JBIG2
Encyclopedia
JBIG2 is an image compression
standard for bi-level image
s, developed by the Joint Bi-level Image Experts Group
. It is suitable for both lossless
and lossy
compression. According to a press release from the Group, in its lossless mode JBIG2 typically generates files one third to one fifth the size of Fax Group 4
and one half to one quarter the size of JBIG
, the previous bi-level compression standard released by the Group. JBIG2 has been published in 2000 as the international standard ITU T.88, and in 2001 as ISO
/IEC
14492.
images, and regions of other data. Regions which are neither text nor halftones are typically compressed using a context-dependent arithmetic coding
algorithm called the QM coder. Textual regions are compressed as follows: the foreground pixels in the regions are grouped into symbols. A dictionary of symbols is then created and encoded, typically also using context-dependent arithmetic coding, and the regions are encoded by describing which symbols appear where. Typically, a symbol will correspond to a character of text, but this is not required by the compression method. For lossy compression the difference between similar symbols (e.g., slightly different impressions of the same letter) can be neglected; for lossless compression, this difference is taken into account by compressing one similar symbol using another as a template. Halftone images may be compressed by reconstructing the grayscale image used to generate the halftone and then sending this image together with a dictionary of halftone patterns. An overview of JBIG2 may be found in. Overall, the algorithm used by JBIG2 to compress text is very similar to the JB2 compression scheme used in the DjVu
file format for coding binary images.
PDF
files versions 1.4 and above may contain JBIG2 compressed data. Open source
decoders for JBIG2 are jbig2dec, the java-based jbig2-imageio and the decoder found in versions 2.00 and above of xpdf
. An open source encoder is jbig2enc.
data in which the same shapes appear repeatedly and the bi-level image is segmented into three regions: text, halftone, and generic regions. Each region is coded differently and the coding methodologies are described in the following passage.
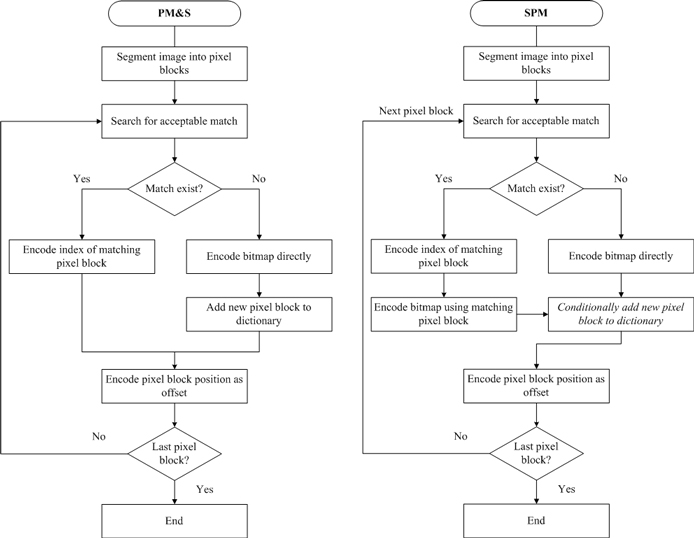 Pattern matching and substitution: After performing image segmentation and match searching, and if a match exists, we code an index of the corresponding representative bitmap in the dictionary and the position of the character on the page. The position is usually relative to another previously coded character. If a match is not found, the segmented pixel block is coded directly and added into the dictionary. Typical procedures of pattern matching and substitution algorithm are displayed in the left block diagram of the figure below. Although the method of PM&S can achieve outstanding compression, substitution errors could be made during the process if the image resolution is low.
Pattern matching and substitution: After performing image segmentation and match searching, and if a match exists, we code an index of the corresponding representative bitmap in the dictionary and the position of the character on the page. The position is usually relative to another previously coded character. If a match is not found, the segmented pixel block is coded directly and added into the dictionary. Typical procedures of pattern matching and substitution algorithm are displayed in the left block diagram of the figure below. Although the method of PM&S can achieve outstanding compression, substitution errors could be made during the process if the image resolution is low.
