Isovaleric acidemia
Encyclopedia
Isovaleric acidemia, also called isovaleric aciduria or isovaleric acid CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, is a rare autosomal recessive
metabolic disorder
which disrupts or prevents normal metabolism of the branched-chain amino acid leucine
. It is a classical type of organic acidemia
.
In about half of cases, the signs and symptoms of this disorder become apparent within a few days after birth and include poor feeding, vomiting, seizure
s, and lack of energy that can progress to coma
. These medical problems are typically severe and can be life-threatening. In the other half of cases, the signs and symptoms of the disorder appear during childhood and may come and go over time. They are often triggered by an infection or by eating an increased amount of protein-rich foods.
, allowing for early diagnosis. Elevations of isovalerylglycine in urine and of isovalerylcarnitine in plasma are found.
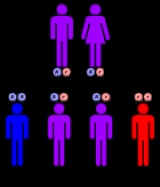
 The disorder has an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, which means the defective gene
The disorder has an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, which means the defective gene
is located on an autosome
, and two copies of the gene - one from each parent - must be inherited to be affected by the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are carriers
of one copy of the defective gene, but are usually not affected by the disorder.
Mutations in both copies of the IVD gene result in isovaleric acidemia.
. During acute episodes, glycine
is sometimes given, which conjugates with isovalerate forming isovalerylglycine, or carnitine
which has a similar effect.
Elevated hydroxyisovalerate is a clinical marker of biotin
deficiency. Without biotin, leucine and isoleucine cannot be fully metabolized. This leads to the formation of hydroxyisovalerate instead of the normal useful byproducts of leucine and isoleucine catabolism. Elevated hydroxyisovalerate can be caused be genetic conditions or dietary deficiency of biotin, and many patients with organic acidemias related to incomplete leucine catabolism can benefit from supplemental biotin . Biotin deficiency on its own can have severe physiological and cognitive consequences that closely resemble symptoms of organic acidemias.
.http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition=isovalericacidemia?wf=1
Recessive
In genetics, the term "recessive gene" refers to an allele that causes a phenotype that is only seen in a homozygous genotype and never in a heterozygous genotype. Every person has two copies of every gene on autosomal chromosomes, one from mother and one from father...
metabolic disorder
Inborn error of metabolism
Inborn errors of metabolism comprise a large class of genetic diseases involving disorders of metabolism. The majority are due to defects of single genes that code for enzymes that facilitate conversion of various substances into others...
which disrupts or prevents normal metabolism of the branched-chain amino acid leucine
Leucine
Leucine is a branched-chain α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2. Leucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid due to its aliphatic isobutyl side chain. It is encoded by six codons and is a major component of the subunits in ferritin, astacin and other 'buffer' proteins...
. It is a classical type of organic acidemia
Organic acidemia
Organic acidemia, also called organic aciduria, is a term used to classify a group of metabolic disorders which disrupt normal amino acid metabolism, particularly branched-chain amino acids, causing a buildup of acids which are usually not present....
.
Symptoms
A characteristic feature of isovaleric acidemia is a distinctive odor of sweaty feet. This odor is caused by the buildup of a compound called isovaleric acid in affected individuals.In about half of cases, the signs and symptoms of this disorder become apparent within a few days after birth and include poor feeding, vomiting, seizure
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
s, and lack of energy that can progress to coma
Coma
In medicine, a coma is a state of unconsciousness, lasting more than 6 hours in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light or sound, lacks a normal sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. A person in a state of coma is described as...
. These medical problems are typically severe and can be life-threatening. In the other half of cases, the signs and symptoms of the disorder appear during childhood and may come and go over time. They are often triggered by an infection or by eating an increased amount of protein-rich foods.
Diagnosis
The urine of newborns can be screened for isovaleric acidemia using mass spectrometryMass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
, allowing for early diagnosis. Elevations of isovalerylglycine in urine and of isovalerylcarnitine in plasma are found.
Genetics

Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and two copies of the gene - one from each parent - must be inherited to be affected by the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are carriers
Genetic carrier
A genetic carrier , is a person or other organism that has inherited a genetic trait or mutation, but who does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. They are, however, able to pass the gene onto their offspring, who may then express the gene...
of one copy of the defective gene, but are usually not affected by the disorder.
Mutations in both copies of the IVD gene result in isovaleric acidemia.
Pathophysiology
The enzyme encoded by IVD, isovaleric acid-CoA dehydrogenase , plays an essential role in breaking down proteins from the diet. Specifically, the enzyme is responsible for the third step in processing leucine, an essential amino acid. If a mutation in the IVD gene reduces or eliminates the activity of this enzyme, the body is unable to break down leucine properly. As a result, isovaleric acid and related compounds build up to toxic levels, damaging the brain and nervous system.Treatment
Treatment consists of dietary protein restriction, particularly leucineLeucine
Leucine is a branched-chain α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2. Leucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid due to its aliphatic isobutyl side chain. It is encoded by six codons and is a major component of the subunits in ferritin, astacin and other 'buffer' proteins...
. During acute episodes, glycine
Glycine
Glycine is an organic compound with the formula NH2CH2COOH. Having a hydrogen substituent as its 'side chain', glycine is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG cf. the genetic code.Glycine is a colourless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid...
is sometimes given, which conjugates with isovalerate forming isovalerylglycine, or carnitine
Carnitine
Carnitine is a quaternary ammonium compound biosynthesized from the amino acids lysine and methionine. In living cells, it is required for the transport of fatty acids from the cytosol into the mitochondria during the breakdown of lipids for the generation of metabolic energy. It is widely...
which has a similar effect.
Elevated hydroxyisovalerate is a clinical marker of biotin
Biotin
Biotin, also known as Vitamin H or Coenzyme R, is a water-soluble B-complex vitamin discovered by Bateman in 1916. It is composed of a ureido ring fused with a tetrahydrothiophene ring. A valeric acid substituent is attached to one of the carbon atoms of the tetrahydrothiophene ring...
deficiency. Without biotin, leucine and isoleucine cannot be fully metabolized. This leads to the formation of hydroxyisovalerate instead of the normal useful byproducts of leucine and isoleucine catabolism. Elevated hydroxyisovalerate can be caused be genetic conditions or dietary deficiency of biotin, and many patients with organic acidemias related to incomplete leucine catabolism can benefit from supplemental biotin . Biotin deficiency on its own can have severe physiological and cognitive consequences that closely resemble symptoms of organic acidemias.
Epidemiology
Isovaleric acidemia is estimated to affect at least 1 in 250,000 births in the United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
.http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition=isovalericacidemia?wf=1

