Isidro Barradas
Encyclopedia
Isidro Barradas was a Spanish general sent to Mexico in 1829, eight years after Mexican independence
, to try to reconquer the country for the Spanish Crown.
, with the object of reconquering Mexican territory.
 Spanish Brigadier Isidro Barradas arrived secretly in Havana from Spain on June 2, 1829. He assembled an expedition of 3,000 to 4,000 men, and on July 5 he sailed for Mexico. The fleet included one ship of the line, El Soberano, 2 frigates, 2 gunboats and 15 transports. Admiral Ángel Laborde was in command of the fleet. The expedition included many of the Spaniards exiled in 1827 who wanted to return to the country. The exiles had convinced Barradas that Mexico was eager to return to Spanish sovereignty.
Spanish Brigadier Isidro Barradas arrived secretly in Havana from Spain on June 2, 1829. He assembled an expedition of 3,000 to 4,000 men, and on July 5 he sailed for Mexico. The fleet included one ship of the line, El Soberano, 2 frigates, 2 gunboats and 15 transports. Admiral Ángel Laborde was in command of the fleet. The expedition included many of the Spaniards exiled in 1827 who wanted to return to the country. The exiles had convinced Barradas that Mexico was eager to return to Spanish sovereignty.
Barradas was apparently a disagreeable person, quarreling with Admiral Laborde and generally disliked by the troops under his command.
Three days out of Havana, the fleet was dispersed by a violent storm in the Bay of Campeche
. The rallying point was the Isla de Lobos (Veracruz
), but the weather made it difficult to reassemble. The frigate Amalia and four transports arrived there on July 14. More ships arrived in the following week. By July 22, nearly all had reached the reassembly point. One transport with 400 troops was forced to go to New Orleans for repairs.
. On the 27th the first operation began, with 25 skiffs and 750 men, but the surf did not allow them to land. Admiral Laborde had to offer one ounce of gold to any man who would swim to shore for fresh news about the state of defense the country was in.
Eugenio Aviraneta e Ibargoyen accepted. He took 12 ounces of gold and a bottle containing proclamations. Once ashore, he spoke to four Indigenous Huastecos. They told him that there were no troops near about, but that General Lagarza was in Tampico with a thousand troops to guard against a possible uprising by Antonio López de Santa Anna
. Aviraneta was informed that Lagarza did not know of the arrival of the Spaniards. He paid his informants three ounces of gold. They told him the best place to disembark but refused to accompany him to Tampico, fearing reprisals.
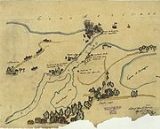
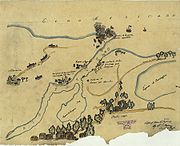
The disembarkation began at 2:00 that afternoon, at the place pointed out by the Huaxtecos. The force began marching toward Tampico, and the Spanish ships were sent to the Río Pánuco.
On the 31st the first fight with Mexican forces occurred, at Los Corchos, 20 km southeast of Pueblo Viejo, Veracruz.
Meanwhile, Santa Anna had been preparing for the expedition, and had assembled 1,000 infantrymen, 500 cavalry, four pieces of artillery and a fleet of 3 brigs, 4 schooners and 5 boats. Santa Anna did not attempt a direct assault, but rather laid siege to Barradas's forces.
President Vicente Guerrero
had sent Santa Anna to oppose the Spanish, and he also sent Vice-President General Anastasio Bustamante
to Jalapa
in reserve to oppose any other Spanish landing along the coast. Bustamante took that opportunity to lead his troops in revolt and overthrow Guerrero.
Mexican War of Independence
The Mexican War of Independence was an armed conflict between the people of Mexico and the Spanish colonial authorities which started on 16 September 1810. The movement, which became known as the Mexican War of Independence, was led by Mexican-born Spaniards, Mestizos and Amerindians who sought...
, to try to reconquer the country for the Spanish Crown.
The background
The General Law of Expulsion was promulgated in Mexico in 1827. This law ordered the expulsion of all foreigners from the country, particularly all Spaniards. In January 1829 Feliciano Montenegro, Mexican counsel in New Orleans, informed his government that a Spanish expeditionary force was being assembled in HavanaHavana
Havana is the capital city, province, major port, and leading commercial centre of Cuba. The city proper has a population of 2.1 million inhabitants, and it spans a total of — making it the largest city in the Caribbean region, and the most populous...