Soft pattern matching: In addition to a pointer to the dictionary and position information of the character, refinement data is also required because it is a crucial piece of information used to reconstruct the original character in the image. The deployment of refinement data can make character-substitution error mentioned earlier highly unlikely. The refinement data contains the current desired character instance which is coded using the pixels of both the current character and the matching character in the dictionary. Since it is known that the current character instance is highly correlated with the matched character, the prediction of the current pixel is more accurate.
images can be compressed using two methods. One of the methods is similar to the context-based arithmetic coding
algorithm which adaptively positions the template pixels in order to obtain correlations between the adjacent pixels. In the second method, descreening is performed on the halftone image so that the image is converted back to grayscale. The converted grayscale values are then used as indexes of fixed-sized tiny bitmap patterns contained in a halftone bitmap dictionary. This allows decoder to successfully render a halftone image by presenting indexed dictionary bitmap patterns neighboring with each other.
, and generic regions may all use arithmetic coding. JBIG2 specifically uses the MQ coder.
Image compression
The objective of image compression is to reduce irrelevance and redundancy of the image data in order to be able to store or transmit data in an efficient form.- Lossy and lossless compression :...
standard for bi-level image
Binary image
A binary image is a digital image that has only two possible values for each pixel. Typically the two colors used for a binary image are black and white though any two colors can be used. The color used for the object in the image is the foreground color while the rest of the image is the...
s, developed by the Joint Bi-level Image Experts Group
Joint Bi-level Image Experts Group
The Joint Bi-level Image Experts Group is a group of experts nominated by national standards bodies and major companies to work to produce standards for bi-level image coding. The 'joint' refers to its status as a committee working on both ISO and ITU-T standards...
. It is suitable for both lossless
Lossless data compression
Lossless data compression is a class of data compression algorithms that allows the exact original data to be reconstructed from the compressed data. The term lossless is in contrast to lossy data compression, which only allows an approximation of the original data to be reconstructed, in exchange...
and lossy
Lossy data compression
In information technology, "lossy" compression is a data encoding method that compresses data by discarding some of it. The procedure aims to minimize the amount of data that need to be held, handled, and/or transmitted by a computer...
compression. According to a press release from the Group, in its lossless mode JBIG2 typically generates files one third to one fifth the size of Fax Group 4
Group 4 compression
Group 4 compression, usually abbreviated as G4, is a method of image compression used in Group 4 fax machines, defined in the ITU-T T.6 fax standard. It is only used for monochrome images. G4 compression is also available in the TIFF image file format, as well as in the PDF document format....
and one half to one quarter the size of JBIG
JBIG
JBIG is a lossless image compression standard from the Joint Bi-level Image Experts Group, standardized as ISO/IEC standard 11544 and as ITU-T recommendation T.82. It is widely implemented in fax machines. Now that the newer bi-level image compression standard JBIG2 has been released, JBIG is also...
, the previous bi-level compression standard released by the Group. JBIG2 has been published in 2000 as the international standard ITU T.88, and in 2001 as ISO
International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
/IEC
International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission is a non-profit, non-governmental international standards organization that prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies – collectively known as "electrotechnology"...
14492.
Functionality
Ideally, a JBIG2 encoder will segment the input page into regions of text, regions of halftoneHalftone
Halftone is the reprographic technique that simulates continuous tone imagery through the use of dots, varying either in size, in shape or in spacing...
images, and regions of other data. Regions which are neither text nor halftones are typically compressed using a context-dependent arithmetic coding
Arithmetic coding
Arithmetic coding is a form of variable-length entropy encoding used in lossless data compression. Normally, a string of characters such as the words "hello there" is represented using a fixed number of bits per character, as in the ASCII code...
