
J
Encyclopedia
Ĵ or ĵ is a letter in Esperanto orthography
representing the sound ʒ.
While Esperanto orthography uses a diacritic
for its four postalveolar consonants, as do the Latin-based Slavic
alphabets, the base letters are Romano-Germanic. Ĵ is based on the French
letter j to better preserve the shape of borrowings from that language (such as ĵurnalo from journal) than Slavic ž would.
Where type with diacritics is not available, L. L. Zamenhof
allowed its substitution by jh. Recently, the use of jx instead of ĵ has also become popular; see x-convention.
Esperanto orthography
Esperanto is written in a Latin alphabet of twenty-eight letters, with upper and lower case. This is supplemented by punctuation marks and by various logograms, such as the numerals 0–9, currency signs such as $, and mathematical symbols....
representing the sound ʒ.
While Esperanto orthography uses a diacritic
Diacritic
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter, or basic glyph. The term derives from the Greek διακριτικός . Diacritic is both an adjective and a noun, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritical marks, such as the acute and grave are often called accents...
for its four postalveolar consonants, as do the Latin-based Slavic
Slavic languages
The Slavic languages , a group of closely related languages of the Slavic peoples and a subgroup of Indo-European languages, have speakers in most of Eastern Europe, in much of the Balkans, in parts of Central Europe, and in the northern part of Asia.-Branches:Scholars traditionally divide Slavic...
alphabets, the base letters are Romano-Germanic. Ĵ is based on the French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
letter j to better preserve the shape of borrowings from that language (such as ĵurnalo from journal) than Slavic ž would.
Where type with diacritics is not available, L. L. Zamenhof
L. L. Zamenhof
Ludwig Lazarus Zamenhof December 15, 1859 – April 14, 1917) was the inventor of Esperanto, the most successful constructed language designed for international communication.-Cultural background:...
allowed its substitution by jh. Recently, the use of jx instead of ĵ has also become popular; see x-convention.
In mathematics
- The letter
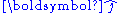 is sometimes used to denote a unit vector in mathematics.
is sometimes used to denote a unit vector in mathematics.
See also
- ĈCĈ or ĉ is a consonant in Esperanto orthography, representing the sound .Esperanto orthography uses a diacritic for all four of its postalveolar consonants, as do the Latin-based Slavic alphabets...
- ĜGG is the seventh letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter 'G' was introduced in the Old Latin period as a variant of ⟨c⟩ to distinguish voiced, from voiceless, . The recorded originator of ⟨g⟩ is freedman Spurius Carvilius Ruga, the first Roman to open a fee-paying school,...
- ĤHH .) is the eighth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The Semitic letter ⟨ח⟩ most likely represented the voiceless pharyngeal fricative . The form of the letter probably stood for a fence or posts....
- ŜSS is the nineteenth letter in the ISO basic Latin alphabet.-History: Semitic Šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative . Greek did not have this sound, so the Greek sigma came to represent...
- ŬUU is the twenty-first letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter U ultimately comes from the Semitic letter Waw by way of the letter Y. See the letter Y for details....

