
Japanese Experiment Module
Encyclopedia
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
ese science module for the International Space Station
International Space Station
The International Space Station is a habitable, artificial satellite in low Earth orbit. The ISS follows the Salyut, Almaz, Cosmos, Skylab, and Mir space stations, as the 11th space station launched, not including the Genesis I and II prototypes...
(ISS) developed by JAXA. It is the largest single ISS module. The first two pieces of the module were launched on space shuttle
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle was a manned orbital rocket and spacecraft system operated by NASA on 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. The system combined rocket launch, orbital spacecraft, and re-entry spaceplane with modular add-ons...
missions STS-123
STS-123
-Mission parameters:* Mass:* Orbiter liftoff: * Orbiter landing: * Perigee: 336 kilometers * Apogee: 346 kilometers * Inclination: 51.6 degrees* Period: 91.6min-Mission payloads:...
and STS-124
STS-124
STS-124 was a Space Shuttle mission, flown by Space Shuttle Discovery to the International Space Station. Discovery launched on 31 May 2008 at 17:02 EDT, moved from an earlier scheduled launch date of 25 May 2008, and landed safely at the Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility, at 11:15...
. The third and final components were launched on STS-127
STS-127
STS-127 was a NASA Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station . It was the twenty-third flight of . The primary purpose of the STS-127 mission was to deliver and install the final two components of the Japanese Experiment Module: the Exposed Facility , and the Exposed Section of the...
.
Components
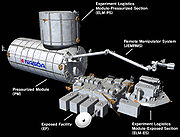
Kibō consists of six major elements: 1) Pressurized Module (PM), 2) Exposed Facility (EF), 3) Experiment Logistics Module-Pressurized Section (ELM-PS), 4) Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section (ELM-ES), 5) Japanese Experiment Module Remote Manipulator System (JEMRMS), and 6) Inter-orbit Communication System (ICS).Pressurized Module

Exposed Facility
The Exposed Facility (EF), also known as "Terrace", is located outside the port cone of the PM (which is equipped with an airlocked hatch). The EF has 12 EFU (Exposed Facility Unit) Ports that attach to PIU (Payload Interface Unit) Connectors on EF-EEUs (EF-Equipment Exchange Units). All experiment payloads are fully exposed to the space environment. For Proper functioning of these experiments, the payload requires an ORU (Orbital Replacement Unit) which consists of the EPS (Electrical Power System), CT (Communications & Tracking) and the TCS (Thermal Control System). Of the 12 ORUs, 8 are replaceable by the JEMRMS while the other 4 are EVA replaceable.Experiment Logistics Module
The Experiment Logistics Module (ELM), is now on orbit and includes two sections:- The Japanese Experiment Logistics Module, Pressurized Section (ELM-PS) –- also called the JLP –- is a pressurized addition to the PM. The module is a storage facility that provides storage space for experiment payloads, samples and spare items.
- The unpressurized (external) section (ELM-ES) will serve the EF. It is intended as a storage and transportation module.
Remote Manipulator System
The Remote Manipulator System (JEMRMS) is a robotic arm, mounted at the port cone of the PM, intended to service the EF and to move equipment from and to ELM. The RMS control console was launched in the ELM-PS. The main arm was launched with the PM. The "Small Fine Arm", which attaches to the end effector of the main arm, was launched aboard HTV-1HTV-1
HTV-1, also known as the HTV Demonstration Flight or HTV Technical Demonstration Vehicle, was the first Japanese Space Agency H-II Transfer Vehicle, launched in September 2009 to resupply the International Space Station and support the JAXA Kibo laboratory or JEM...
.
Launch sequence
NASANASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
launched the JEM complex over three flights:
- On 12 March 2007 the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section (ELM-PS) arrived in Kennedy Space CenterKennedy Space CenterThe John F. Kennedy Space Center is the NASA installation that has been the launch site for every United States human space flight since 1968. Although such flights are currently on hiatus, KSC continues to manage and operate unmanned rocket launch facilities for America's civilian space program...
