
Itinerarium
Encyclopedia
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
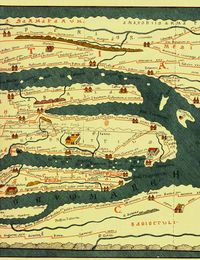
road map in the form of a listing of cities, villages (vici
Vicus (Rome)
In ancient Rome, the vicus was a neighborhood. During the Republican era, the four regiones of the city of Rome were subdivided into vici. In the 1st century BC, Augustus reorganized the city for administrative purposes into 14 regions, comprising 265 vici. Each vicus had its own board of...
) and other stops, with the intervening distances. One surviving example is the Peutinger Table; another is the Antonine Itinerary
Antonine Itinerary
The Antonine Itinerary is a register of the stations and distances along the various roads of the Roman empire, containing directions how to get from one Roman settlement to another...
.
The Romans and ancient travelers in general did not use maps. They may have existed as specialty items in some of the libraries, but they were hard to copy and were not in general use. On the Roman road
Roman road
The Roman roads were a vital part of the development of the Roman state, from about 500 BC through the expansion during the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. Roman roads enabled the Romans to move armies and trade goods and to communicate. The Roman road system spanned more than 400,000 km...
system, however, the traveller needed some idea of where he was going, how to get there, and how long it would take. The itinerarium filled this need. In origin it was simply a list of cities along a road: "at their most basic, itineraria involve the transposition of information given on milestone
Milestone
A milestone is one of a series of numbered markers placed along a road or boundary at intervals of one mile or occasionally, parts of a mile. They are typically located at the side of the road or in a median. They are alternatively known as mile markers, mileposts or mile posts...
s, which were an integral feature of the major Roman road
Roman road
The Roman roads were a vital part of the development of the Roman state, from about 500 BC through the expansion during the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. Roman roads enabled the Romans to move armies and trade goods and to communicate. The Roman road system spanned more than 400,000 km...
s, to a written script." It was only a short step from lists to a master list. To sort out the lists, the Romans drew diagrams of parallel lines showing the branches of the roads. Parts of these were copied and sold on the streets. The very best featured symbols for cities, way stations, water courses, and so on. The maps did not represent landforms but they served the purpose of a simple schematic diagram for the user.
The Roman government from time to time undertook to produce a master itinerary of all Roman roads. Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman and a distinguished writer of Latin prose. He played a critical role in the gradual transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire....
and Mark Antony
Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius , known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general. As a military commander and administrator, he was an important supporter and loyal friend of his mother's cousin Julius Caesar...
commissioned the first known such effort in 44 BC. Zenodoxus, Theodotus and Polyclitus, three Greek geographers, were hired to survey the system and compile a master itinerary. This task required over 25 years. The result was a stone engraved master itinerarium set up near the Pantheon
Pantheon, Rome
The Pantheon ,Rarely Pantheum. This appears in Pliny's Natural History in describing this edifice: Agrippae Pantheum decoravit Diogenes Atheniensis; in columnis templi eius Caryatides probantur inter pauca operum, sicut in fastigio posita signa, sed propter altitudinem loci minus celebrata.from ,...
, from which travelers and itinerary sellers could make copies.
Archaeology has turned up some itinerary material in unexpected places. The Cups of Cadiz, four silver cups found by workmen excavating a foundation at Bracciano in 1852, are engraved with the names and distances of stations between Cadiz and Rome. The term itinerary changed meaning over the centuries. In the Itinerarium Burdigalense
Itinerarium Burdigalense
The Itinerarium Burdigalense is the oldest known Christian itinerarium, written by an anonymous pilgrim from Burdigala...
(Bordeaux Pilgrim, 333 AD), the itinerary is a description of what route to take to the Holy Land. The Itinerarium Alexandri
Itinerarium Alexandri
The Itinerarium Alexandri is a 4th century Latin Itinerarium - a travel guide in the form of a listing of cities, villages and other stops, on a journey with the intervening distances given....
is a list of the conquests of Alexander the Great. Today it means either a travel journal or a list of recommended stops.
The term also refers to medieval guide-books written by travellers: most of these are accounts of pilgrimage
Pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey or search of great moral or spiritual significance. Typically, it is a journey to a shrine or other location of importance to a person's beliefs and faith...
s to the Holy Land
Holy Land
The Holy Land is a term which in Judaism refers to the Kingdom of Israel as defined in the Tanakh. For Jews, the Land's identifiction of being Holy is defined in Judaism by its differentiation from other lands by virtue of the practice of Judaism often possible only in the Land of Israel...
.

