
Isserlis Gaussian moment theorem
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
, Isserlis’ theorem or Wick’s theorem is a formula that allows one to compute higher-order moments of the multivariate normal distribution in terms of its covariance matrix.
This theorem is particularly important in particle physics
, where it is known as Wick’s theorem after the work of . Other applications include the analysis of portfolio returns, quantum field theory and generation of colored noise.
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
, Isserlis’ theorem or Wick’s theorem is a formula that allows one to compute higher-order moments of the multivariate normal distribution in terms of its covariance matrix.
This theorem is particularly important in particle physics
Particle physics
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
, where it is known as Wick’s theorem after the work of . Other applications include the analysis of portfolio returns, quantum field theory and generation of colored noise.
Theorem statement
If (x1, …, x2n) is a zero mean multivariate normal random vector, then-

where the notation ∑ ∏ means summing over all distinct ways of partitioning x1, …, x2n into pairs.. This yields terms in the sum. For example, for fourth order moments (four variables) there are three terms. For sixth-order moments there are 3 × 5 = 15 terms, and for eighth-order moments there are 3 × 5 × 7 = 105 terms (as you can check in the examples below).
terms in the sum. For example, for fourth order moments (four variables) there are three terms. For sixth-order moments there are 3 × 5 = 15 terms, and for eighth-order moments there are 3 × 5 × 7 = 105 terms (as you can check in the examples below).
In his original paper, proves this theorem by mathematical induction, generalizing the formula for the fourth-order moments, which takes appearance-
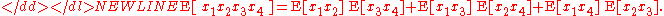
Another example of Isserlis' theorem is:
-