, with the object of reconquering Mexican territory.
The expedition

Barradas was apparently a disagreeable person, quarreling with Admiral Laborde and generally disliked by the troops under his command.
Three days out of Havana, the fleet was dispersed by a violent storm in the Bay of Campeche
Bay of Campeche
The Bay of Campeche is the southern bight of the Gulf of Mexico. It is surrounded on three sides by the Mexican states of Campeche, Tabasco and Veracruz. It was named by Francisco Hernández de Córdoba and Antonio de Alaminos during their expedition in 1517...
. The rallying point was the Isla de Lobos (Veracruz
Veracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave , is one of the 31 states that, along with the Federal District, comprise the 32 federative entities of Mexico. It is divided in 212 municipalities and its capital city is...
), but the weather made it difficult to reassemble. The frigate Amalia and four transports arrived there on July 14. More ships arrived in the following week. By July 22, nearly all had reached the reassembly point. One transport with 400 troops was forced to go to New Orleans for repairs.
Operations in Mexico
On July 26 the fleet arrived off Cabo Rojo, near TampicoTampico
Tampico is a city and port in the state of Tamaulipas, in the country of Mexico. It is located in the southeastern part of the state, directly north across the border from Veracruz. Tampico is the third largest city in Tamaulipas, and counts with a population of 309,003. The Metropolitan area of...
. On the 27th the first operation began, with 25 skiffs and 750 men, but the surf did not allow them to land. Admiral Laborde had to offer one ounce of gold to any man who would swim to shore for fresh news about the state of defense the country was in.
Eugenio Aviraneta e Ibargoyen accepted. He took 12 ounces of gold and a bottle containing proclamations. Once ashore, he spoke to four Indigenous Huastecos. They told him that there were no troops near about, but that General Lagarza was in Tampico with a thousand troops to guard against a possible uprising by Antonio López de Santa Anna
Antonio López de Santa Anna
Antonio de Padua María Severino López de Santa Anna y Pérez de Lebrón , often known as Santa Anna or López de Santa Anna, known as "the Napoleon of the West," was a Mexican political leader, general, and president who greatly influenced early Mexican and Spanish politics and government...
. Aviraneta was informed that Lagarza did not know of the arrival of the Spaniards. He paid his informants three ounces of gold. They told him the best place to disembark but refused to accompany him to Tampico, fearing reprisals.
The disembarkation began at 2:00 that afternoon, at the place pointed out by the Huaxtecos. The force began marching toward Tampico, and the Spanish ships were sent to the Río Pánuco.
On the 31st the first fight with Mexican forces occurred, at Los Corchos, 20 km southeast of Pueblo Viejo, Veracruz.
Meanwhile, Santa Anna had been preparing for the expedition, and had assembled 1,000 infantrymen, 500 cavalry, four pieces of artillery and a fleet of 3 brigs, 4 schooners and 5 boats. Santa Anna did not attempt a direct assault, but rather laid siege to Barradas's forces.
Surrender
On September 11, 1829, Barradas, cut off from supplies and with his troops weakened by disease, signed the Capitulation of Pueblo Viejo with Santa Anna and General Manuel Mier y Terán. Santa Anna was hailed as the savior of the Republic. This was the final consummation of Mexican independence.President Vicente Guerrero
Vicente Guerrero
Vicente Ramón Guerrero Saldaña was one of the leading revolutionary generals of the Mexican War of Independence, who fought against Spain for independence in the early 19th century, and served briefly as President of Mexico...
had sent Santa Anna to oppose the Spanish, and he also sent Vice-President General Anastasio Bustamante
Anastasio Bustamante
Anastasio Bustamante y Oseguera was president of Mexico three times, from 1830 to 1832, from 1837 to 1839 and from 1839 to 1841. He was a Conservative. He first came to power by leading a coup against president Vicente Guerrero...
to Jalapa
Xalapa
Xalapa-Enríquez, commonly Xalapa or Jalapa, is the capital city of the Mexican state of Veracruz and the name of the surrounding municipality. In the year 2005 census the city reported a population of 387,879 and the municipality of which it serves as municipal seat reported a population of...
in reserve to oppose any other Spanish landing along the coast. Bustamante took that opportunity to lead his troops in revolt and overthrow Guerrero.