(KSC) from Japan. It was stored in the Space Station Processing FacilitySpace Station Processing FacilityThe Space Station Processing Facility is a three-story, 42,500 m2 buildinglocated in the Kennedy Space Center industrial area, just east of the Operations and Checkout Building....
until launched into orbit aboard as part of the STS-123STS-123-Mission parameters:* Mass:* Orbiter liftoff: * Orbiter landing: * Perigee: 336 kilometers * Apogee: 346 kilometers * Inclination: 51.6 degrees* Period: 91.6min-Mission payloads:...
mission. At first the ELM-PS was connected to a temporary location into Harmony Module (Node 2) and later, on 6 June 2008, was moved to its final destination into the PM's upper section. - On 30 May 2003 the Pressurized Module (PM) arrived in KSC from Japan. It was stored in the Space Station Processing Facility until launched into orbit aboard as part of the STS-124STS-124STS-124 was a Space Shuttle mission, flown by Space Shuttle Discovery to the International Space Station. Discovery launched on 31 May 2008 at 17:02 EDT, moved from an earlier scheduled launch date of 25 May 2008, and landed safely at the Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility, at 11:15...
mission. On 3 June 2008 the PM was connected to the Harmony Module. - The EF and ELM-ES arrived at KSC on 24 September 2008.
The Exposed Facility (EF) and ELM-ES were launched on STS-127
STS-127
STS-127 was a NASA Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station . It was the twenty-third flight of . The primary purpose of the STS-127 mission was to deliver and install the final two components of the Japanese Experiment Module: the Exposed Facility , and the Exposed Section of the...
, on 15 July 2009. The ELM-ES was brought back to Earth at the end of the mission. The assembly of the EF was completed during the fifth spacewalk.
Specifications
Kibō is the largest single ISS module.- Pressurized Module
- Length: 11.19 m (36.7 ft)
- Diameter: 4.39 m (14.4 ft)
- Mass: 14800 kg (32,628.4 lb)
- Experiment Logistics Module
- Length: 4.21 m (13.8 ft)
- Diameter: 4.39 m (14.4 ft)
- Mass: 8386 kg (18,488 lb)
Current external experiments on Kibo
- MAXIMAXI (ISS Experiment)The Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image is an X-ray slit camera aboard the International Space Station. The device is part of the Japanese Experiment Module.MAXI conducts a full sky survey every 96 minutes searching for variations in X-ray sources....
X-ray astronomy from 0.5 to 30 keV - SMILES observes and monitors very weak sub-millimeter wave emission lines of trace gas molecules in the stratosphere
- SEDA-AP (Space Environment Data Acquisition equipment-Attached Payload) measures neutrons, plasma, heavy ions, and high-energy light particles in ISS orbit.
- HREP (Hyperspectral Imager for the Coastal Ocean (HICO) & Remote Atmospheric & Ionospheric Detection System (RAIDS) Experimental Payload)
Planned external experiments on Kibo
- CALET Observation for high energy. Launch 2012 through H-II Transfer VehicleH-II Transfer VehicleThe H-II Transfer Vehicle , called , is an unmanned resupply spacecraft used to resupply the Kibō Japanese Experiment Module and the International Space Station . The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency has been working on the design since the early 1990s. The first mission, HTV-1, was originally...
, Mass: 2500 kg
Current internal experiments on Kibo
Japanese:- RYUTAI Rack Fluid Physics Experiment Facility (FPEF), Solution Crystallization Observation Facility (SCOF), Protein Crystallization Research Facility (PCRF), Image Processing Unit (IPU)
- SAIBO Rack Cell Biology Experiment Facility (CBEF), Clean Bench (CB)
- KOBAIRO Rack Gradient Heating Furnace (GHF)
- MPSR Multi-Purpose Small payload Rack
American:
- EXPRESS Rack 4 Biotechnology Specimen Temperature Controller (BSTC), Gas Supply Module (GSM), Space Acceleration Measurement System-II (SAMS-II), Biotechnology Specimen Temperature Controller (BSTC)
- EXPRESS Rack 5
- MELFI-1