algorithm called the QM coder. Textual regions are compressed as follows: the foreground pixels in the regions are grouped into symbols. A dictionary of symbols is then created and encoded, typically also using context-dependent arithmetic coding, and the regions are encoded by describing which symbols appear where. Typically, a symbol will correspond to a character of text, but this is not required by the compression method. For lossy compression the difference between similar symbols (e.g., slightly different impressions of the same letter) can be neglected; for lossless compression, this difference is taken into account by compressing one similar symbol using another as a template. Halftone images may be compressed by reconstructing the grayscale image used to generate the halftone and then sending this image together with a dictionary of halftone patterns. An overview of JBIG2 may be found in. Overall, the algorithm used by JBIG2 to compress text is very similar to the JB2 compression scheme used in the DjVu
DjVu
DjVu is a computer file format designed primarily to store scanned documents, especially those containing a combination of text, line drawings, and photographs. It uses technologies such as image layer separation of text and background/images, progressive loading, arithmetic coding, and lossy...
file format for coding binary images.
Portable Document Format
Portable Document Format is an open standard for document exchange. This file format, created by Adobe Systems in 1993, is used for representing documents in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems....
files versions 1.4 and above may contain JBIG2 compressed data. Open source
Open-source software
Open-source software is computer software that is available in source code form: the source code and certain other rights normally reserved for copyright holders are provided under a software license that permits users to study, change, improve and at times also to distribute the software.Open...
decoders for JBIG2 are jbig2dec, the java-based jbig2-imageio and the decoder found in versions 2.00 and above of xpdf
Xpdf
Xpdf is an open-source PDF viewer for the X Window System and Motif.Xpdf runs on practically any Unix-like operating system. Xpdf can decode LZW and read encrypted PDFs. The official version obeys the DRM restrictions of PDF files, which may prevent copying, printing, or converting some PDF files...
. An open source encoder is jbig2enc.
Technical details
Typically, a bi-level image consists mainly of a large amount of textual and halftoneHalftone
Halftone is the reprographic technique that simulates continuous tone imagery through the use of dots, varying either in size, in shape or in spacing...
data in which the same shapes appear repeatedly and the bi-level image is segmented into three regions: text, halftone, and generic regions. Each region is coded differently and the coding methodologies are described in the following passage.
Text image data
Text coding is based on the nature of human visual interpretation. A human observer cannot tell the difference of two instances of the same characters in a bi-level image even though they may not exactly match pixel by pixel. Therefore, only the bitmap of one representative character instance needs to be coded instead of coding the bitmaps of each occurrence of the same character individually. For each character instance, the coded instance of the character is then stored into a “symbol dictionary”. There are two encoding methods for text image data: pattern matching and substitution (PM&S) and soft pattern matching (SPM). These methods are presented in the following subsections.
Soft pattern matching: In addition to a pointer to the dictionary and position information of the character, refinement data is also required because it is a crucial piece of information used to reconstruct the original character in the image. The deployment of refinement data can make character-substitution error mentioned earlier highly unlikely. The refinement data contains the current desired character instance which is coded using the pixels of both the current character and the matching character in the dictionary. Since it is known that the current character instance is highly correlated with the matched character, the prediction of the current pixel is more accurate.
Halftones
HalftoneHalftone
Halftone is the reprographic technique that simulates continuous tone imagery through the use of dots, varying either in size, in shape or in spacing...
images can be compressed using two methods. One of the methods is similar to the context-based arithmetic coding
Arithmetic coding
Arithmetic coding is a form of variable-length entropy encoding used in lossless data compression. Normally, a string of characters such as the words "hello there" is represented using a fixed number of bits per character, as in the ASCII code...
algorithm which adaptively positions the template pixels in order to obtain correlations between the adjacent pixels. In the second method, descreening is performed on the halftone image so that the image is converted back to grayscale. The converted grayscale values are then used as indexes of fixed-sized tiny bitmap patterns contained in a halftone bitmap dictionary. This allows decoder to successfully render a halftone image by presenting indexed dictionary bitmap patterns neighboring with each other.
Arithmetic entropy coding
All three region types including text, halftoneHalftone
Halftone is the reprographic technique that simulates continuous tone imagery through the use of dots, varying either in size, in shape or in spacing...
, and generic regions may all use arithmetic coding. JBIG2 specifically uses the MQ coder.

