Jackson-Weiss syndrome
Encyclopedia
Jackson-Weiss syndrome is a genetic disorder
characterized by foot abnormalities and the premature fusion of certain bones of the skull (craniosynostosis
), which prevents further growth of the skull and affects the shape of the head and face. It can also cause mental retardation and sometimes crossed eyes as well.
It was characterized in 1976.
cause Jackson-Weiss syndrome. The FGFR2 gene produces a protein
called fibroblast growth factor receptor 2
. It occurs in chromosome number 10. Among its multiple functions, this protein signals immature cells to become bone cells in a developing embryo
and fetus
. A mutation
in a specific part of the FGFR2 gene alters the protein and causes prolonged signaling, which promotes the premature fusion of bones in the skull and feet.
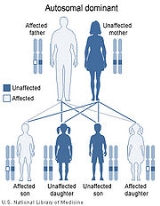
 This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, which means one copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder.
This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, which means one copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder.
Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is an illness caused by abnormalities in genes or chromosomes, especially a condition that is present from before birth. Most genetic disorders are quite rare and affect one person in every several thousands or millions....
characterized by foot abnormalities and the premature fusion of certain bones of the skull (craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis is a condition in which one or more of the fibrous sutures in an infant skull prematurely fuses by ossification, thereby changing the growth pattern of the skull...
), which prevents further growth of the skull and affects the shape of the head and face. It can also cause mental retardation and sometimes crossed eyes as well.
It was characterized in 1976.
Presentation
Many of the characteristic facial features of Jackson-Weiss syndrome result from the premature fusion of the skull bones and foot bones. The head is unable to grow normally, which can lead to a misshapen skull, widely spaced eyes, and a bulging forehead. Foot abnormalities are the most consistent characteristic, as not all individuals with Jackson-Weiss syndrome have abnormal skull or facial features. The big toes are enlarged and bend away from the other toes. Hand abnormalities are rare. People with Jackson-Weiss syndrome usually have normal intelligence and a normal life span.Genetics
Mutations in the FGFR2 geneGene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
cause Jackson-Weiss syndrome. The FGFR2 gene produces a protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
called fibroblast growth factor receptor 2
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 also known as CD332 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGFR2 gene residing on chromosome 10...
. It occurs in chromosome number 10. Among its multiple functions, this protein signals immature cells to become bone cells in a developing embryo
Embryo
An embryo is a multicellular diploid eukaryote in its earliest stage of development, from the time of first cell division until birth, hatching, or germination...
and fetus
Fetus
A fetus is a developing mammal or other viviparous vertebrate after the embryonic stage and before birth.In humans, the fetal stage of prenatal development starts at the beginning of the 11th week in gestational age, which is the 9th week after fertilization.-Etymology and spelling variations:The...
. A mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
in a specific part of the FGFR2 gene alters the protein and causes prolonged signaling, which promotes the premature fusion of bones in the skull and feet.


