
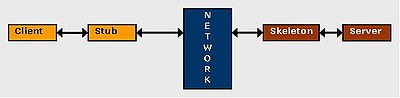
Java remote method invocation
Encyclopedia
Application programming interface
An application programming interface is a source code based specification intended to be used as an interface by software components to communicate with each other...
(API), or Java RMI, is a Java
Java (programming language)
Java is a programming language originally developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems and released in 1995 as a core component of Sun Microsystems' Java platform. The language derives much of its syntax from C and C++ but has a simpler object model and fewer low-level facilities...
application programming interface that performs the object-oriented equivalent of remote procedure call
Remote procedure call
In computer science, a remote procedure call is an inter-process communication that allows a computer program to cause a subroutine or procedure to execute in another address space without the programmer explicitly coding the details for this remote interaction...
s (RPC).
- The original implementation depends on Java Virtual MachineJava Virtual MachineA Java virtual machine is a virtual machine capable of executing Java bytecode. It is the code execution component of the Java software platform. Sun Microsystems stated that there are over 4.5 billion JVM-enabled devices.-Overview:...
(JVM) class representation mechanisms and it thus only supports making calls from one JVM to another. The protocol underlying this Java-only implementation is known as Java Remote Method Protocol (JRMPJRMPJRMP, or Java Remote Method Protocol is the Java technology-specific protocol for looking up and referencing remote objects. It is a wire level protocol running at the level under Remote Method Invocation and over TCP/IP.-Details:...
). - In order to support code running in a non-JVM context, a CORBACommon Object Request Broker ArchitectureThe Common Object Request Broker Architecture is a standard defined by the Object Management Group that enables software components written in multiple computer languages and running on multiple computers to work together .- Overview:CORBA enables separate pieces of software written in different...
version was later developed.
Usage of the term RMI may denote solely the programming interface or may signify both the API and JRMP
JRMP
JRMP, or Java Remote Method Protocol is the Java technology-specific protocol for looking up and referencing remote objects. It is a wire level protocol running at the level under Remote Method Invocation and over TCP/IP.-Details:...
, whereas the term RMI-IIOP
RMI-IIOP
RMI-IIOP denotes the Java Remote Method Invocation interface over the Internet Inter-Orb Protocol , which delivers Common Object Request Broker Architecture distributed computing capabilities to the Java 2 platform...
(read: RMI over IIOP) denotes the RMI interface delegating most of the functionality to the supporting CORBA
Çorba
Chorba , ciorbă , shurpa , shorpo , or sorpa is one of various kinds of soup or stew found in national cuisines across Middle East...
implementation.
The programmers of the original RMI API generalized the code somewhat to support different implementations, such as a HTTP
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol is a networking protocol for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web....
transport. Additionally, the ability to pass arguments "by value" was added to CORBA in order to support the RMI interface. Still, the RMI-IIOP and JRMP implementations do not have fully identical interfaces.
RMI functionality comes in the package , while most of Sun's implementation is located in the
sun.rmi package. Note that with Java versions before Java 5.0 developers had to compile RMI stubs in a separate compilation step using rmic. Version 5.0 of Java and beyond no longer require this step.Jini
Jini
Jini , also called Apache River, is a network architecture for the construction of distributed systems in the form of modular co-operating services.Originally developed by Sun, Jini was released under an open source license...
offers a more advanced version of RMI in Java. It functions similarly but provides more advanced searching capabilities and mechanisms for distributed object applications.
Example
The following classes implement a simple client-server program using RMI that displays a message.RmiServer class—Listens to RMI requests and implements the interface which is used by the client to invoke remote methods.import java.rmi.Naming;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.RMISecurityManager;
import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;
import java.rmi.registry.*;
public class RmiServer extends UnicastRemoteObject
implements RmiServerIntf {
public static final String MESSAGE = "Hello world";
public RmiServer throws RemoteException {
}
public String getMessage {
return MESSAGE;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("RMI server started");
// Create and install a security manager
if (System.getSecurityManager null) {
System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager);
System.out.println("Security manager installed.");
} else {
System.out.println("Security manager already exists.");
}
try { //special exception handler for registry creation
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
System.out.println("java RMI registry created.");
} catch (RemoteException e) {
//do nothing, error means registry already exists
System.out.println("java RMI registry already exists.");
}
try {
//Instantiate RmiServer
RmiServer obj = new RmiServer;
// Bind this object instance to the name "RmiServer"
Naming.rebind("//localhost/RmiServer", obj);
System.out.println("PeerServer bound in registry");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("RMI server exception:" + e);
e.printStackTrace;
}
}
}
RmiServerIntf class—Defines the interface that is used by the client and implemented by the server.import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public interface RmiServerIntf extends Remote {
public String getMessage throws RemoteException;
}
RmiClient class—This is the client which gets the reference (a proxy) to the remote object living on the server and invokes its method to get a message. If the server object implemented java.io.Serializable instead of java.rmi.Remote, it would be serialized and passed to the client as a value .import java.rmi.Naming;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.RMISecurityManager;
public class RmiClient {
// "obj" is the reference of the remote object
RmiServerIntf obj = null;
public String getMessage {
try {
obj = (RmiServerIntf)Naming.lookup("//localhost/RmiServer");
return obj.getMessage;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("RmiClient exception: " + e);
e.printStackTrace;
return e.getMessage;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Create and install a security manager
if (System.getSecurityManager null) {
System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager);
}
RmiClient cli = new RmiClient;
System.out.println(cli.getMessage);
}
}
Before running this subj, we need to make 'Stub' file of interface we used. For this task we have RMI compiller - 'rmic'
- Note: we make stub file from *.class with implementation remote interface, not '*.java'*
rmic RmiServer
server.policy—This file is required on the server to allow TCP/IP communication for the remote registry and for the RMI server.grant {
permission java.net.SocketPermission "127.0.0.1:*", "connect,resolve";
permission java.net.SocketPermission "127.0.0.1:*", "accept";
};
The server.policy file should be used using the D switch of Java RTE, e.g.:
java.exe -Djava.security.policy=server.policy RmiServer
client.policy—This file is required on the client to connect to RMI Server using TCP/IP.grant {
permission java.net.SocketPermission "127.0.0.1:*", "connect,resolve";
};
no.policy—Also if you have any troubles with connecting, try this file for server or client.grant {
permission java.security.AllPermission;
};
External links
- The Java RMI tutorial - a good starting point to learn RMI. Also check the Hello World in RMI
- the Java RMI online training - Very good for training JavaRMI and as reference
- The RMI page in the JDK docs (Sun's Java API Reference for the RMI package)
- The RMI forum on java.sun.com

