
Intrinsic termination
Encyclopedia
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of creating a complementary RNA copy of a sequence of DNA. Both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language that can be converted back and forth from DNA to RNA by the action of the correct enzymes...
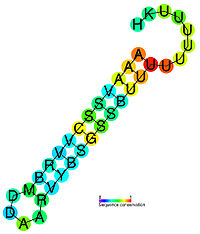
to be stopped. In this mechanism, the mRNA contains a sequence that can base pair with itself to form a stem-loop
Stem-loop
Stem-loop intramolecular base pairing is a pattern that can occur in single-stranded DNA or, more commonly, in RNA. The structure is also known as a hairpin or hairpin loop. It occurs when two regions of the same strand, usually complementary in nucleotide sequence when read in opposite directions,...
structure 7-20 base pairs in length that is also rich in cytosine
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine . It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached . The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine...
-guanine
Guanine
Guanine is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine . In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with...
base pairs. These bases form three hydrogen bonds between each other and are therefore particularly strong. Following the stem-loop structure is a chain of uracil
Uracil
Uracil is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of RNA that are represented by the letters A, G, C and U. The others are adenine, cytosine, and guanine. In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine.Uracil is a common and...
residues. The bonds between uracil and adenine
Adenine
Adenine is a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide , and protein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA...
are very weak. A protein bound to RNA polymerase (nusA) binds to the stem-loop structure tightly enough to cause the polymerase to temporarily stall. This pausing of the polymerase coincides with transcription of the poly-uracil sequence. The weak Adenine-Uracil bonds lower the energy of destabilization for the RNA-DNA duplex, allowing it to unwind and dissociate from the RNA polymerase.
Stem-loop structures that are not followed by a poly-Uracil sequence cause the RNA polymerase to pause, but it will typically continue transcription after a brief time because the duplex is too stable to unwind far enough to cause termination.
Rho-independent transcription termination is a frequent mechanism underlying the activity of cis-acting RNA regulatory elements, such as riboswitch
Riboswitch
In molecular biology, a riboswitch is a part of an mRNA molecule that can directly bind a small target molecule, and whose binding of the target affects the gene's activity. Thus, an mRNA that contains a riboswitch is directly involved in regulating its own activity, in response to the...
es.

