- http://www.nrmp.org

